Taxonomy and Scientific Classification of Onion
- Kingdom: Plantae.
- Order: Asparagales.
- Family: Alliaceae.
- Genus: Allium.
- Species: A. cepa.
Onion belongs to the oAlliaceae family and genus Allium. It is one of the oldest vegetables with several economic benefits. The common name of the species Allium cepa is garden onion or bulb onion and shallot (Grubben and Denton, 2004). There are further classifications that can be seen among the species. For instance, the fresh market onion (Allium cepa L.) has been classified to the Liliaceae and belongs to the genus Allium, section “Schoenoprasum”. Even today the wild onions grow in Central Asia that is said to be the place of origin of the entire family of onions. Botanists have places Allium cepa genus as part of the lily family. There are totally 325 species of onions, among these there are more than 50 of which that grow in North America. The family of allium comprises of varieties such as onions, shallots, green onions also called scallions, chives, leeks, and garlic (vegparadise.com, 2008).
Morphology and Anatomy
Onion is a biennial plant as a consequence they blossom only in the second year after its plantation. There are special ways of cultivation it. It grows only in places with specific climatic and soil conditions. The length of the day determines the growth and propagation of onion. Studies have proven that the only when the optimal day length is reached the swelling of the leaf base followed by the bulb formation initiates. The exception is only in some of the special varieties or more specifically the short-day varieties where in the swelling of the base initiates at a day length of 11 hours. In normal varieties or the long-day varieties require a day length of 15 – 16 hours for the bulb formation. The high yielding of onion prerequisites or depends on the formation of assimilation surface in the period before the formation of the bulb.
The farmers and those involved in the cultivation of onion need to remember that both autumn sown and spring sown onions, need adequate time, before the critical day length is reached for proper growth and maturation. In case if these required conditions are not met there can be low growth of deformities such as formation of thick necks, especially in some late maturing autumn sown onions.
The bulb serves as a storage organ during adverse conditions especially for cold and dry periods. The bulb mainly consists of water and nutrients. In other words, it can be said that after the maturation process the onion enters a phase called the sprouting resistance. In fact, at this stage the onion can be used for storage. Studies have proven that the duration of this stage vary with the different variety. From the structure it can be noted that in order to maintain the vital functions during the germ rest, the outermost onion scales are dry and less in water content. This outer most drylayer protects the inner layers from loss of water in the inner layers. The water and nutrients remain in the bulbs till the sprouting time when the water and nutrients are extracted from all skins. As a result the bulb becomes soft and the storage period ends. Researchers have found that low temperatures can lengthen the sprouting resistance. On the other hand any disturbance including physical stimuli such as transportation, temperature changes, changes in atmospheric humidity, light, etc. can have serious disturbance on the sprouting resistance (agri-saaten.de, N.D.).
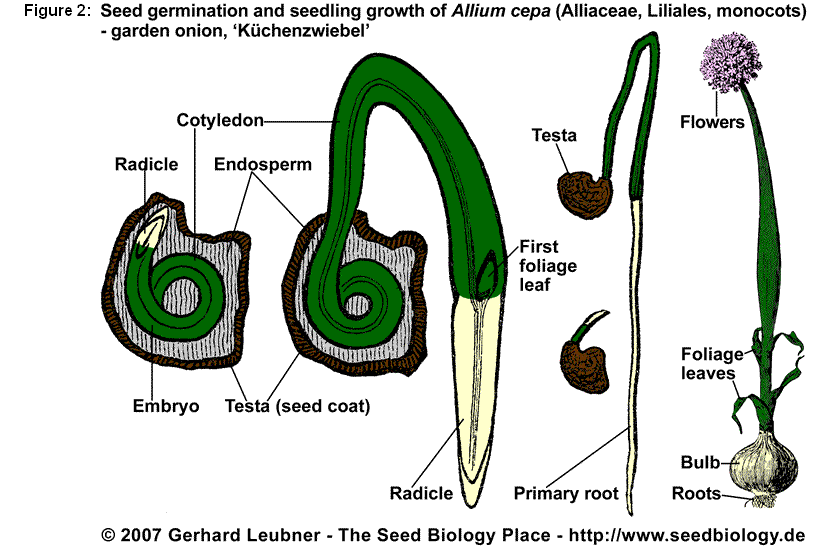
Onion has a monocot seed and the curved embryo has only one cotyledon which is embedded in endosperm tissue. This endosperm tissue which is surrounded or enclosed by testa or the seed coat is the main food storage tissue of monocot seeds. The morphophysiological dormancy is common among most Allium seeds, as a result they can be stored for several months. Additionally, this also give the embryos time to grow. Once the seeds germinate the testa and endosperm remain attached to the single cotyledon while the seedling primary root grows into the soil. The endosperm supplies the required nutrient to the developing seedling through the cotyledon. The cotyledon that is green in color also takes up the role of photosynthesis contributing considerably to the food supply of the developing seedling. The plumule or the young foliage leaves surfaces from the protective, sheath like base of the cotyledon, elongates, and forms the foliage leaves of the seedling (Figure 1).
