Introduction
Numerous Information Systems projects fail after having undergone extensive research in their development phases. In order to ensure that no shortfall from the individual and collective ends of the personnel involved, the British Computer Society (BCS) has developed a code of conduct as a criteria for membership that defines the fundamental guidelines to which IT professionals are to adhere in all development and execution phases of their Information Systems projects In the coming paragraphs, a brief analysis of a few of the fundamental guidelines of the BCS Code of Conduct (BCS 2008).
The BCS Code of conduct states that the IT professional will keep the general health and safety of the public and the environment his first priority in all his actions. This clause can be observed to have direct impacts upon the formulation and the eventual outcome of any Information Systems project that involves social elements.
The BCS Code of conduct also applies rigid restrictions where the safety of third parties is concerned. By ensuring the safety of third party concerns, the code of conduct allows for the establishment of a cooperative setup of interaction between the people working on an Information Systems Project. The clause that deals with third part concerns also encompasses competitors and any members of the public who may be affected by the system.
The code of conduct is particular about the information that the personnel working on an Information Systems project harbor. The clause that deals with this matter is particularly specific about the fact that it is mandatory for the IT professional to have complete information regarding not only the rules and regulations of the organization but also with the rules and legislation that are applicable from the government’s aspect. Needless to say, this clause acts as a line for IT professionals that they cannot cross in their operations and gives them the cover of government support. However, it is important to note at this point that the paragraphs above are merely reflecting the aspect of Public Interest that the code of conduct covers.
Besides the aspect of Public Interest, The code of conduct is based on a total of seventeen clauses with the following sections under the titles of Duty to Relevant Authority, Duty to the Profession and Professional Competence and Integrity.
In Duty of Relevant Authority, the BCS Code of Conduct defines workplace ethics in terms of the necessity of appropriate authorization regarding the disclosure of information to third parties. While doing so, the code of conduct makes sure that the IT professional realizes that the individual incorporates loyalty to the task at hand and understands the necessity of operating within the time and resource constraints. One can realize that these clauses are of prime importance when viewed in the ever decreasing global availability of time and resources. This section also serves to establish a code regarding keeping important information concealed, particularly in cases where the disclosure of the information can save the involved parties from loss of life or limb.
Further on, in the section titled Duty to Profession, the BCS code of conduct begins by highlighting the importance of keeping the name of the British Computer Society held high and to make sure that the reputation of the British Computer Society is not trodden upon anywhere. The BCS code of conduct suggests that this measure is exercised through sincerity to the profession. The code of conduct also highlights the fact that all members of the BCS have to make sure that they exercise appropriate behavior with their fellow BCS members. In their actions, they are to exercise integrity and genuineness in their words and intentions.
The BCS code of conduct also provides legal guidelines to its members. In case a member is convicted of having committed a criminal offence, the member is under obligation to report the BCS immediately. This clause also holds if the member holds a directorial position and the respective organization has gone bankrupt. During this time, the member is also not allowed to make any statements on behalf of the BCS unless authorized to do so.
The last section of the code of conduct is based on the duty of an IT professional to the continuous desire for an increase in knowledge and understanding in the area of concern. By doing so, the BSC code of conduct encourages the BCS members to refine their knowledge and skills in their area of profession.
The Data Protection Act of 1998
This act establishes Data Protection Principles through eight sections. The Data Protection Act begins by defining data and continues to provide a comprehensive framework for the acquiring, usage, distribution and concealment of data.
Data cannot be used for any purpose other than the purpose of collection that was stated at the time of accumulation of data.
The second and the third clause can be combined to form the understanding that data concerning one party cannot be forwarded to a third party without the consent of the subject party. Neither can a third party attempt to obtain that data. However, the individual/party about whom the data is concerned can access the data about him/her/them. According to this law, this combination of the second and the third clause is void only where the acquiring or distribution of the data can help detect and/or prevent crime (OPSI 2008).
The process of keeping the information that is considered to be personal by the subject of the information up to date must not be kept for longer periods than absolutely necessary.
Since the law has been designed to protect the interests of the UK populace, it prohibits the transmission of personal information outside the perimeter of the European Economic Area. This clause does not hold if the individual/party whom the information concerns has no clearly stated that it has no objection to the transmission of that information.
If information collection is being carried out by an organization, then it is mandatory for the organization to register with the Information Commissioner’s Office. It is also mandatory for these organizations to make sure that appropriate data security measures are set up to ensure that the data is not used, or distributed for unethical causes or by unauthorized personnel. The law also gives the subjects of the information the right to have any information corrected however the correction must be based on fact and does not encompass one’s opinion in this regard.
Compliance with the Disability Discrimination Act through IT
The Disability Discrimination Act was introduced in 1995 in order to bring an end to the discrimination against people who have disabilities. In the modern day world, information technology plays an ever increasingly important role in allowing organizations to comply with the Disability Discrimination Act. There are large number of instruments that can be brought into use for this purpose. For instance, speech recognition, one hand typing, video magnifier, electronic reading aids, using a computer without vision and amplifiers.
