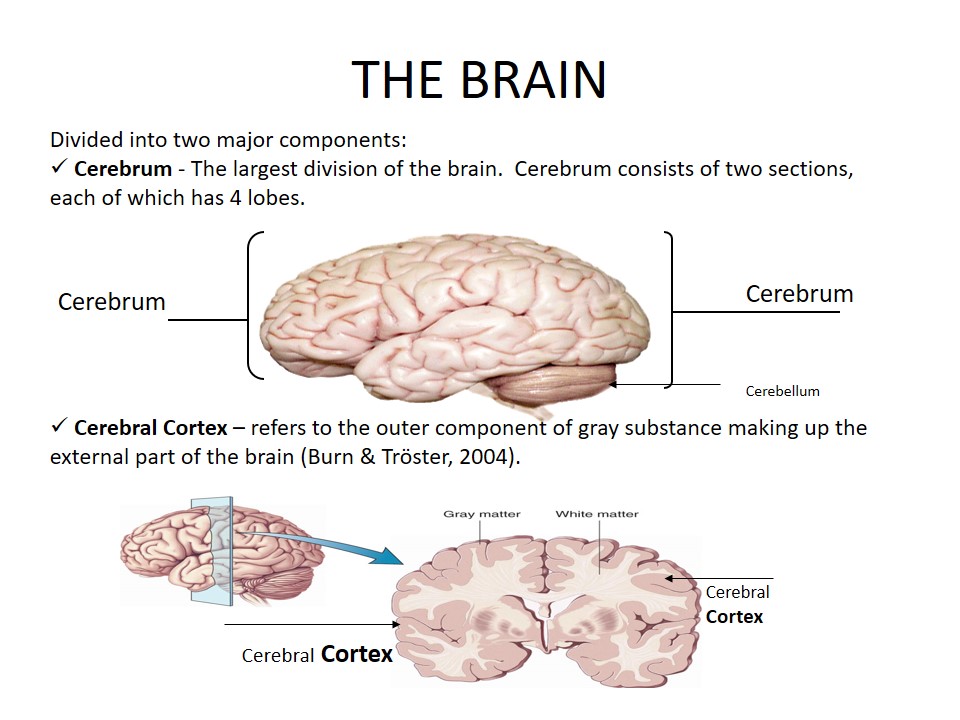
The Brain
Divided into two major components:
- Cerebrum – The largest division of the brain. Cerebrum consists of two sections, each of which has 4 lobes.
- Cerebral Cortex – refers to the outer component of gray substance making up the external part of the brain (Burn & Tröster, 2004).
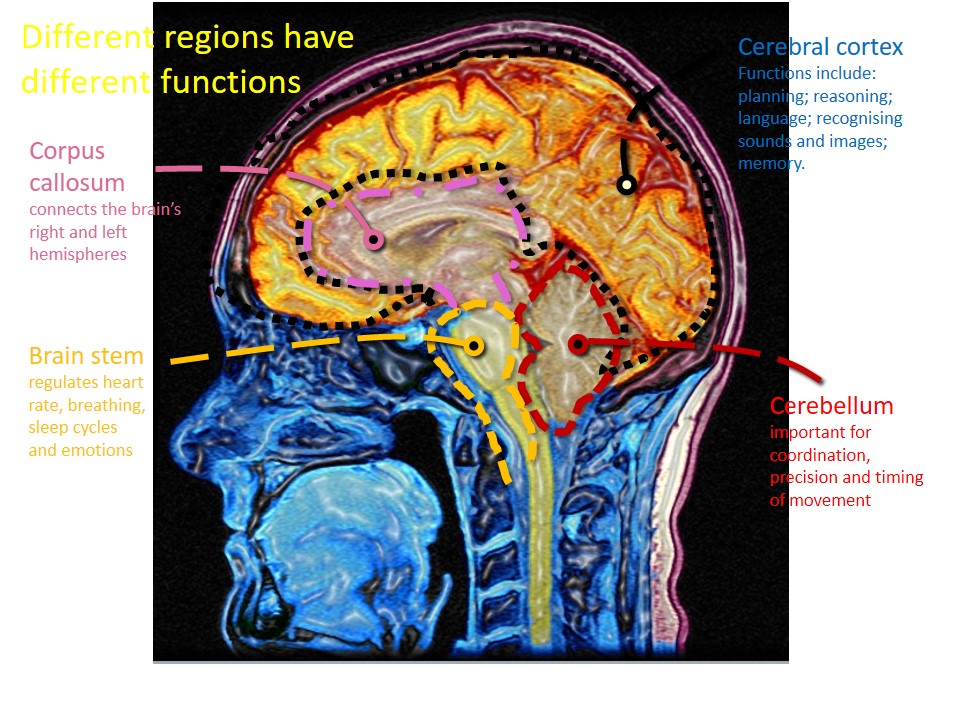
Different regions have different functions:
- Corpus callosum
- connects the brain’s right and left hemispheres.
