Introduction
In every market, the price of a particular product is significantly determined by the supply and the prices of the inputs. The prices of the inputs determine the total costs of producing a certain product in the market (Henderson 2004).
When the price of chicken food goes up, this will have a significant impact on all the chicken products and the substitute goods. Among the products that will be affected include eggs, Chicken sausages, Crispy Chicken Strips, Feathers, and Chicken manure. Due to the increase in chicken food, the prices of these products will automatically rise.
Market 1- Eggs market
One of the main products from chicken is eggs. When the price of chicken food goes up, then the prices of eggs will automatically go up. This is because the costs of maintaining chicken will automatically be higher.
Increase in the chicken food will affect the supply side of the eggs market. Due to increase in the prices of the chicken food, the total cost of production will go up hence affecting the supply of eggs in the market. Since the cost of egg production will be relatively higher, this will affect the supply negatively. Increase in the prices of inputs shifts the supply curve resulting in the equilibrium price, which is higher than the quantity demanded (Mankiw 2011).
The law of demand states that other factors held constant, the higher the price of a certain good, the less the quantity of the product demanded (Trading Charts 2011). When the prices of eggs go up, then the demand for the eggs will tend to be relatively lower. Therefore, an increase in the prices of chicken food will shift the eggs’ supply curve to the left. This results from the reduction in the supply of eggs hence shifting the egg supply curve to the left.
At any prices below py, farmers will not be willing to supply the eggs in the market because the prices are below the new equilibrium. Since the costs of production are now relatively higher, any prices below py will discourage farmers from supplying the eggs. Therefore, any prices below that will not be equilibrium.
When the price of a certain product is below equilibrium, the demand of the product will significantly rise. Consumers will be more willing to buy more of the product. This will lead to shortage of the product. Therefore, the prices of the eggs will adjust until the prices stabilize at py.
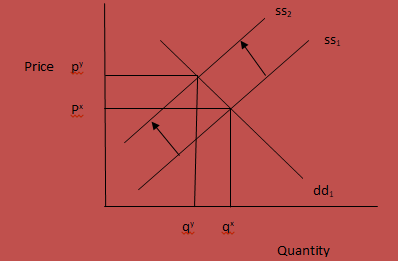
Market 2- Chicken sausages market
An increase in the prices of chicken food will also affect the chicken sausages market. Chicken sausages are one of the chicken products. Therefore, any slight change in chicken supply will directly affect the supply of chicken sausages. An increase in chicken food will therefore cause the supply for the chicken sausages to shift to the left.
Before an increase in the chicken food, suppliers will be willing to supply quantity qx of chicken sausages at price px. Any prices below or above this will lead to imbalances.
An increase in the chicken food causes the supply curve for chicken sausages to shift to the left. Consequently, the quantity of chicken sausages supplied will be less than the quantity demanded by the consumers. As a result, the prices will tend to increase up to py where the quantity of chicken sausages demanded will equate. The new equilibrium price will be py. Any price below or above py will not be equilibrium and will therefore lead to imbalances.
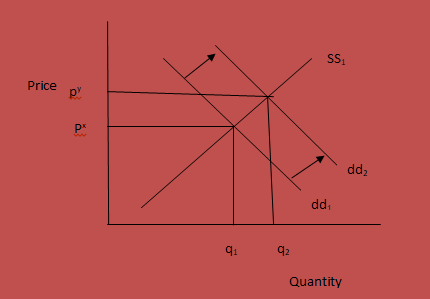
Market 3- Beef market
Beef and chicken meat are close substitutes. In most cases, people will tend to consume either chicken or beef as their main source of proteins. Therefore, an increase in the price of either of the two can lead to substitution.
In this case, an increase in chicken feed will automatically lead to an increase in the chicken meat prices. As a result, the chicken meat will become relatively more expensive than the beef. Assuming that the prices of beef remain constant, consumers will tend to substitute beef for the now relatively expensive chicken meat. Consequently, the demand for beef will tend to increase.
