Introduction
Despite the fact that project management is an art and a science, the backbone of a successful project lies in application of soft skills in deliverable variables. These variables authenticate project leadership and management science, risk assessment, and analysis which are basically the soft skills in project management.
Project Management is done to prepare, synchronize, and manage the multifarious activities of business projects. Project management is normally compared to the three balls that are juggled by the circus performers. By developing Project management, it is possible to visualize the future risks and hurdles in the implementation of any project in order to take suitable remedial measures.
Risks and opportunities are inversely proportional to each other. When there is any risk, some opportunities might be there and similarly, in opportunities there are bound to be risks. However, if the anticipated gains are more than the losses, then the risks are acceptable.
Thus, this reflective treatise attempts to explicitly present a protagonist approach in the notion that projects are more about the soft skills rather than the technical skills. Specifically, the treatise expounds on the management of the Caribana Parade project of the Toronto Sun through the project task, deliverables, risks, critical path, and quality management plan.
Project Charter and Plan
Objectives of the project
The primary objective of this project proposal is to systematize involvement of Toronto Sun at the event christened Caribana Parade Festival.
The objective is to be met through deployment and critical design of a float parade (consisting of float pieces, a truck, and design), conscription and micromanagement of several volunteers, procurement of entertainment besides giveaway materials within a timeframe of 57 days, and proactive control of the tasks during the parade day on August 2, 2008 as from 10.00 am.
The giveaway materials will consist of t-shirts, necklaces, volunteer kit, snacks, sunscreen, water bottles, whistles, and candies. Besides, the team will have to procure advertising banners and decorators for the company float.
Significance of the project
The Caribana Parade project will indicate the dominance and activities of the Toronto Sun as a strategic partner and sponsor of the annual event in Toronto.
Thus, successfully carting the float of the Toronto Sun during the annual Caribana parade, which is the biggest and most attended annual event in the city, will give the company a competitive advantage through extra marketing exposure. Besides, the success of the Toronto Sun during the event will contribute to sustainability and increased return on investment as a result of the marketing exposure.
Critical issues facing Morrison
Cost constraint: Relatively low budget of only $400 in cash besides offers of contra advertisements.
Time constraint: Morrison has only 40 days to complete the project, before August 2, 2008.
Scope constraint: There are series of milestones and multiple deliverables. The ability to realize these deliverables and milestones is solely dependent on stakeholders’ availability and corporation.
Stakeholders and their interests in the project
Schedule and resource requirements
Project management includes planning, making the required arrangements, selecting the right staff, providing instructions, keeping a tap on the progress, executing remedial measures, being innovative, and finally coordinating with the customers. All project management applications have fixed guidelines that plan and then execute. A project can never be successful if there is no team work.
The top management should leave their egos and work as a team (Muller & Turner, 2007). Only then can the project achieve its success.
For the case of the Caribana Parade, the resource requirements include hiring a flat bed truck before 10.00 am on the first day of August, 2008, ensuring that truck driver shows up for the event an hour before the start, ensuring that the safety waiver forms are accented by all volunteers thirty minutes before the commencement of the event, and ensuring that the float is procured in time.
Project planning
Project planning divides activity into four key areas which are “setting objectives, identifying deliverables, planning the schedule and making supporting plans. Supporting plan may include communication methods, human resources, and risk management” (Manas, 2008, p. 19). There should be a proper time management framework for project activities. This will ensure success during execution.
The project plan outlines activities that have to be carried out to ensure completion of the project. It also shows the other activities which need to be carried out alongside the main activities. Critical path is the path taken by the main activities in the chart. Activities which fall along the critical path must be executed within the allocated time.
However, regardless of how well a projected is well managed or evaluated, delays are inevitable. Such delays may arise from a number of factors such as sudden snow fall and delays in delivery of suppliers among others. Causes of delays should be addressed as soon as possible. This will help in avoiding further delays.
Work breakdown structures
An effective performance measurement system will always provide with significant and constructive information. Such information assists the assessment makers to arrive at an appropriate decision. The daily operations are affected by these systems. Through the help of change control procedure, the incorporated alterations will be exactly distinct, assessed, and accepted before the realization of the Caribana Parade project.