- Brain stem
- regulates heart rate, breathing, sleep cycles and emotions.
- Cerebral cortex
- Functions include: planning; reasoning; language; recognising sounds and images; memory.
- Cerebellum
- important for coordination, precision and timing of movement.
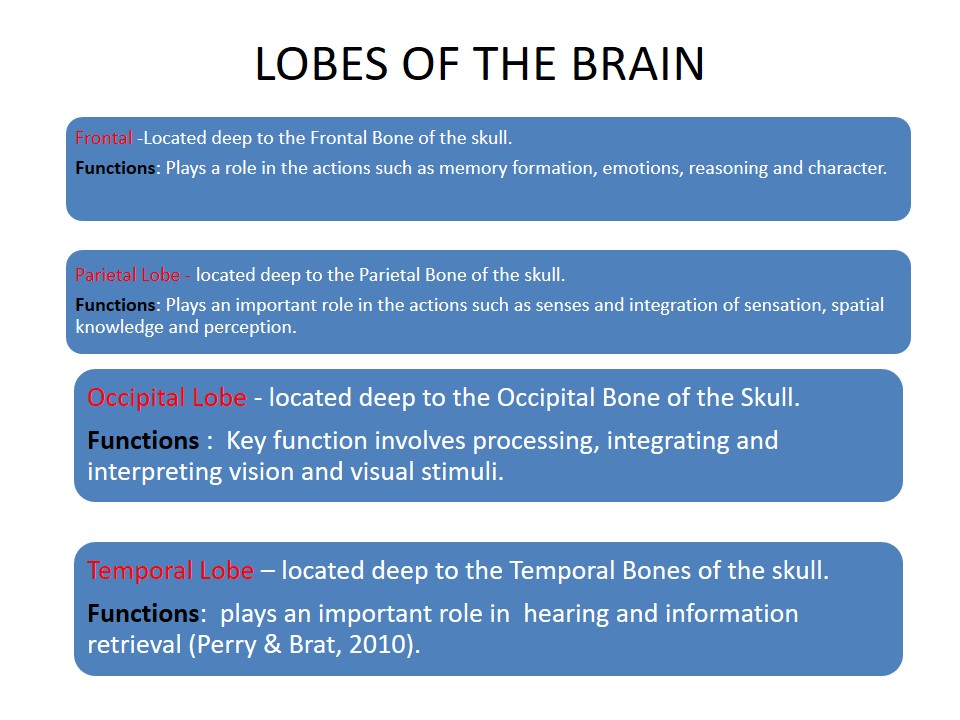
Lobes of the Brain
- Frontal -Located deep to the Frontal Bone of the skull.
- Functions: Plays a role in the actions such as memory formation, emotions, reasoning and character.
- Parietal Lobe – located deep to the Parietal Bone of the skull.
- Functions: Plays an important role in the actions such as senses and integration of sensation, spatial knowledge and perception.
- Occipital Lobe – located deep to the Occipital Bone of the Skull.
- Functions : Key function involves processing, integrating and interpreting vision and visual stimuli.
- Temporal Lobe – located deep to the Temporal Bones of the skull.