As a result of an increase in the prices of chicken meat as a result of an increase in chicken food prices, consumers will tend to substitute chicken meat with beef. As a result, the demand for beef will increase shifting the demand curve to the right. The demand curve will shift from dd1 to dd2.
At the prevailing prices of beef, the suppliers will not be ready to meet the massive increase in demand. At quantity q2, the suppliers will not be willing to supply beef at the prevailing prices px. As a result, the price of beef will increase up to the level where the quantity of beef demanded equals the quantity supplied.
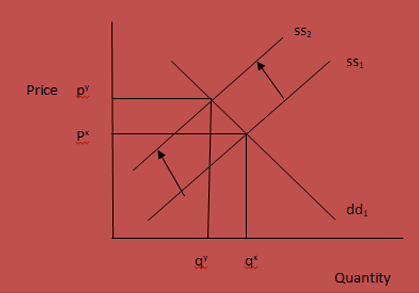
Market 4- Crispy Chicken Strips market
An increase in the prices of chicken food will also affect the Crispy Chicken Strips market. Crispy Chicken Strips is a chicken product and therefore, any slight change in chicken supply will directly affect its supply. An increase in chicken food will therefore cause the supply for the Crispy Chicken Strips to shift to the left.
An increase in the chicken food causes the supply curve for Crispy Chicken Strips to shift to the left. Consequently, the quantity of Crispy Chicken Strips supplied will be less than the quantity demanded by the consumers in the prevailing prices. As a result, the prices will tend to increase up to py where the quantity of Crispy Chicken Strips demanded will equate. The new equilibrium price will be py. Any price below or above py will not be equilibrium and will therefore lead to imbalances.
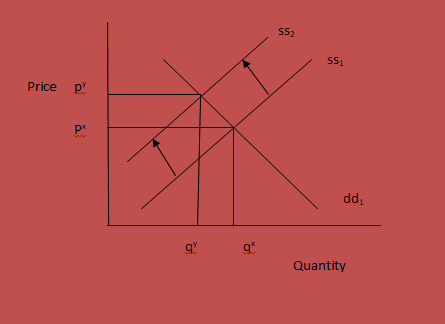
Market 5- Feathers market
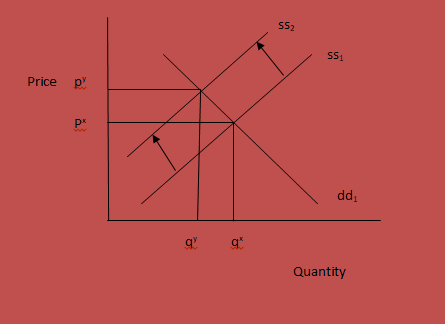
An increase in the chicken food will also affect the market for feathers. When the cost of chicken food increases, the cost of maintaining chicken will increase and therefore the costs of feather production will be relatively higher.
Before an increase in the chicken food, the equilibrium price at the feathers market is px. At this price, farmers will be willing to supply quantity qx of feathers. At this price, the market for feathers clears. Any price above or below this will not be equilibrium. The market for any particular product clears only at the equilibrium level (Adil 2006).
An increase in the prices of chicken food will cause the supply curve for the feathers to shift to the left from ss1 to ss2. When the demand curve shifts to the left, the quantity demanded will be less than the quantity supplied at the old equilibrium price. Therefore, the market for feathers will not clear at the initial equilibrium price. The farmers will not be able to meet the prevailing demand at the old prices. This will therefore push the prices of feathers upwards until it reaches py where the market clears with the new equilibrium price being py.
Reference List
Adil, J.R. (2006). Supply and Demand. New York: Capstone Press.
Henderson, H.D. (2004). Supply and Demand. U.S.A: Kessinger Publishing.
Mankiw, G. (2011). Principles of Economics. Mason, OH. Cengage Learning.
Trading Charts. (2011). How Supply and Demand Determine Commodities Market Prices. Web.