Whenever any written request for a change in the procedure is received, all the team members will be consulted before arriving at any conclusion. Whatever decision is taken, the same will be informed to the concerned parties. In case of changes in the project progress procedure, the required amendments will be made in the documentation. The work breakdown structure is summarized in the table below.
Activities and scheduling
The Caribana Parade project is scheduled for the second day of August, 2008. Project scheduling, estimation, and cost controls are the main factors of a project management system. There are four criteria of scheduling and controlling cost for the Caribana Parade project.
These criteria are directing progress, directing actions, controlling results, and conserving resources. Project schedule and cost control procedures are very important for any project. This is indicated in the diagram below.
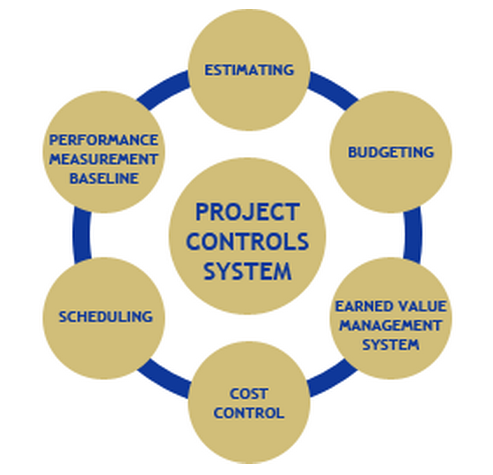
(Source: Manas, 2008)
If one of the criteria is changed, the others will automatically have to change. Suppose if the deadline is shifted ahead, the cost of the project will increase due to the resources involved.
Similarly, if the estimate is reduced by a specific amount, the duration of the project will have to be increased because the resources cannot be increased and with the same resources, more time will be required. The methods to be used to measure the performance of the Caribana Parade project are:
- The specific milestones are identified and determined.
- The scope of work is well defined.
- Risk plan is made pertaining to all the variables.
- Ways of averting these risks are clearly defined.
- The project plan is executed in an effective manner and in accordance to the guidelines laid down by the management.
Resource and communication planning
A project manager needs to identify the impact of delay on the whole project. As a priority, a project manager should first consider the possibility of continuing with other non critical path activities. This is possible when there are delays affecting critical path activities.
This will help reduce the overall impact of delay on the project. In the Caribana project scenario, since the delay will affect both critical and non critical activities, the project manager should allocate available resources to the critical step. As a matter of fact, “delaying any activity along the critical path end up delaying the whole project” (Manas, 2008, p. 28). Therefore, all critical path activities should be completed within the scheduled time.
In the case of the Caribana project, the plan will be communicated through face to face meetings and official emails. The progress will be communicated after every three days. The documentation needed is training pamphlets, risk monitoring books, and storage file for each mitigation strategy proposed.
There are several steps involved in managing the communication plan. The first step will be prioritizing the tasks. This is followed by grouping the tasks in terms of materials needed for implementation. The third step will be to conduct stakeholder awareness and participation training. The fourth step will be internalizing the suggestions through open and consultative meetings with all the stakeholders.
The action plan will be monitored everyday during the first month. Reports on its progress will be made after every two days. After completion of the complex parts, the plan will be assimilated into the stakeholders’ training module for it to become part of the Caribana Parade project.
The success will be measured in terms of responses from the stakeholders after every stage of implementation. Since the whole process is flexible, evaluation will be based on the key parameters of operations management strategies such as the level of awareness, consciousness, and participation among the stakeholders.
After management review of the progress systems, it is healthy to fuse the similar normative references since they share same scope in definition and terms of reference. The system should then factorize similar progress adjustments in order to tone down noticeable variances such as records of control and frequency of recording.
When this is successfully assimilated into the latter, it is within desirable limits to roll out the integration procedure to include entire control and evaluation changes (Muller & Turner, 2007). In the process of doing so, it is possible to create a complete and comprehensive progress system which incorporates variances that might exist in the Caribana Parade project.
At the same time, the progress system will be intrinsic of management reviews and audits that are recorded periodically in line with evaluation records of the project coordination officer.
Realistic milestones

Reflectively, the Gantt project is a success measuring tool for cross platform review of the entire procedures and stages of project implementation. This tool has application which monitors resources of the project, time allocation and completion tracking.