In order to establish a data flow diagram for the given process, the flow of data has been broken into two separate flows of data. One before the students have sat the examination, in the compilation of the examination paper, and one for after the students have sat the examination, in the compilation of the results.
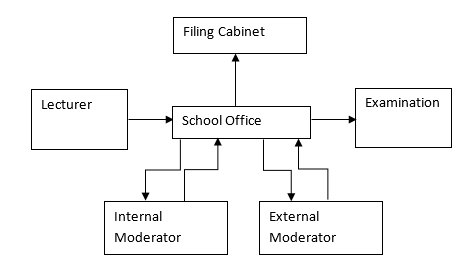
In the above data flow diagram, the information takes origin from the lecturer who generates the first draft and sends it to the school office. Once this has happened, there is no more interaction between the lecturer and the examination paper. The school office holds the responsibility of keeping a record of the exam paper beyond this point. The first draft is stored in the filing cabinet and a copy is sent to the internal moderator, with whom interaction takes place twice.
Once the paper has been analyzed by the internal moderator, the school office receives it, and as it concludes interaction with the internal moderator, a similar interaction is made with the external moderator, who give his comments on the paper and returns it to the school office. Once this has happened, the final phase that the information (examination paper) goes through is the actual examination.
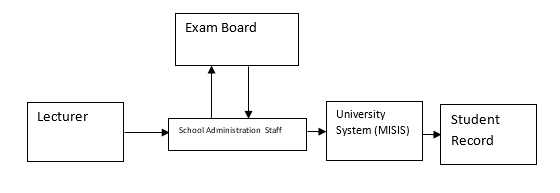
Once the students have given the examination, the last step is for the lecturer to scrutinize the attempted papers that the students have been subjected to. As the lecturer does so, he/she keeps entering the data through a spreadsheet into the data base of the School Administration Staff, which sends copies to the Exam Board and enters the data into the University System, namely MISIS. The data is then entered into the Student Record.
Application Service Providers allow their clients to increase productivity by using web based solutions to their operational problems (Maccelli Gartenfeld & Mockler 2007). As the cost of specialized software development continues to increase with clients asking for more and more convenience from their software, the significance of Application Service Providers continues to increase as well (Hall & Frey 2007).
Modern day Application Service Providers provide a wide array of services to their clients. For instance, Microsoft offers a wide range of services such as creating a free website, registering a domain name, getting free website hosting, storing documents online, sharing documents with others, backing up files online and collaborate online.
Key ways that ATP Life Assurances use to ascertain that their IT projects are completed successfully and support the goals of the business
In order to carry out a comprehensive analysis of the degree of risk in the market, ATP Life Assurances makes extensive use of analytical tools to calculate and analyze its return on investment in the financial perspective. These tools are sequentially applied on each individual IT project and business project that ATP Life Assurances is running. By placing every individual IT project in its own individual frame of reference and then subjecting it to the above mentioned tools of analysis, ATP Life Assurances makes the development of a development analysis possible. This allows managers to make any mid-way changes in the IT project that are required to steer the project on to the path towards the desired results and outcomes. Extensive use of an Investment Tracking Database is also made by ATP Life Assurances.
Six things to ensure that the success of an IT project
Implementation of Information Technology in the operational framework of the organization is undeniably essential in order to ensure that the organization measures up to modern day technological trends and operational platforms let alone succeed. The need for a strong information technology framework in organizations is extremely essential.
In order for an IT project to be successful, it is necessary that evaluating procedures are exercised frequently at all points of the evolution process of the project (IBM 2001). Implementation of evaluation procedures without cost management analysis at subsequent stages would leave the evaluation only partially completed. An analysis of cost is essential at every stage of the evolution of the project. The use of Application Service Providers can be augmented into the frame work to reduce costs while causing an increase in the efficiency of the project (Mockler 2005).
The implementation of these elements, the organization will be able to carry out operations such as data gathering, quality analysis, integration and aggregation with efficiency and effectiveness (Thrasher 2007).
List of References
BCS (2008) Code of Conduct. Web.
Hall, T. & Frey, K. (2007) Application Service Provider and Software as a Service Agreements Line by Line: A Detailed Look at ASP and Saas Agreements and How to Change Them to Meet Your Needs. Aspatore Books.
IBM (2001) IBM IT Optimization Services. Web.
Maccelli, L., Gartenfeld, M. & Mockler, R. (2007) Application Service Providers In Business. Routledge.
Mockler, R. (2005) Application Service Providers In Business. Routledge.
OPSI. (2008) Data Protection Act 1998. Web.
Thrasher, H. (2007) Boiling the IT Frog: How to Make Your Business Information Technology Wildly Successful Without Having to Learn Anything Technical. BookSurge Publishing.