Introduction
Strategic management involves using past and present data/statistics within a company to predict, plan, and manage future business endeavours; a budget is a management tool that uses business statistics to make future predictions. Business information must assist a company to remain focused on the goals and objectives of its establishment.
Management scholars have developed different management tools to forecast future operational levels; one of the oldest futuristic analytical tools is budget. A budget is a management tool that uses past and present information to predict future costs and expenses. When budgets are made, they assist the management to forecasts the future using the available information and providing an operating framework. Management accountants are responsible for advising an organization’s top management and policymakers on matters regarding finances to ensure there are effectiveness, efficiency and optimal use of resources (Horngren, 2009).
The Airline industry, in the United States of America and the world, is general, is highly competitive; companies in the sector need to predict, plan and prepare for future engagements in the rapidly changing sector. There is an increased innovation of services and equipment and customer needs have also changed.
Emirates Airline company (mostly referred to just as Emirates) is an international company that require decisions responsive to the airline market today; to make futuristic decisions, the company employees budgeting as one method of setting goals and strategies to have them attained (Jawahar, 2008). This paper discusses the concept of budgeting using Emirates as a sample company.
The budgetary process
A budgetary process is a systematic approach where the management uses past and present data within their organisation to set practical goals and objectives. Planning is crucial for business strategic move and focus; planning is done to prepare the pathway for future business operations, it involves making an analysis that compares actual business performance and the standard rate. With budgeting, management is kept active to come up with the right strategies to remain competitive in the business. Budgets are made in advance of operation thus they offer management the framework to control costs and maximize profits.
Depending on the task that a certain budget is wanted to manage, it takes different making processes; at Emirates, management accountants make sure that different budgets maintained have a detailed plan of operations expected for a specific period. The main characteristics of Emirates budget system are: they are prepared in advance to offer guidance to plans, the budgets aim at relating future periods with futuristic goals and objectives and it forms a statement expressed in monetary/physical units prepared for the formulation of set policy (Jiambalvo, 2007).
The budgetary committee at Emirates has the following objectives when making a budget:
- Effective resource allocation
- In evaluating and appraising projects where the outcome is weighed against the expected results (budget results)
- To establish areas of inefficiency and probable the way the company can improve the system
- To facilitate efficiency in an organisation
- For futuristic purposes: to predict the future from previous budget trends
- To keep the operation on track as the outcome is gauged from time to time with the budgeted outcome (Ray, Eric, Brewer, 2009)
Budgetary methods adopted at Emirates
To come up with an operational budget, Emirates has two main approaches to budgeting: a functional based method and a flexibility basis. Under the functional basis, the company ensures that it has a budget for every activity or project within the organisation; the approach means that every activity within the organisation is documented, goals set, and management strategies adopted. The period that functional based methods budgets cover is determined with the particular activity that the budget is required to fulfil; for instance, if the company is having a single research project, from the masters budget kitty of research, another budget will be made to cover the period.
Emirates has a number of budgets that falls under the frameworks of functional basis, they include cash budgets, master budget, and operating and financial budgets (Warren, James and Duchac, 2008).
Under the frameworks of flexibility-based budgets, the company has fixed and flexible budgets. Fixed budgets address those issues that are not likely to change in the foreseeable future or the time that the budget is expected to cover, they address the known expenditure and outcome as a result. Flexible budgets are also called variable budgets, are prepared when the costs, expenditure, and outcomes, as a result, keep changing or varies with time (Maher, Stickney and Roman, 2006).
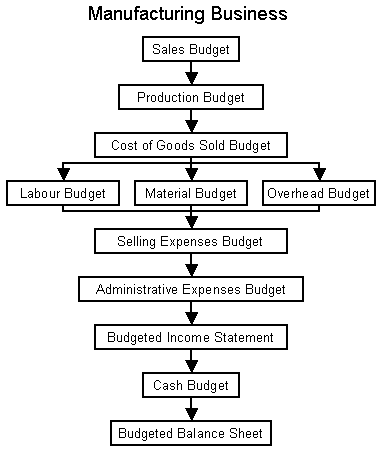
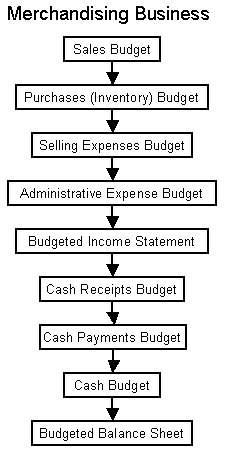
Sample of Master budgets (functional budgeting method)
The master budget
The emirate has a master budget that determines the movement of its other budgets as follows:
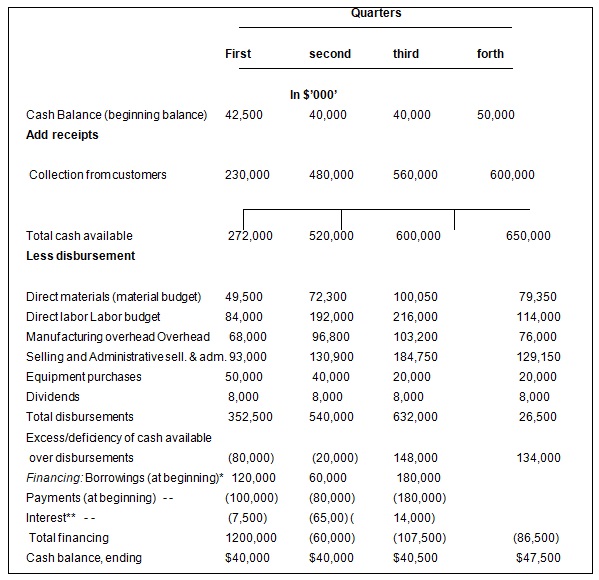
In the above cash budget, cash receipts and cash payments budgets can be summed together with a single cash budget.