Since it is flexible in creating project tracking charts, this tool is necessary in communication and promotion of the project deliverable variables since it classify each according to the stages, timeframes, and milestones (Muller & Turner, 2007).
In implementing this project effectiveness tracking tool, soft skills come in at the point of relevance and procedural adjustments that might be needed following the series of project management dynamics.
Specifically, this tool is relevant in tracking and managing timeframes allocated for each project milestone since it can be modified to address changes that might occur in each stage of the Caribana project management. For the Caribana project, the Gantt chart is summarized in the table below.
Cost projection
The project will involve procurement of several giveaway materials such as T-shirts, necklaces, volunteer kit, snacks, sunscreen, water bottles, whistles, and candies. Besides, the team will have to procure advertising banners and decorators for the company float. The cost estimation is summarized below.
Hiring driver for 8 hours at $26 per hour = $208
Hiring the truck for a whole day = $192
Hiring a float for a whole day=$150
Printing and shipment of 100 T-shirts = $2,000
Procurement of other giveaways = $ 1,000
Food and snacks =$1,000
Miscellaneous =$ 500
Total cost = $5,050
Risk documentation
SWOT of the risks
Risk identification in the Caribana project
Operational risk
The main risk identified in the Caribana project is the inability to achieve the project milestone and goals since the project blueprint does not capture a comprehensive project plan. Besides, there were no regular assessment procedures for governance of the project’s structural framework.
Financial risk
The other risk identified in implementation of the Caribana project is the errors in the financial data and inventory information since the plan ignore some of the miscellaneous costs and overheads. Besides, the budget is not flexible to market rate dynamics that inflated some of the costs of the project.
Misunderstanding among stakeholders
The last main risk in the Caribana project is the misunderstanding among the project stakeholders. This is as a result of unclear role and duty assigned to each stakeholder, especially the volunteers. Besides, the stakeholders might have divergent opinions on the approach to be adopted in actualizing the project blueprint.
Risk analysis in the Caribana project
Classification of the risks in terms of impact and probability
Summary of the project impact impact/probability
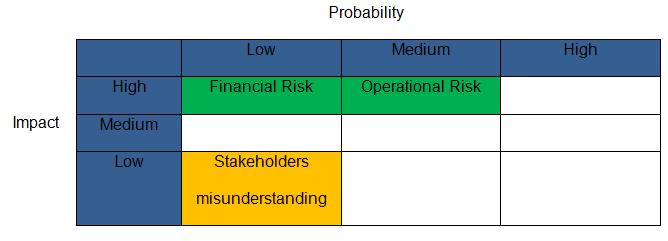
Explanation of the above risk impact/probability in the Caribana project
Risk response strategies in the Caribana project
Different risks have different impacts on a project. For instance, operational risks include the ability of the Caribana project implementation personnel to executive the project deliverable. Therefore, it is necessary to apply soft skills such as offering efficient training to project management personnel to equip them with adequate skills for quality project execution.
Financial risk
Financial risks include the fiscal resources that the Caribana project may demand in order to be completed within time. Due to economic swings as a result of market inflation, financial risk presents the greatest threat towards successful completion of the Caribana project.
Thus, intrinsic financial management tools are necessary in mitigation of this project risk. This is corrected through budget review to include the aspect of flexibility and budget testing besides introducing the financial decision making rationale tests.
Operational risk
In order to mitigate this risk, it is necessary to design a practical project tracking plan and progress assessment criteria through application of project leadership and management soft skills. The Caribana project tracking plan will evaluate the aspects of efficiency in operations and review decision rational to ensure Pareto efficiency.
Misunderstanding among stakeholders
This can be quickly resolved through establishment of a proactive project charter with clear roles of each of the stakeholders. As a result, the disagreements will be resolved as each stakeholder will have a defined responsibility in the process of project implementation.
Action plan for implementing those risk treatments
The plans need to be adaptable. At this point, the risk mitigations plan is ready in action. Though weekly analysis and monitoring of the progress, the plan will be able to classify the success of the risk management within the Caribana project.
The action plan can be effective through following the risk procedure to check the progress. The plan will be broken to monitor one risk activity at a time (Manas, 2008). The results of each activity will be merged together to identify any overlap or conflict within action plan. The plan will run for five weeks.
