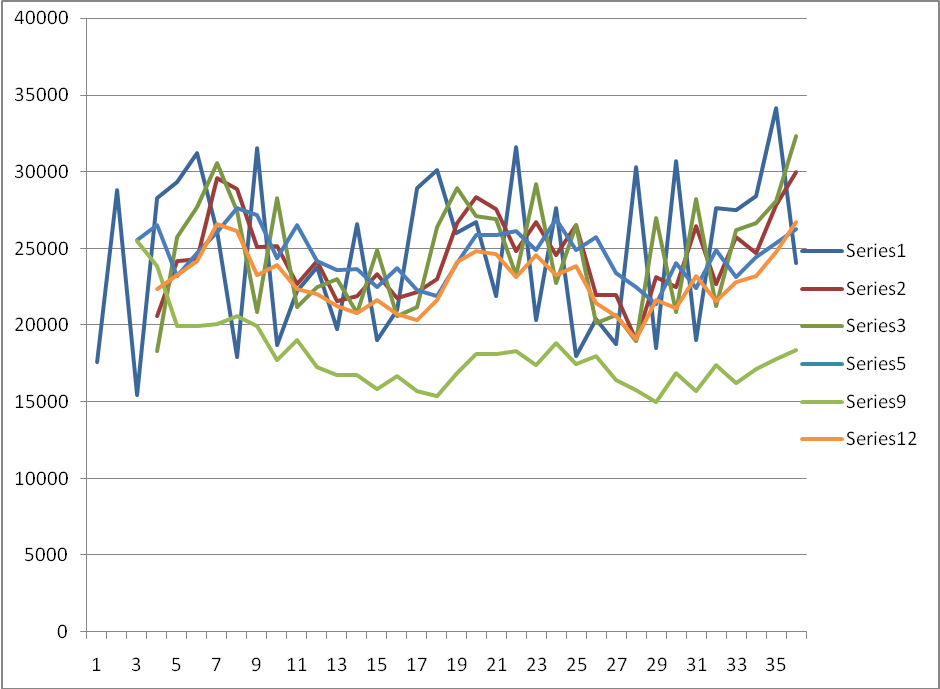
Business Forecasting
From the graph indicated above, it can be deduced that the most realistic trend is that of exponential smoothing. This is the only series that has provided a vivid trend that can be followed keenly and depict prediction while making out forecasts. This is therefore the most likely data that can give the best description of what can be expected. In comparison to the moving avarages, they are all treated equally while in exponential smothing, they are assigned a decreasing weight over the duration that data was collected. “Double exponential will also not be realistic because the data has some trend that cannot be applied” Clement and Hendry (1998, p 270). This makes the exponential smoothing the best and the very realistic measure for the forecasting in this context.
Forecasting predicts targets to be anticipated and can be used to estimating future aspect of business or other related operations when used as a technique. Volume of sales can be forecasted basing on past data. Production schedules, purchasing plans for raw materials. Business policies regarding will thus be affected by such forecasts that may laead to poor planning and increased cost to the business.
“Review of sales forecast marks an important part in business planning over a specific period” Armstrong (2001, p 543). One will then be capable to efficiently identify factors that boost his sales of the business and he or she can generate data for future sales.
“Qualitative forecasting can be carried out using the Delphi method that seeks to extract the group consensus from a panel of experts depending on the set information” Makridakis et al (2003, p 242). Scenario setting can also be utilised as it bases its approach on a set off assumptions and the likely impact of the business outcome is extracted from that data. Development of time series includes various factors that include; trend components, cyclical or repetitive mechanisms, seasonal functions that are based on peaks of either high or low times, and irregularly determined components. All these when integrated provide a specific value for the time series which can be seen as a precise forecast.
Modes of transport
This is not a good decision to make because sales are dependent on customer willingness to buy the goods and services provided. More so, “the high transport cost will impact on the final goods selling price” Goodman (2009, p 73). This has an impact on the clients whose effect has not yet been pre-determined. “The extra increase in inventory and ware housing all affect the final cost of the goods” Leland and Bailey (2006, p 225). The company will also increase their expenses. This is very insecure because the goods may not sell due to the change in the prices as customers may decide to opt for alternatives and avoid buying the goods supplied by the company since consumers have the freedom of choice. If the company has to increase the price of goods in order to balance the profit margin. “It will be to the disadvantage of the company because it will be total loss to the company, which makes futile the whole objective of the business” Fogli (2005, p 123). This therefore does not support making the decision in favour of the advice at any cost because it will only predispose the business to risks that might lead to closure of the business.