- Functions: plays an important role in hearing and information retrieval (Perry & Brat, 2010).
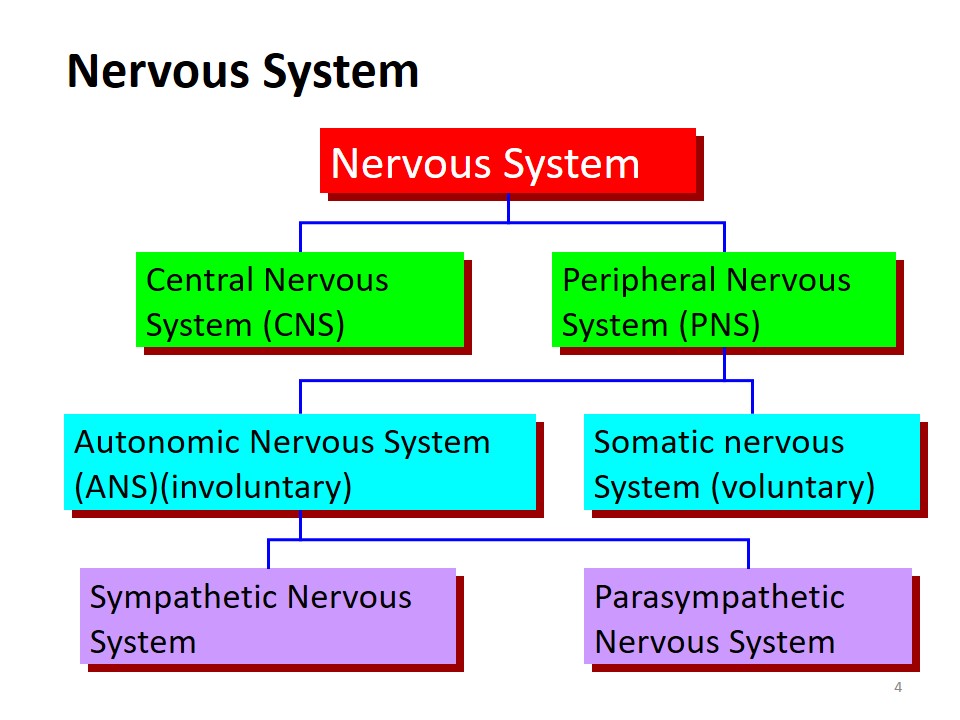
Nervous System
- Nervous System:
- Central Nervous System (CNS).
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)(involuntary).
- Somatic nervous System (voluntary).
- Sympathetic Nervous System.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System.
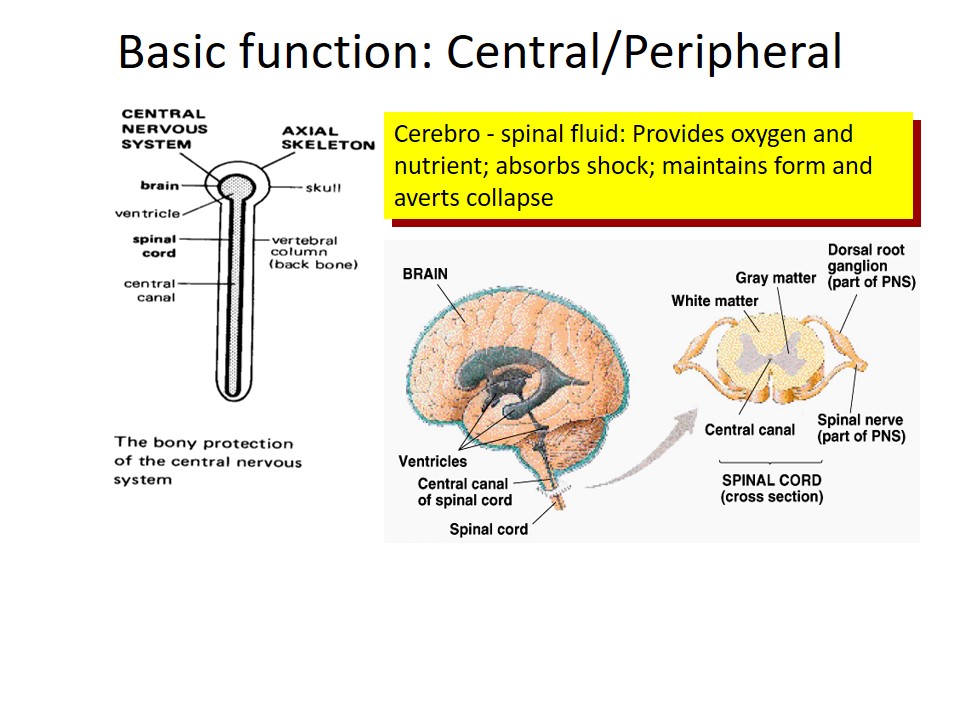
Basic function: Central/Peripheral
Cerebro – spinal fluid: Provides oxygen and nutrient; absorbs shock; maintains form and averts collapse.