Managing the project critical path
Project Critical Path
Critical path is important in actualizing the project life and making projections in terms of time involved in each stage. From the high level activity precedence table created by the management of the project, the precedence network drawn below was derived.
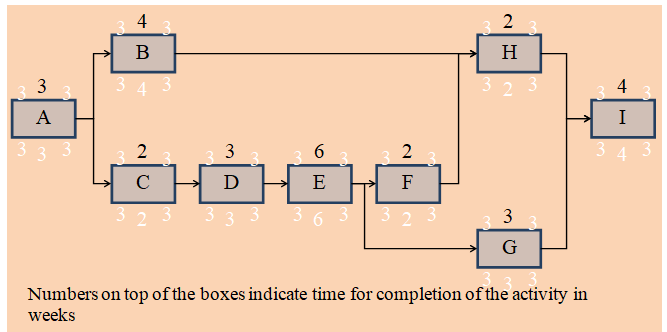
In order to determine the critical path, calculations will be done for duration of each stage of the project as indicated below.
Path 1: A → B → H → I = 1 + 2 + 2 + 1 = 6 weeks
Path 2: A → C → D → E → F → H → I = 1 + 2 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 7 weeks
Path 3: A → C → D → E → G → I = 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 6 weeks
Apparently, Path 2 becomes the critical path since it is the longest. Path 3’s float is 6 weeks while that of Path 1 is 6 weeks. This is presented in the diagram below where Path 2 (critical path) is highlighted.
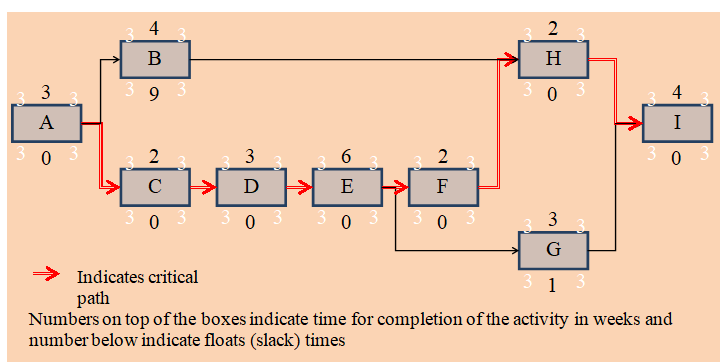
In order to establish the late start-late finish, and early start-early finish, the network is subjected through a critical backward and forward pass as indicated in the diagram below.
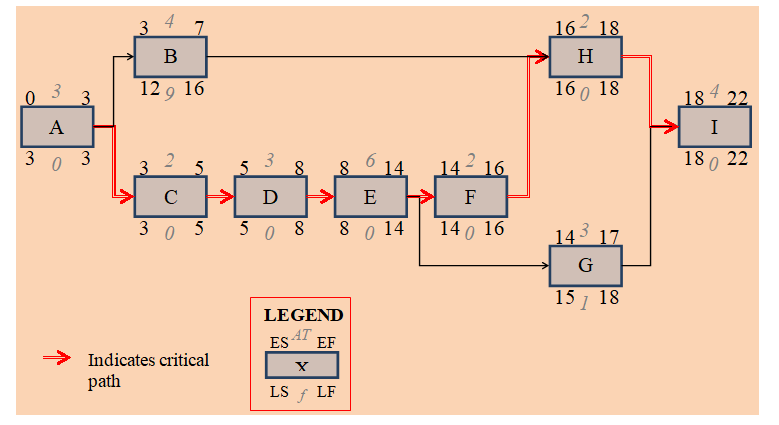
The diagram confirms Path 2 as was previously decided to be the critical path of the project.
Quality management plan
For a project to meet its objectives, the aspect of scientific management is necessary in addition to proactive leadership approach. As a matter of fact, in project execution, project leadership, and project management complement each other. Project management focuses on the objectives and set goals that are to be achieved through project implementation.
These goals are designed on the basis of rational decision making in line with the target of each objective within a defined period of time. The set goals have success measurement parameters that must be achieved through specific micro project management soft skills. On the other hand, though a complement of project management, project leadership surpasses the defined objectives and goals (Muller & Turner, 2007).
