Introduction
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are disorders affecting the urinary system.
- UTI’s are the most prevalent hospital-acquired infections.
- Catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) occur due to the use of catheters.
- 75% of UTIs in hospitals arise from catheter usage.
- Approximately 15 to 25% of hospitalized patients receive urinary catheters.
- The exact causes of CAUTIs are illustrated by the fishbone diagram in Figure 1.
The urinary tract system includes the bladder, urethra, ureter, and kidney. Infections of the urinary system are among the most common diseases that patients contract during their hospital stay (Lo et al., 2014).
Catheters are tubes introduced into the bladder through the urethra to remove urine in a process known as catheterization.
This process often occurs in patients in the intensive care unit.
Overstaying with catheters and unhygienic conditions during the insertion process are mostly to blame for CAUTIs.
The large incidence of hospital-acquired infections including CAUTIs have prompted the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid to stop reimbursing hospitals for the treatment costs incurred in the treatment of such infections.
Therefore, this move has forced most hospitals to initiate quality improvement strategies.
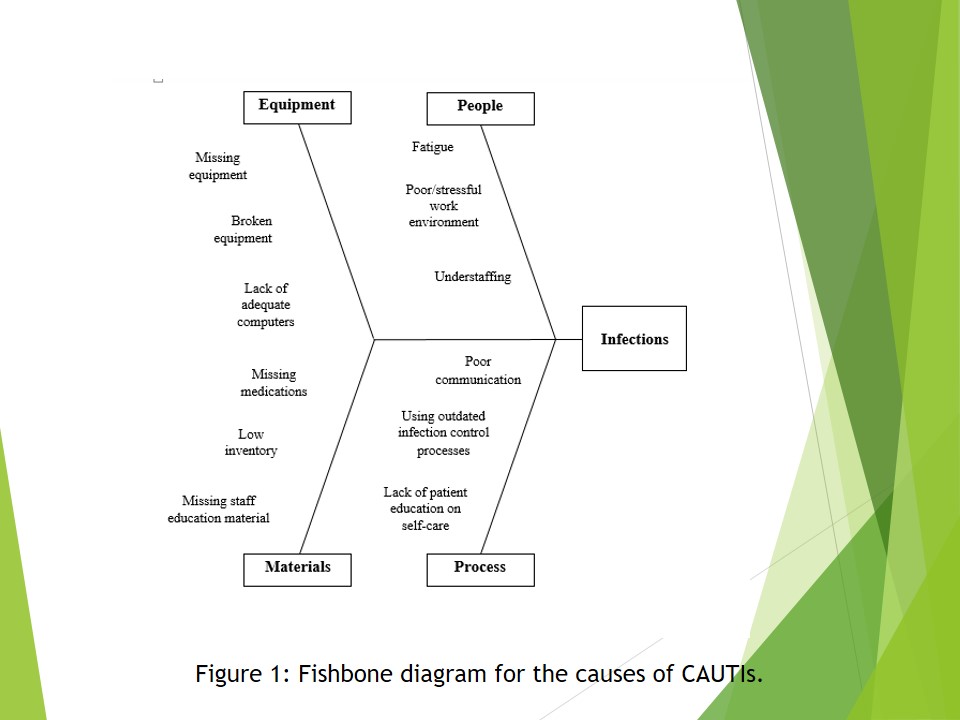
The causes of CAUTIs are broadly classified into four main groups namely equipment, people, materials, and process.
Equipment causes include the lack of adequate equipment in the insertion and removal of catheters, broken facilities and the lack of adequate computers to help in the monitoring of catheter insertion and removal in patients.
The people factors include fatigue, stressful work environments and understaffing. These factors lower the efficiency of the workers thus exposing patients to the risk of infections such as CAUTIs.
The materials factors include missing medications, low inventory (inadequate supplies to facilitate the aseptic insertion and removal of catheters) and the lack of staff education materials such as posters, and charts. Nurses may be willing to use the proper procedures in catheterization. However, limited resources may work against their good intentions.
The process factors include poor communication among employees, using outdated infection control processes, and the lack of patient education on self-care.
Patients play a significant role in their own wellbeing through self-care. However, without adequate and accurate information from their providers, it is impossible for them to take good care of themselves.
Strategies for Quality Improvement
- Use of proper staffing approaches:
- To reduce workload per nurse and hence fatigue.
- Introducing education and behavioral interventions.
- Behavioral interventions:
- Catheter restraint.
- Adherence to catheter removal protocols.
- Aseptic techniques during the insertion of catheter and obtaining of urine samples.
- Avoiding irrigation to prevent infections.
- Use of device-days rather as opposed to patient-days in measuring catheter duration.
- Encouraging nurses disclosure of patients predisposed to infection:
- For proactive or interventional measures to be taken.
- To reverse the magnitude of the outcomes.
- Educational interventions to enhance the correct catheter placement.
- Fine-tuning the nurses’ work environment to make it friendly:
- By considering the opinions of nurses.
- Ensuring flexible work schedules.
- Attractive remuneration.
- Providing the necessary resources.
- Friendly work environments lead to:
- Increased retention of nurses;
- Improved quality of care;
- Increased job satisfaction.
- Obtaining adequate materials, technology, and equipment:
- Introducing specific technologies, for example, bladder ultrasound.
- Providing the supplies required for aseptic techniques during catheter insertion.
The successful execution of the above strategies of quality improvement will involve the use of the following tools:
- RCA (Root Cause Analysis):
- It will contribute to unearthing the actual cause of poor infection control.
- It will guide the development of practical and viable solutions to optimal infection control.
- SWOT Analysis:
- Will influence the organization’s ability to provide a fertile place for the change/ improvement to thrive.
- It will expose the weaknesses, strengths and opportunities.
- FMEA (Failure Mode and Effect Analysis):
- Enables the mapping of possible routes of failure.
- Facilitates the planning of proactive or recovery measures.
Staffing approaches entail ensuring adequate manpower to prevent overworking the nurses. The effectiveness of nurses reduces during fatigue hence increasing the probability of slipups and infections.
Proper staffing methods also entail ensuring that the staff are qualified to deliver quality healthcare services, which can be done through training.
Training aims to change the behavior of the employees regarding catheter usage.
This strategy also involves ensuring that the employees’ behavior does not put patients at risk through behavioral interventions.
Encouraging nurses to disclose instances where patients are likely to contract infections is helpful because it provides room to correct the situation and prevent infection (Krein et al., 2012). Disclosure should not be taken as admission of guilt but as a way of ensuring the best patient outcomes.
Proper education on catheter use prevents common mistakes such as incorrect and unnecessary insertion (Woolforde & Castro, 2013).
Fine-tuning the environment to make it friendly may motivate nurses to do their best and in so doing the incidence of CAUTIs will be reduced.
Availing the required materials in the right quantities increases the probability of correct catheter insertion and removal thus minimizing infections.
Ensuring that nurses have access to adequate resources (materials, technology, and equipment) will make it possible for them to work effectively and reduce the incidence of CAUTIs.
For example, providing adequate supplies of disinfectants will ensure that aseptic techniques are used in the insertion and removal of catheter, which will minimize the chances of infection.
For all the above-mentioned strategies to be effective, three main tools will be used to evaluate the quality initiative. They include a root cause analysis, SWOT and FMEA.
The root cause analysis would contribute to unearthing the actual cause of poor infection control by bringing on board various organizational factors such as human resources, processes, and materials to determine where the real cause lies (Miniati, Frosini & Dori, 2015).
The success of the strategies proposed by a root cause analysis depends on the ability of the organization to align various components with the accompanying change.
A SWOT analysis makes it possible to carry out a thorough evaluation of the intervention by uncovering the strengths, weaknesses and opportunities. Therefore, potential problems can be identified early enough, which will facilitate the solving of the problems before their adverse effects are felt (Westgard & Westgard, 2014).
The long-term applicability of an improvement strategy to reduce the occurrence of infections require a pre-assessment to obtain a vantage point about making the necessary arrangements if the failure occurs. The FMEA tool is useful in this regard (Miniati, Frosini & Dori, 2015).




