Educational Requirements
- At least a Master’s Degree in Psychiatry;
- Communication skills;
- Patient education skills;
- Problem-solving abilities;
- Effective time management;
- Basic emotional intelligence.
Becoming a Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner (PMHNP) entails a wide range of responsibilities and quality standards that one has to uphold in order to deliver high-quality care. To be qualified for the position of a PMHNP in Minnesota, one will need to have at least a Master’s Degree in Psychiatry. In addition, it is critical for a PMHNP to demonstrate the skills required to perform the key tasks with due diligence and efficiency (Orthwein, 2017). For instance, a PMHNP has to develop problem-solving skills, empathy and critical thinking, and the ability to manage advanced technological tools. Furthermore, communication skills are essential for a PMHNP as the means of encouraging patient education and allowing a nurse to provide patients and their family members with emotional support.

Professional Organizations
- Organizations providing a license for a PMHNP to practice nursing legally in Minnesota:
- American Academy of Nurse Practitioners;
- American Nurse Certification Center.
- If a degree is received in another state:
- RN Licensure by Examination Application;
- Reference: “Steps to becoming an APRN in Minnesota” (n.d.).
In order to get permission for practicing nursing services, a PMHNP must be certified as such by a corresponding organization. In Minnesota, these are the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners (“Steps to becoming an APRN in Minnesota,” n.d.) and the American Nurse Certification Center (n.d.). The specified organizations are eligible for providing a PMHNP with a license allowing them to practice nursing in in Minnesota. However, in case a PMHNP receives education in any other state and intends at practicing nursing in Minnesota, it will be necessary to obtain an approval by using the RN Licensure by Examination Application (“Steps to becoming an APRN in Minnesota,” n.d.).

Minnesota’s Legal Recognition
- Legal support: a crucial element of a PMHNP’s practice;
- Minnesota Board of Nurses (MBON) (a certificate of authority): defining a PMHNP’s scope;
- Minnesota Nurse Practice Act (PNPA): not affecting the scope of a PMHNP’s practice;
- PMHNP’s scope: prescriptive authority, patient education, public health, health policies;
- practice agreements: collaboration with a physician;
- Externship options; local nursing facilities.
Apart from having the official approval of a professional nursing organization, a PMHNP also must be supported with legal recognition. Specifically, the Minnesota Board of Nurses will determine the scope of a PMHNP’s practice and define the roles and responsibilities thereof. One should keep in mind that the Minnesota Nurse Practice Act (PNPA) (a substitute for the certificate of authority) is not used to determine the scope of a PMHNP’s work. Currently, a PMHNP is responsible for prescribing medications, encouraging patient education, addressing public health issues linked to psychiatry, and contributing to the development of health policies (Townsend & Morgan, 2017). Practice agreements include active collaboration with a physician. Externship options are provided by local healthcare facilities.

Practice Group or Institution
- Fairview Health Services: a company addressing psychiatric health concerns;
- Job opening: a qualified PMHNP able to participate in interdisciplinary collaboration;
- Collaborative learning as the platform for the corporate philosophy.
The practice of a PMHNP is supported by local nursing and healthcare organizations. The Fairview Health Services organization can be considered an example of a Minnesota company that employs PMHNPs to address the needs of people with psychiatric disorders (Brown, McKenna, & Furness, 2018). The specified institution seeks qualifies PMHNP staff members who will be able to manage psychiatry-related issues, at the same time maintaining the cross-disciplinary dialogue with physicians and other members of the facility. Fairview Health Services emphasizes the positive effects of collaborative learning and patient education specifically as the path to successful treatment.