Cash budget
A cash budget is prepared to predict, control, manage and monitor the flow of cash within an organisation; it considers the outflow and inflow of cash from and to different business activities. On the side of cash outflows, the main sources of funds considered are cash sales, collection from creditors, capital injections, sale of fixed assets among other sources of funds.
In the case of Emirates, the main source of funds is the transport collections (from both cargo and passenger planes), investments incomes, and other incomes. The role of the cash budget is to bring these incomes to charge. On the inflow side of the budget, the funds will be used to finance different activities within the company’s operation; they represent certain cash items like paying of distribution costs, paying off financing activities, and other business-related expenditures (Don, and Mowen, 2006)
As far as budgets are used to monitor and control the use of funds, managers have the task of ensuring that the goal has been attained effectively. Management should maintain a finance department that is mandated with the task of ensuring that all financial transitions in the company are well vetted. The department does not work in autonomy but collaborates with other departments. When making an allocation or releasing one, the management should ensure that the right channel of accessing funds has been followed; this will facilitate compliance with the budget.
The company has an internal audit/ internal control system that ensures that there are adequate checks and balances. Internal controls are checks and balances in an organization that aims to maintain integrity in the company’s process. It ensures that funds are not misappropriated and are managed for the good of the organization. This ensures that a company has better fund management. Management accountants are responsible for maintaining good working internal controls (Carter, 2005).
Policies to support the budgetary system
Other than maintaining a robust management accounting system, the company should not ignore the need for knowledge management and business information tools in addition to existing management accounting tools. When this information is made available in the company, it will assist in making better and timely decisions.
The quality and timeliness of a decision determine the competitiveness of a company. For example, there has been a move to low-cost planes alongside the use of Jumbo planes. When the company maintains a pool of information on the market trends, it will be able to make decisions that are timely regarding what point they should engage in low-cost planes and which routes should they use Jumbo planes (Weygandt, Kimmel and Kieso, 2009).
When a company maintains a rich knowledge and nurtures its intellectual assets, it gets a chance to orient and trains new staff more effectively. For example, engineers maintained in the firm can use their pool of knowledge to show new employees on mechanical issues they can expect from a certain plane and how to handle it. Another example is in service delivery. Experienced hostesses are able to handle hostile passengers more effectively and thus the general service of the company increases (Bragg, 2001).
Conclusion
Budgets are cost management tools that assist a company to predict future business levels and keeping track of its expenses and incomes; they an old management tools whose relevance remains high in the contemporary business world. When making budgets, the most important thing that managers should look into is matching organisational targets with the potential of an organisation. In companies that have managed to have effective budgetary systems, there is a need to support them with other quality management strategies.
References
Bragg, M.(2001).Cost accounting: a comprehensive guide. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Carter, K. (2005). Cost Accounting. New Jersey: Cengage Learning.
Don, R. and Mowen, M. (2006). Managerial Accounting. New Jersey: Cengage Learning.
Horngren, T. (2009). Cost accounting: a managerial emphasis. Pearson Prentice Hall.
Jawahar, L. (2008). Cost Accounting. New Jersey: Tata McGraw-Hill Education.
Jiambalvo, J. (2007). Managerial Accounting. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Maher, M., Stickney, P. and Roman, L. (2006). Managerial accounting: an introduction to concepts, methods, and uses. New Jersey: Cengage Learning.
Ray, H., Eric, W., Brewer, P.(2009). Managerial Accounting London: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Warren, C., James, M. and Duchac, J.(2008). Managerial Accounting. New Jersey: Cengage Learning.
Weygandt, J., Kimmel, P. and Kieso, D. (2009). Managerial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Appendixes
Appendix 1: Sample Master Budget for a manufacturing company