Through application of special skills such as motivation, inspiration, and revitalization of the project personnel, project leadership skills for the Caribana project will nurture collective and self responsibility to perform optimally in the environment of project execution. Thus, project leadership will be necessary in connecting the mission, vision and objectives of a project to the unique dynamics of project management environment.
Due to the high level of commitment that the Caribana project demands, project leadership skills will intertwine the purpose and scope of the project, besides defining deliverable project variables in order to make a project successful (Manas, 2008). Project leadership skills will introduce the aspect of creativity and innovativeness in the process of project management.
Possession of relevant project leadership skills is an appropriate recipe for an all round and effective implementation strategies of a project. Through supplementary implementation of project management and project leadership skills, the culture of team work and common purpose will eventually climax in successful project execution.
In order to prepare and conduct a successful internal audit of the Caribana Parade project, the project manager will adopt a macro adjustment within micro units of evaluation. This procedure involves micro audits carried out to macro manage a firm and review the same for quality in management system.
At personal level, the manager will concentrate the audit to communication and logistic support in order to determine documentation and integration of the channels for communication within the project progress. In the audit statement, the underlying key procedure for reviewing authenticity of information obtained will rely on cost and time variances measurement in line with modern quality control organs running the project.
Special attention will be directed towards measuring compliance and consistency indicators and matrixes of performance evaluation through integration of a proactive, objective oriented, and goal facilitated behavior audit. In addition, it is vital to identify specific operations that are quantifiable and controlled from the central organs of management.
This is necessary to monitor achievement compliance and efficiency in resource use and reuse. When these contingencies are balanced and quantified, an independent audit report is likely to be within reach. Though the whole process is dynamic and requires flexibility in carrying out evaluation, the basic underlying concepts and aspects of accountability and responsibility should be part and parcel of every procedure.
Despite the fact that the degree of accuracy on reviewing quality of the Caribana Parade project management may present some challenges, it is possible to build a framework for operation monitoring process which incorporates preventive and corrective actions to make such process consistent.
Closing the project
It is unfair to ignore the contribution of project management personnel in terms of efforts and skills when classifying projects on the matrix of success. Therefore, the ability to oversee, influence, delegate, assign and proactively supervise a project depends on the soft skills such as management and leadership, and risk mitigation rationale.
Though the technical skills are part of a project, soft skills transform the blueprint into actual measurable activity. Reflectively, interpersonal skills in project management have an immeasurable value in the success of a project, irrespective of its magnitude (Muller &Turner, 2007).
Besides, the behavioral skills of project personnel such as style, personal conduct, and approach will eventually determine the success of a project. Among the vital soft skills that will be discussed in this paper include project leadership and management skills, risk assessment skills, and rational decision making in the process of micro management of a project.
In order to make the Caribana Parade project a success, the internal stakeholders should adopt transformational leadership characteristics such as diversity management, development of an insight that accommodates application of task oriented supervision in line with the project’s demands.
Despite task orientation being rated as a high self leadership assessment strategy, action planning is of essence in creating solution oriented task and strategy implementation session for quantifying task orientation levels that is required in the success of this project.
Samantha Morrison is a visionary leader who is competent in planning and deliberation of duties. Besides, she is an organized and goal oriented leader who is keen on transactional discourse of the project. Moreover, she is an effective team player who has managed to delegate duties to different parties in the project conceptualization.
Conclusion
The success and failure of project management is dependent on project management process since it provides planning, integration of project organization framework, and control. In order to strike an optimal performance balance, the process of project management should commence with a clear overview description of the project initiation: budgeting, objectivity, and scheduling.
In addition, this part should include control procedures and assessment. In order to come up with a viable project, it is of essence to include quality control, communication with stakeholders, progress measurement, and flexibility in planning to accommodate any eventuality. Therefore, the Caribana Parade project is likely to be completed before the second day of August, 2008.
References
Manas, J. (2008). Napoleon on Project Management: Timeless Lessons in Planning, Execution, and Leadership. Nashville, Tennessee: Thomas Nelson Inc.
Muller, R., and Turner, J. R. (2007). Matching the project manager’s leadership style to project type. International Journal of Project Management, 25, 21–32.