Job Description
- Employment requirements: a PMHNP is needed;
- Role and responsibilities: promoting health and educating patients;
- Focus: cooperation within an interdisciplinary team (Weber, Delaney, & Snow, 2016).
- Skills: writing, typing, using a computer; assisting patients;
- Goals: collaborating patient teaching.
A range of nursing organizations are currently searching for a PMHNP who is ready to acquire new skills and gain new knowledge. According to a typical description provided by such companies, a PMHNP that will take the job will have to meet the responsibilities associated with the promotion of health management of patients’ current health needs, and patient education (Weber et al., 2016). A nurse must also be able to cooperate and be a part of an interdisciplinary team. In addition, the job will require strenuous physical activities involving walking, lifting, pushing, and pulling (Halter, 2017). The skills associated with a desk job, particularly, typing and being able to use computer programs, are also listed among the key requirements (Weber et al., 2016).

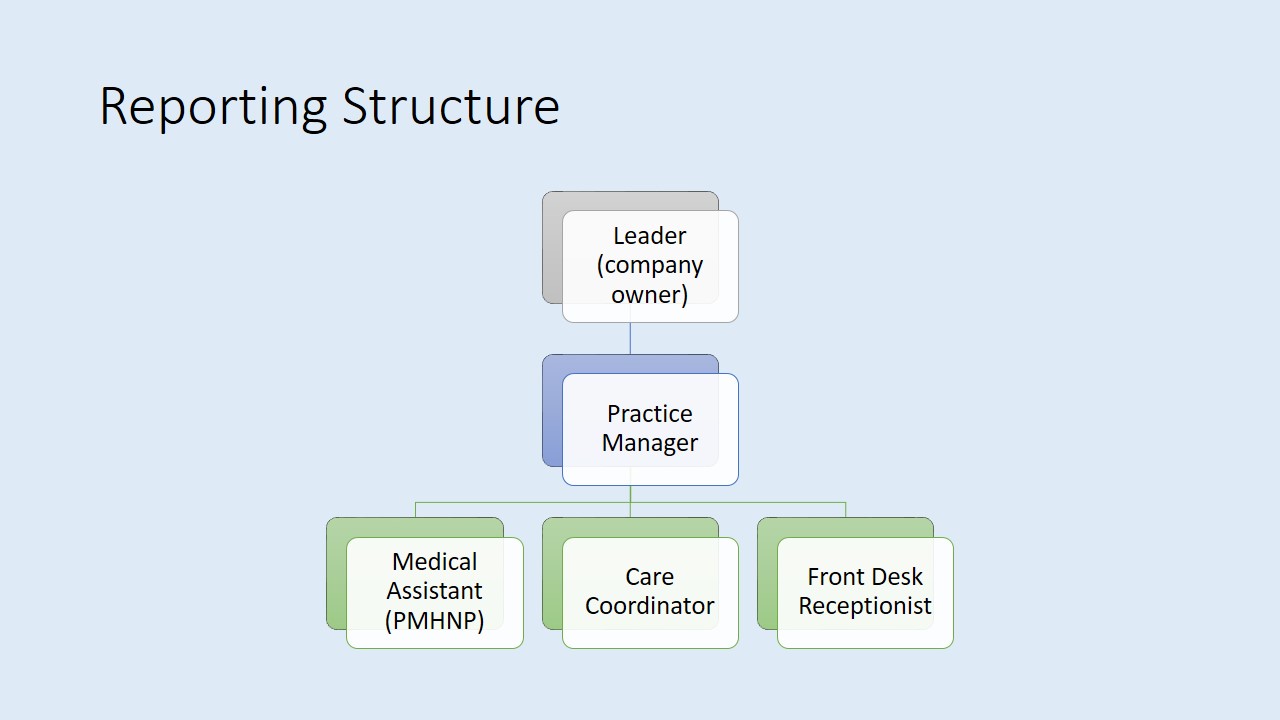
Reporting Structure
It is also worth mentioning that a PMHNP will need to follow a rigid reporting structure when operating in an organizational setting. Specifically, the cases associated with malpractice and breach of instructions must be reported respectively. The procedure of reporting is linked directly to the company hierarchy, which suggests that the process of reporting should flow from a nurse or a care coordinator to the practice manager to the owner of an organization (Keltner & Steele, 2018).
Evaluation Criteria
- Immediate management of patients’ needs (diagnosis and treatment);
- Professionalism and knowledge;
- Technical skills and information management;
- Patient education quality;
- Promotion of public health.
In order to assess the efficacy of a PNHMP’s work, one will have to focus on different aspects thereof and embrace a large number of qualities and characteristics that a PMHNP must possess. For instance, it will be necessary to consider a PMHNP’s diagnosing skills, the ability to identify and meet patients’ needs, the skills of establishing a dialogue with culturally diverse patients, the quality of communication between a patient and a nurse, and the extent to which patient education is implemented. Furthermore, the evaluation criteria must include a nurse’s technological prowess, their ability to encourage a positive change, and their management of public health concerns.

