Introduction
The modern growingly complex word introduces diverse tasks for individuals working in different spheres. The given complexity stipulates the increased sophistication of relations between numerous variables comprising one or another phenomenon. For this reason, the approach known as systems thinking becomes one of the most potent tools to analyze peculiarities of relations and make conclusions about their interaction. It could also be described as the specific set of practices used by managers to consider objects and their interdependence as the system that has its peculiarities and evolves in a particular way (Dalio, 2017).
Systems thinking might also demand visualization to ensure an enhanced understanding of processes (Dalio, 2017). In this regard, loop diagrams become one of the most powerful methods to present a correlation and provide a credible and reliable conclusion about its further evolution. In this regard, the given paper is devoted to the in-depth investigation of the given method, its nature, the way it is applied, and how it now helps managers to achieve particular goals.
Discussion
A causal loop diagram (CLD) could be defined as a specific visualization tool that is aimed at demonstrating how different variables in a particular system interact and precondition the emergence of diverse alterations (“Causal loop diagrams,” n.d.). The traditional CLD could be considered a rather simple thought effective way to explain the behavior of different processes, and how specific responses trigger diverse reactions. The given diagram consists of a set of nodes and edges. (Kim, 1992). These are introduced to represent a connection and relation between the most important variables that can be found in every case. Specifically, nodes are used to visualize all variables or aspects of the system that impact each other (“Causal loop diagrams,” n.d.). Edges stand for links that describe connections or relations between variables that are studied at the moment (Kim, 1992).
Additionally, because there are different kinds of bonds between all aspects of the system, there are positive (+ or s) and negative (- or o) links (Kim, 1992). The positive causal link means that two nodes of a particular correlation move or change in the same direction (Kim, 1992). In other words, the increase in the state of the first variable is also followed by an increase in the state of another. Alternatively, a negative causal link shows that nodes presented in the diagram move in opposite directions (Kim, 1992). If one node is associated with the link increase, another will start to decrease.
Additionally, every loop diagram has closed cycles depicted as loops, or circles. These are very important aspects of every scheme of this sort as they describe peculiarities of every process within the analyzed system and could be united in bigger entities to demonstrate how they interact and what kind of bond exists between them (Lannon, n.d.). These closed cycles could also be referred to as balancing feedback loops in which the alteration of any of the presented variables moves through the created link and returns to the original process reinforcing its initial growth or other meaningful aspects (“System behavior and causal loop diagrams,” n.d.).
In such a way, the loop diagram becomes a simple and efficient way to describe diverse processes and how their basic aspects might vary due to their interconnection and mutual dependence. There are multiple areas in which these diagrams are applied regarding the systematic systems approach and its basic points as their implementation might have to understand the peculiarities of numerous correlations and what outcomes could be expected.
Using casual loop diagrams, specialists might create reports about issues that include several aspects and are considered complex. In such a way, the primary aim for applying this sort of diagrams is to make the understanding of interrelationships within a systems structure more explicit and contribute to the improved outcomes when discussing this very system and its potential development (Lannon, n.d.).
However, causal loop diagrams sphere of application is not limited just by presentations and attempts to make the understanding of some processes better. In modern management and other spheres, they are used to assess the state of different organizations and all relations that are critical for their evolvement. Diagrams wide use is explained by the significant practical use, ability to visualize the most important components of different variables, and its contribution to the further evolution of the process (Lannon, n.d.). In such a way, the modern systems approach rests on the broad implementation of diverse causal loop diagrams as one of the most potent tools that provide investigators with numerous opportunities to find the needed correlation and investigate it comprehensively.
The simplicity and efficiency of this tool could be proven by creating a diagram representing relations within a particular health unit. For instance, we should identify a correlation between quality improvement procedures (additional training) and staff:
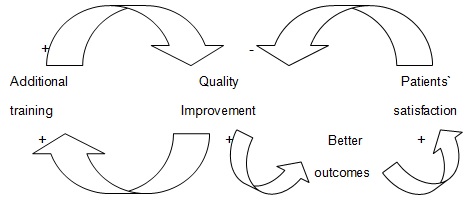
The given casual loop diagram demonstrates the existence of the direct positive relations between quality improvement and additional staff training. Positive links show that the initiation of the procedure results in the increased demand for training that impacts the quality of the suggested services and the variable of quality improvement as it becomes better because of the positive shifts in nurses competencies. At the same time, quality improvement procedures precondition better outcomes (positive link) which stipule the growth in patients satisfaction levels and reduced number of their complaints.
At the same time, this aspect might harm the functioning of the healthcare sector as the lack of negative feedbacks might create the basis for stagnation and disregard of the necessity of change. In such a way, the given causal loop diagram demonstrates the advantages of the suggested tool as one of the potent methods to analyze dependence between the most important variables of a particular case and find out how one aspect impacts another one which is critical for the effective analysis and investigation.
Conclusion
Altogether, causal loop diagrams are potent visualization tools that are used regarding the systems thinking approach. They provide researchers with numerous opportunities to assess selected variables and how they impact each other with the primary aim to predict the further evolution of the system and how alteration of one aspect will affect all other. Loop diagrams are a simple and efficient tool that provides opportunities for better problem-solving and analytical skills (Schuster, 2018). The universal character of the suggested approach results in its wide use in different spheres of human activity. Causal loop diagrams are used in management, science, business activities, healthcare sector, etc. For this reason, the improved understanding of how it could be applied to diverse systems is critical for specialists focused on the in-depth investigation of causal relations between objects or different phenomena.
References
Causal loop diagrams. (n.d.). Web.
Dalio, R. (2017). Principles: Life and work. New York NY: Simon & Schuster.
Kim, D. (1992). Guidelines for drawing causal loop diagrams. The Systems Thinker, 3(1), 5-6.
Lannon, C. (n.d.). Casual loop construction: The basics. Web.
Schuster, S. (2018). The art of thinking in systems: Improve your logic, think more critically, and use proven systems to Solve your problems – strategic planning for everyday life. New York, NY: Amazon.
System behavior and causal loop diagrams. (n.d.). Web.