Customer Service
High cost of transportation means more expenses to the company. Transport infrastructure has been addressed by providing alternative sources and therefore the company has to opt for cheap alternatives. Considering the cost of rail transport over four days, it is relatively cheap basing on the fact rail accommodates a large quantity of good even though it takes very long. More so, other factors such as maintenance of trucks and servicing are also to be accounted as they are extra expenses that need to be incorporated on the cost of transport. However, “another approach can be an integrated system that may combine several transport modes before they get to the destination” European Conference of Ministers (1991, p 26-29). Rail may be used for a section that is convenient and road to take over for the section that befits the road transport. Also, new polluter charges is a big debate for controlling the modes of transport and if these is implemented, then transport business will be hampered because of the heavy taxation limiting the benefits of the business and more especially the road transport.
Rail remains one of the modest transports with little external costs, trucks are likely to cost thrice as much as trains and these does not vary either at peak or wee hours as it has been suggested by Quinet and William ( 2004, p 312.)
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Economic order quantities have been in existence long before the computer came into existence. It is an aspect of inventory management and can be used to set up cost effective solutions to questions such as when, and how much. It was initially referred to as minimum cost quantity. EOQ is simply an accounting procedure that predicts the position at which order costs and inventory are at minimum in order to fix the cost benefit mechanism for companies and organizations. However, determination of performance by the inventory turns out to be very disastrous in the name of inventory management as at times, it may lead to the increase in operational costs.
EOQ is best utilised at any time, one has to have a repetitive purchasing of goods. EOQ are purchases to stock for distributers and make to stock for manufacturers or release for products of the same items. Maintenance of machines, repair of worn out parts and operating Inventory are applications of good practice in EOQ.
“EOQ is in cooperated with the inputs in the calculations, yearly usage which is an input forecasted on annual basis” Hansen et al (2007, p 612). Order cost that is also referred to as set up cost; they are not associated with the quantity of the ordered goods but the physical handling of goods. For goods that are being purchased, they will include cost of entering the purchase order, processing of the receipt, inspection, an invoicing and vendor payments.
Caring cost is the cost of having an inventory at hand. They may include costs for interests, insurance, storage costs and taxes. In case the lead time is changed to 10 days, the reordering will lead to an increase in the order cost and caring cost which do have an impact on the Economic order quantities and may increase extra expenses that are likely to fault the cost of re-order. Also, the assumption that are applied in EOQ will not have a base because it is assumed that the ordering cost will remain constant, “the rate of demand and lead time is fixed while the purchase price of the item is constant with no discounts” United state federal supply service (1957, p 37).
References
Armstrong, J. S., 2001. Principles of forecasting: a handbook for researchers and practitioners. London: Springer.
Clement, P.M. & Hendry, F. D., 1998. Forecasting Economic Time Series. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
European Conference of Ministers., 1991. Social aspects of road transport. Germany. OECD publishing.
Fogli, L., 2005. Customer service delivery: research and best practices. Professional practice series. New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons.
Goodman, A., J., 2009. Strategic Customer Service: Managing the Customer Experience to Increase Positive Word of Mouth, Build Loyalty, and Maximize. USA: AMACOM Div American Mgmt Assn.
Hansen, R. D. Owen, M. M. & Guan, L., 2007. Cost Management: Accounting and Control. 6th Edn. Califonia: Cengage Learning.
Leland, K and Bailey, K., 2006. Customer Service for Dummies. 3rd Ed. Chicago: Dummies.
Makridakis, G. S. Hyndman, J.R. & Wheelwright, C. S., 2003. Forecasting: Methods and Applications. 3rd Ed. San Francisco: Wiley.
Quinet, E. & William, R., 2004. Principles of Transport Economics. USA, Elgar Publishing.
United States federal supply service., 1957. The Economic Order.USA: Govt. Print.