Employment Contract and Collaborative Practice Agreement
- Employment Contract:
- Salary and other payment issues;
- Workplace benefits;
- Number of working hours per week.
- Collaborative Practice Agreement:
- Focus on interdisciplinary cooperation;
- Management of workplace conflicts;
- Enhancement of communication and compromise.
It is also crucial for a PMHNP to be aware of the key elements that are included in the employment contract. As a rule, the specified document addresses the conditions under which a PMHNP will have to work in the selected organization, as well as benefits that a PMHNP will receive and the responsibilities that they will have to meet. The agreement will also include the number of working hours and key job requirements. The salary specified in the contract should be at least as high as the average Minnesota salary.
Practice agreement is another important document that a PMHNP has to sign prior to starting their work in an organizational setting. The collaborative practice agreement is supposed to ensure that the process of interdisciplinary cooperation is launched within an organization. Thus, the threat of interdisciplinary conflicts between a PMHNP and a physician is reduced (Weber et al., 2016).

Credentialing and Medicare Number
- Fairview Health Services: a nursing organization for a PMHNP in Minnesota;
- Rationale: career options, focus on teamwork, management of public health;
- Key financial data: Medicare number and reimbursement;
- Retrieving the personal Medicare number: MyMedicare.gov.
Among the Minnesota nursing organizations for PMHNPs, the Fairview Health Services deserves a particular mentioning as one with the greatest career opportunities and chances for promoting public health (Fairview Health Services, n.d.). As soon as a PMHNP receives a job position within the selected company and is provided with the necessary benefits, they are assigned with a Medicare number that will be used to obtain the specified benefits. Thus, it is imperative for an applicant to ensure that an organization offers the specified opportunity. It is strongly recommended to memorize one’s Medicare number to avoid further complications, yet one may also retrieve it when visiting the official site of Medicare. The following link will help one to get the necessary data about one’s payment issues: MyMedicare.gov (The Official U.S. Site for Medicare, n.d.).

Conclusion
- Numerous responsibilities and roles: key challenge of a PMHNP;
- Opportunities for professional growth: an important advantage;
- Ability to affect the lives of people on a community level;
- Promotion of a positive change in state health policies.
The job of a PMHNP is very challenging due to a vast number of responsibilities and the requirement to build new skills regularly. However, after learning the key information about receiving certification and applying for a PMHNP position, one will be able to find the job of a PMHNP very gratifying and exciting. As a PMHNP, one can affect the current public health levels and shape policies for managing patients’ needs on a statewide level.

References
The American Nurse Certification Center. (n.d.). Psychiatric-Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (across the lifespan) certification (PMHNP-BC). Web.
Brown, T., McKenna, B., & Furness, T. (2018). Impact of a nurse practitioner role on metabolic monitoring completion and referrals for consumers admitted to the intensive care area of an acute inpatient psychiatric unit. International Journal of Mental Health Nursing, 27(1), 341-348. Web.
Fairview Health Services. (n.d.). Who we are. Web.
Halter, M. J. (2017). Varcarolis‘ foundations of psychiatric-mental health nursing: A clinical approach (8th ed.). New York, NY: Elsevier Health Sciences.
Keltner, N. L., & Steele, D. (2018). Psychiatric nursing. New York, NY: Elsevier Health Sciences.
Orthwein, W. C. (2017). Psychiatric and mental health nursing: The craft of caring (2nd ed,). New York, NY: CRC Press.