The Chosen Strategy
- Use of proper staffing approaches:
- Proper staffing approaches will ease the nurses’ workload and provide the necessary expertise to prevent CAUTIs.
- For example, with proper education, nurses will be conversant with proper catheter usage including:
- Conditions that warrant the insertion of catheters.
- How to insert and remove the catheters.
- When to remove the catheters.
- Proper sanitation techniques to prevent the transfer of germs to the patient.
Proper staffing approaches will make nurses comfortable and increase their efficiency. Adequate staffing will increase the nurse-patient ratio and reduce fatigue among nurses. Fatigue has been reported to be the among the leading causes of reduced efficiency among nurses.
Apart from increasing the staffing, it is also important to ascertain that the available members of staff have the right training and attitudes to ensure the safety of patients regarding CAUTIs.
Behavioral and educational interventions included in this strategy will minimize unnecessary catheter insertion and catheter days thus reducing chances of infection.
Even in the absence of sophisticated materials and techniques, these basic steps will reduce the incidence of CAUTIs significantly.

Ideas to Initiate Quality Improvement
- Updating infection control guidelines.
- Creating teams or workgroups to improve communication.
- Developing measures to ensure high adherence to infection control bundles:
- Reducing unnecessary catheter use.
- Observing high standards of hygiene.
Using updated infection control measures will help in the utilization of evidence-based guidelines in catheter use and CAUTI prevention.
Enhancing communication will synchronize care and reduce the incidence of medication mistakes that may result in CAUTIs and other hospital acquired infections (Nadeem et al., 2013).

Connection to the Organization’s Mission, Vision and Value Statement
- Mission: To be a respected institution for brilliance in patient care and individualized synchronized care.
- Vision: To enhance health and promote the healing of the people and communities served.
- Value Statements: Caring, safety, excellence, and integrity.
The hospital’s operations are guided by its mission, vision and value statement.
Therefore, it is necessary for the quality improvement strategies to ensure that the outcomes align with the hospital’s objectives as outlined in the mission, vision and value statement.

Rationale
- Updating infection guidelines will ensure that the patients receive high quality healthcare services.
- Proper communication will enhance the synchronization of care.
- Adherence to infection control bundles will demonstrate caring and ensure the safety of patients.
Overall, reducing CAUTIs and other hospital acquired infections will demonstrate the high standards of care in line with the mission, vision, and value statements.

Conclusion
- Introducing and sustaining quality in an organization requires the conscious effort of employees as well as the management.
- Employees should be willing to make good use of evidence-based practices in upholding quality.
- The management should strive to improve the working conditions of its employees.
- Good working conditions lead to quality outputs from nurses and improved patient outcomes.
The US preventive Services Task Force has published various guidelines used in the prevention of CAUTIs. These guidelines are updated from time to time. It is important for nurses to stay updated with the changes and use the current recommendations in their day-to day operations.