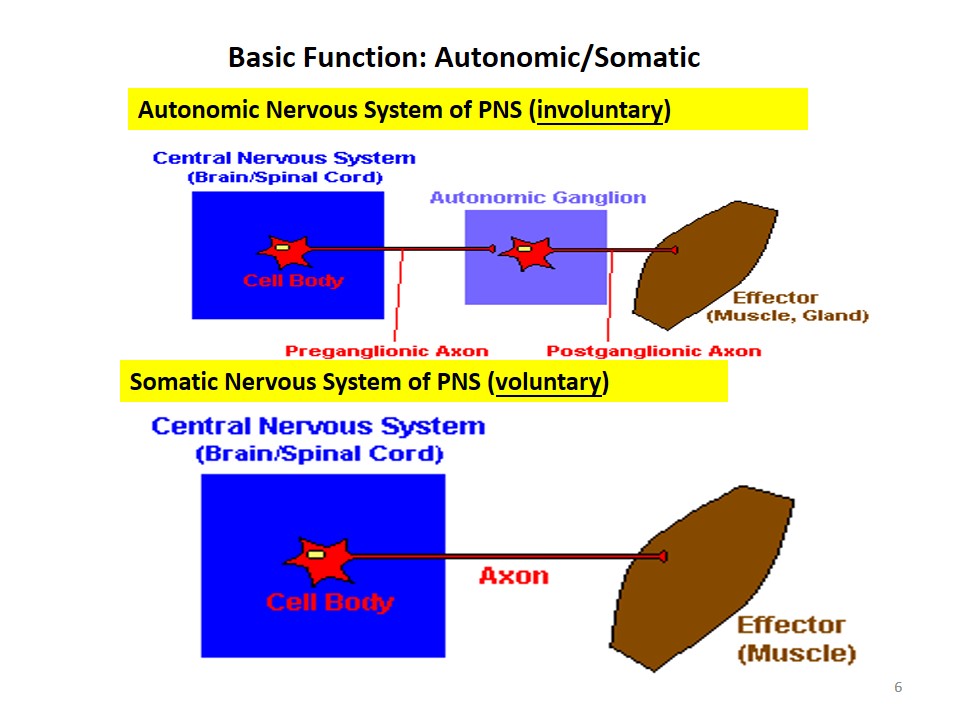
Basic Function: Autonomic/Somatic
- Autonomic Nervous System of PNS (involuntary).
- Somatic Nervous System of PNS (voluntary).