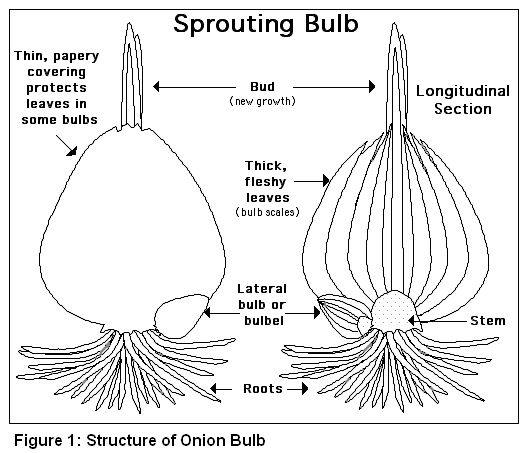
The thick bulbs consist of scale leaves in reaction to specific day lengths and temperatures (see Figure 2). The long-day plant require a minimum of fourteen hours of day length and grows especially in the northern latitudes including Europe requires a minimum of 14 hours of day length to initiate bulb formation. In general the seed or the transplants are sown during early spring. During the summer months the bulb formation takes place which is harvested during the later summer and the fall. Similar, life cycle can be seen with little modification in other Allium species such as garlic (A. sativum), leek (A. ampeloprasum), and Chinese chives (A. tuberosum) (Leubner, 2005).
Historical Significance
Archeologist have not been able to trace the origin of onion as these are small in size and also because their tissues leave little or no trace. There is no solid evidence of the place and the time of origin of onion. But the climatic conditions provide evidence that for its growth and development onions originated in central Asia. It is also suggested that onions were first grown in Iran and West Pakistan (Ehler, 2008). Even before the scientific development of these plants, it is thought that wild variety onion was used as a staple vegetable in the prehistoric diet. Further, when the cultivation began these species gained popularity only about 5000 years or more.
Onion is a vegetable that has a greater shelf life when compared to other vegetables and for this reason probably these were consumed for thousands of years and domesticated simultaneously all over the world. This less perishable quality of onions makes it easy for transportation to different parts and is used in many parts of the world. These are also easy to grow and could be grown in a variety of soils and climates. In early days when the technological development were lacking these onions were useful for sustaining human life as these are known to prevent thirst and could be dried and preserved for later consumption during food scarcity. Historical evidence suggests that onions are known for its medicinal values. It is said that onions grew in Chinese gardens as early as 5000 years ago and are also referenced in some of the oldest Vedic writings from India.
There is great significance of onion in Egypt. Archeologists draw back onions in Egypt to 3500 B.C. Onion has significance in the religious ritual for Egyptians. There are evidences that in ancient Egypt, onions were essentially an object of worship and they buried onions together with their Pharaohs. Several paintings of onion can be seen in the ancient Egyptian pyramids and they linked eternal life in the anatomy of the onion because of its circle-within-a-circle structure. Onions are of great significance during the funeral offerings. Similarly they also take great place during feasts and celebrations. Egyptologists considered onions for their great antiseptic qualities. All through the historical literatures the significance of onion can be noticed. For example, it is mentioned in the Bible, it is also mentioned in the ancient Indian literatures. Romans also considered it to be of great importance (Ehler, 2008).
It is a well known fact that onions are known to make every one cry. This is because of the complex sulphur compounds present in the onion. When an onion is cut there are mainly 2 reactions that occur. The first is the production of strong odor as a result of its enzymes. The release allicin which is a volatile sulfur gas causes irritation of eyes and makes everyone cry.
Economic benefits of Onion
Onions are a major ingredient in several vegetarian and non-vegetarian diets in different parts of the world. In addition to its nutritive value it is also known for its special medicinal values from ancient times. Literature review suggests that even in the sixth century, in India onions were used as a diuretic. Additionally, it is also known to be very beneficial for the heart, the eyes, and the joints. There are also studies that suggest that onions are good for osteoporosis. A glance through the historical medicine literature it can be noted that in United States during the colonial times eating raw wild onions was thought to cure measles (vegparadise.com, 2008).
Chinese medicine has gained popularity all over the world and onions have a major part in these medicines. They have found through their research that globe onions (allium cepa) are good for the liver, can help in increasing the moisture content of the intestines, and are also good for the lungs. In fact the experts in Chinese medicine say that eating raw onions are helpful for constipation. Studies suggest that onions are also helpful in lowering high blood pressure. They are also known for therapeutic properties on wounds or ulcers of the skin. As a result of these findings it can be noted that salads are prepared using fresh cut onions and is a global food. Similarly, spring onions, or scallions (allium fistulosum), help to enhance sweating. People who sweat very little can take spring onions that will help the removal of toxicants from the body through the sweat. In fact there are special preparations for patients with common cold and fever using spring onions that induces sweating and thereby reducing body temperature.
There are several studies that point out that onions are helpful in reducing the cholesterol levels. To be more specific it helps in reducing the Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL) that are harmful and raises the HDL or the high Density Lipoprotein which is considered to be essential for the proper functioning of the cardiovascular system (Prasad et al. N.D.). Researchers have also found that onions have health benefits as raw onions are effective in lowering overall cholesterol while at the same time raising HDLs. These are also effective against infectious bacteria. Onions help diabetics patients and dissolves blood clots. Recent studies also suggest that cancer prevention is also one of the plus points of onion (Stansbury, 1999).
Studies conducted at the University of California at Berkeley found that yellow and red onions, together with shallots, contain a substance known as quercetin which is a powerful antioxidant. This antioxidant acts as an anti-cancer and prevents any kind of mutations from occurring in the cells. This study suggests that if a person takes 1-3 onions daily, it will be sufficient to provide enough quercetin to prevent cancer (Widerbur, 2006). White onions lack quercetin and thereby do not have the antioxidant property. Onions are also beneficial for people suffering from Asthma as the sulfur compound present in the onions prevents the biochemical chain reaction leading to asthma attacks (vegparadise.com, 2008).
Allium family of onions is of great economic significance. Studies suggest that China is first in onion production followed by India, United States, Turkey and others. In fact, it can be said that there will be hardly a country in the world that is not depending on onion for economic benefits. Recent years have proven that onions can be grown to adapt well to their different climatic conditions. Since onions are of diverse colors such as white, brown, yellow, and red, purple and flavors ranging from mild and sweet to strong and biting, these onions have varied commercial and household use. It is common that sweet onions are mostly grown in California and Texas. Onions are also grown in small quantities with Georgia, New Mexico, Washington, and Arizona.
Onions have known to be entered almost all types of cuisine. It not only enhances the flavor of the food but also provides medicinal effects to the consumers. There is several variety of dishes prepared using onion. For instance, in British studded onions are famous, similarly the French created onion soups are of global taste. Onions are used in making pickles which is a spicy food used as a side dish especially in India. In the same way Onion bhaji’s are favorites of Indians. Onion also plays an important role in preparing non-vegetarian dishes. When it is added together with ginger and garlic pastes, it gives the mouthwatering taste to the dishes prepared.
There are also several other economic benefits of onion. For instance, in many cases the outermost skin of onion is thrown away. However some times these skins are used to enrich the soups with golden color. In Egypt, onions have high place in the religious rituals. Similarly, in the Greeks tradition the use red onion-skins are used to dye their Easter eggs. Several types of salads are prepared using onion which is considered to be beneficial for health as well as taste.
The nutritional benefits of onion are high. For instance, onion is a low calories substance and can suit the need of a person who is dieting. It is easy for them to take advantage from the low-calorie content of sweet raw onions. It is estimated that a 1/2-cup of cooked onions provides about 1.4 gms of proteins and the raw ones give about 0.9 gms. Onions are also known for the folic acid content. Fat content is very low in onions. Onions are also a store house for several vitamins and minerals. For instance, both raw and cooked onions have trace amounts of vitamin B, vitamin C, together with iron, zinc, potassium, magnesium, and calcium (vegparadise.com, 2008). Similarly, different varieties of onion have different micro and macro nutrients.
This paper has discussed in detail the botanical aspects such as taxonomy, morphology, anatomy, life history, historical importance, economic value, of onions. Onions have not only known for the nutritious values but also for its medicinal values. It also plays an important role in certain rituals in some of the cultures. These are found in a various recipes and preparations ranging from almost the totality of the world’s cultures. These are also easy for preservations as they can be used as fresh, frozen, canned, pickled, powdered, and dehydrated forms. Since these are grown in different climatic conditions, these are commonly available in most parts of the world. This is a plant of great significance from the prehistoric times till date.
References
- agri-saaten.de, (N.D.) Botany and taxonomy of the onion. Web.
- Ehler, J. T. (2008) Onion History. Web.
- Grubben, G.J.H. & Denton, O.A. (2004) Plant Resources of Tropical Africa 2. Vegetables. PROTA Foundation, Wageningen; Backhuys, Leiden; CTA, Wageningen.
- Leubner G. (2005) Seed Structure and Anatomy, The Seed Biology Place, Web.
- Prasad, K. et al. (N.D.) A diet rich in garlic, shallots and onions may cut the risk of prostate cancer in half, according to a study.
- Stansbury,J.E. (1999) Cancer Prevention Diet Nutrition Science News.
- vegparadise.com, (2008) Onion Aficionados Weep. Web.
- Widerbur, P. (2006) The Incredible Tasty Yet Mysterious Onion.