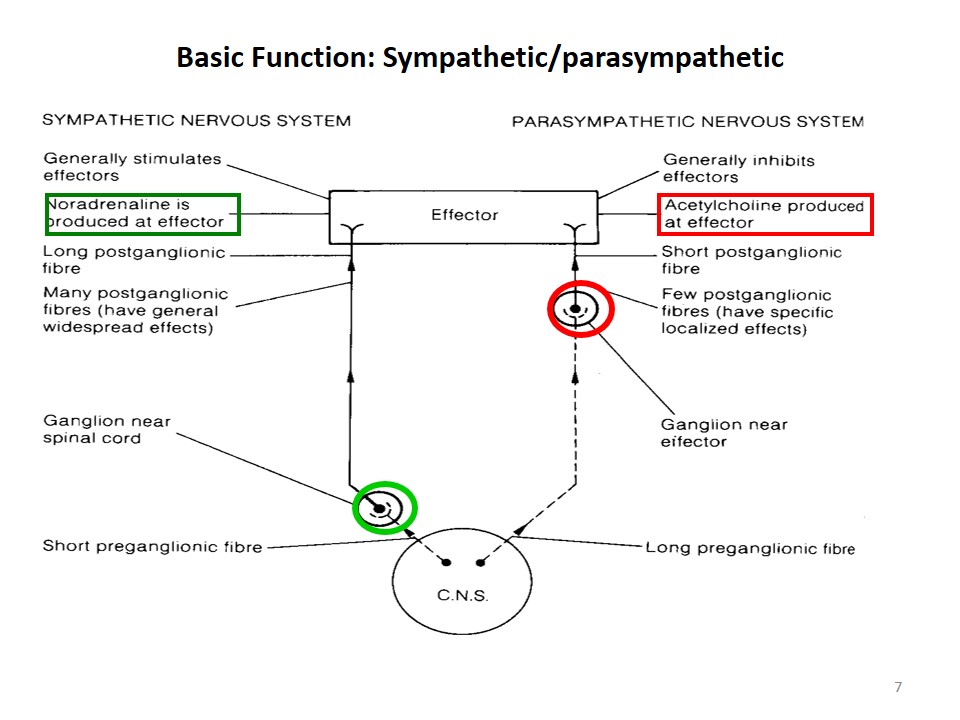
Basic Function: Sympathetic/parasympathetic
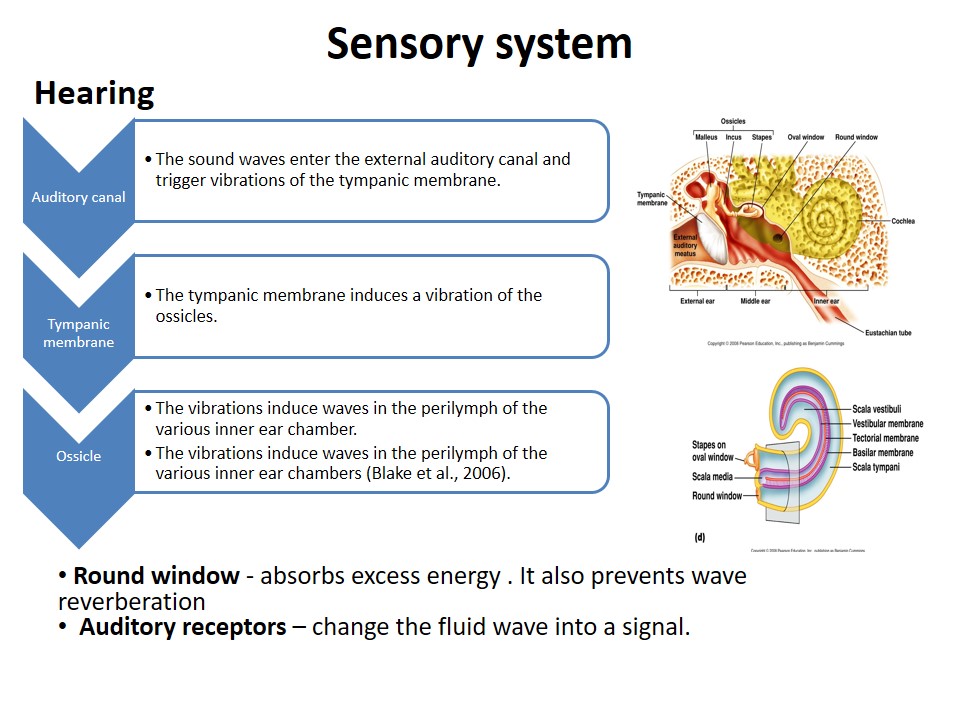
Sensory system
Hearing
- Auditory canal:
- The sound waves enter the external auditory canal and trigger vibrations of the tympanic membrane.
- Tympanic membrane:
- The tympanic membrane induces a vibration of the ossicles.
- Ossicle:
- The vibrations induce waves in the perilymph of the various inner ear chamber.
- The vibrations induce waves in the perilymph of the various inner ear chambers (Blake et al., 2006).
- Round window – absorbs excess energy . It also prevents wave reverberation
- Auditory receptors – change the fluid wave into a signal.
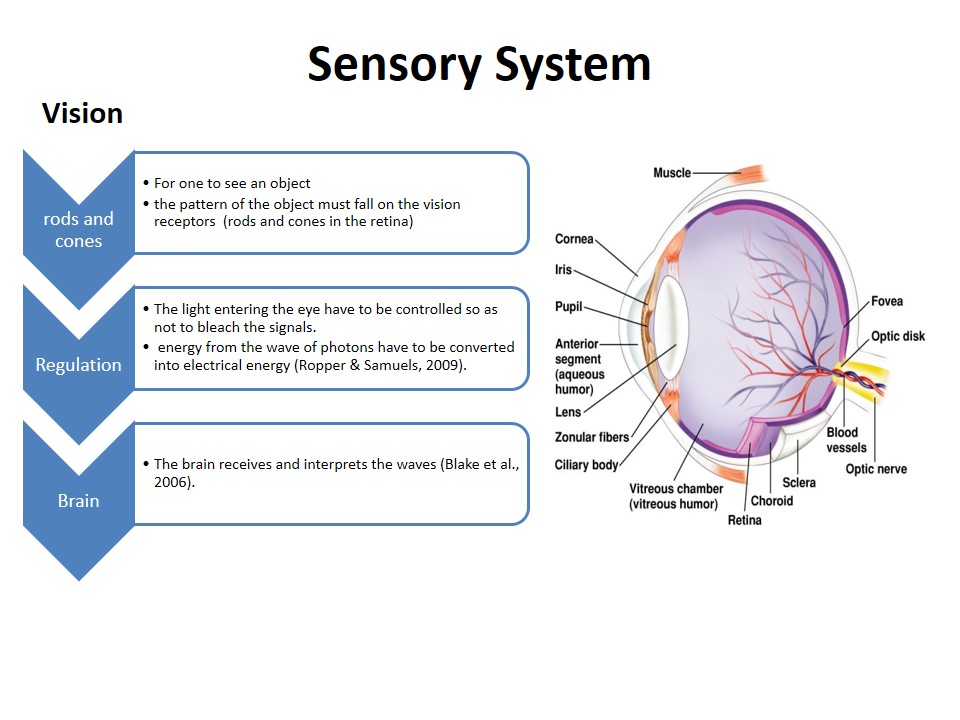
Vision
- Rods and cones:
- For one to see an object.
- The pattern of the object must fall on the vision receptors (rods and cones in the retina).
- Regulation
- The light entering the eye have to be controlled so as not to bleach the signals.
- Energy from the wave of photons have to be converted into electrical energy (Ropper & Samuels, 2009).
- Brain
- The brain receives and interprets the waves (Blake et al., 2006).
References
Blake, T., Heiser, A., Caywood, M., Merzenich, M. (2006). Experience-dependent adult cortical plasticity requires cognitive association between sensation and reward. Neuron, 52(2),371–81.
Burn, D. & Tröster, A. (2004). Neuropsychiatric complications of medical and surgical therapies for Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology, 17(3), 172—180.
Perry, A., & Brat, D. (2010). Neuropathology patterns and introduction. In A. Perry & D. Brat DJ (eds.), Practical Surgical Neuropathology. Elsevier, Churchill Livingstone: Philadelphia.
Ropper, A., & Samuels, M. (2009). Adams and Victor’s Principles of Neurology (9th ed.). New York, McGraw-Hill Professional.