Introduction
Citibank uses segmentation, targeting, and positioning to know the types of customers that need their services and the products that the customers need most. Citibank uses these three market strategies to know the competing company they should focus on and provide a precise and best location to meet their current demands (Megargel et al., 2018). Citibank’s most preferred market strategy is segment strategy because it increases the number of customers and earns more profit.
Discussion
Citibank uses diverse targeting strategies to give customers the best services, such as banking, market security, and institutional services. Citibank’s targeted audience includes high-income earners, recently graduated students, laborers, low-income earners, and businessmen (Liang & Nguyen, 2018). Citibank has become the best company in selecting the best customers and other components, making it more competitive than other banking companies that do not know how to target the right audience.
Citibank has a large customer base that reduces the buyers’ bargaining power and also provides an opportunity for Citibank to improve its production, increasing its sales. Production of new products by Citibank has ensured a reduction in competitors’ defection of the available customers. The company’s creativity in developing new items can lessen consumers’ influence in negotiations.
The clientele that Citibank aims to attract consists of a wide range of socioeconomic classes. Thus, this is done so that Citibank may zero in on the most profitable clients (Liang & Nguyen, 2018). Citigroup markets itself as a market-disrupting, cutting-edge financial institution that streamlines the banking experience and makes reaching customers’ financial goals hassle-free. Improvements to measurement and reporting are being implemented as part of Citi’s strategic refresh to ensure that it is in line with the company’s vision and strategy and better equips Citi to make choices on resource and investment distribution and evaluate business performance.
Citi bank is launching a new division focused on private banking and wealth management as part of its expansion (Wewege & Thomsett, 2020). The private bank will be part of the Global Wealth Management division, which will also encompass personal banking operations in the United States (Mosteanu & Faccia, 2020). In 2021, Citi also announced that its consumer banking franchises in Asia and EMEA would concentrate on the four wealth hubs of Singapore, Hong Kong, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and London as part of the strategy refresh. Therefore, Citi is actively exploring the sale of its consumer.
Citi bank has strong support from Citigroup and prefers multiple segments to increase the number of customers to make more profit. The quintessence of Citibank’s corporate aim is to improve the quality of service they offer to its customers. Citibank has credit cards that provide access to all services provided at the bank. Citibank’s credit cards are suitable for all levels, such as low-income earners, highly paid people, graduates, businessmen, and laborers.
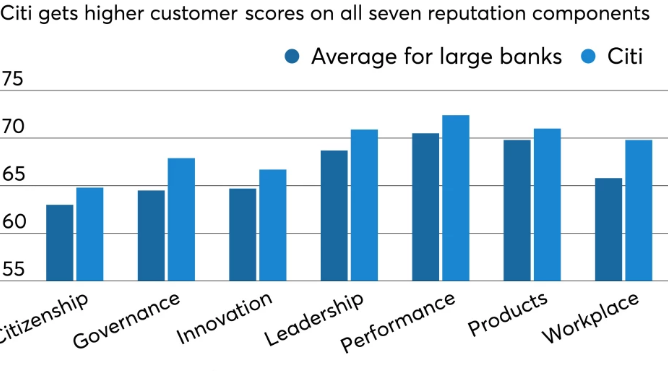
Citibank applies for more valuable propositions to compete with its competitors. Figure 1 below shows how Citibank had the highest customer scores in all components. The main goal of Citibank is to have more customers than its competitors. For instance, Citibank’s Prestige Card is its most popular product. Although the Citi Prestige card’s yearly income must be at least RM200 000, and there is an RM1060 annual fee, this card has grown in popularity among customers who want to use it for travel (Autio & Thomas, 2018). It is because having a Citi Prestige Card makes one feel incredibly opulent and pompous. For example, Cardholders can use numerous perks such as a complimentary Priority Pass with unlimited access to airport lounges worldwide, a free upgrade to Starwood Preferred Guest Gold Status, and complimentary green fees at 2400 golf facilities worldwide.
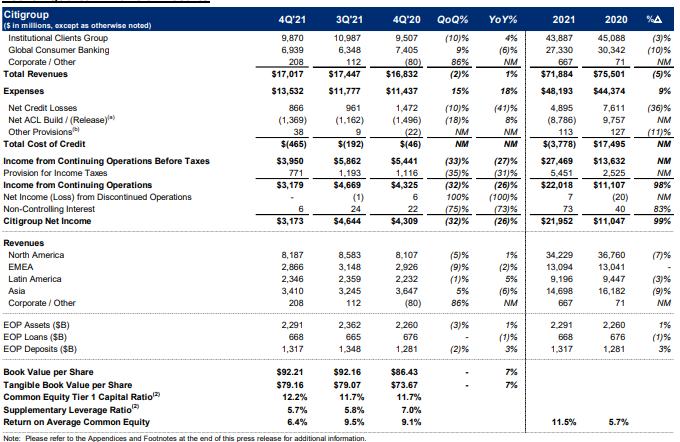
A decrease in the cost of credit, which made up for more significant expenses and reduced revenues to produce a net income of $15.7 billion, improved it by 36% over the previous year (Mattioli, F. (2020). Revenues declined by 9% in Mexico due to lower revenues from markets and securities services, primarily offset by higher revenues from banking (Aliapoulios et al., 2021). In North America 7% increase in banking revenues due to high sales of credit cards (Aliapoulios et al., 2021). The revenue distributions are shown in figure 2 below. Revenues from markets and securities services were down 11%, principally due to a normalization of revenues from fixed-income markets, which were partially offset by increases in revenues from equities markets and securities services.
Competitive Analysis
HSBC
The marketing strategy of HSBC is comparable to that of Citibank in the sense that the firm aims to attract a more significant number of clients by supplying those customers with credit cards that are appropriate for all levels of workers. They concentrate on revenue management and keeping their operational expenses as low as possible, which enables them to pass the benefit on to the customer and ultimately results in a more significant profit for the company (Gupta, 2018). HSBC can provide several points of contact with its consumers because the company has more than 4,700 locations spread out over more than 100 countries.
HSBC banking has global internet access, and global mobile banking has its customers use the internet to conduct financial transactions and access their websites rather than have them physically visit a branch (Gupta, 2018). Individuals with disposable incomes in the upper middle class make up the bulk of HSBC’s clientele, while businesses looking to take advantage of HSBC’s wealth management, investment advisory, and other financial services are considered corporate customers. The use of mobile banking and access to the account at any time makes it more competitive in the banking sectors today. Table 1 below shows the SWOT analysis of HSBC in the order of its strengths, weakness, opportunity, and threats.
Table 1: The weaknesses and strengths of the HSBC
HSBC’s global expansion has allowed them to dominate many economic sectors, making it more competitive than Citibank. As a participant in the international banking sector, HSBC has the potential to capitalize on exciting new avenues and expand its customer base to outgrow Citibank. HSBC needs to reevaluate its approach to the market by taking stock of its advantages and disadvantages in addition to the prospects and dangers it faces (Lenferna, 2018). With cutting-edge technologies like blockchain, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, HSBC is “digitizing banking” for the convenience and safety of its clientele.
JPMorgan Chase
JPMorgan Chase stands out from other banks thanks to its long history, extensive industry knowledge, and competitive pricing. It has used strategic acquisitions of smaller competitors to stifle competition and gain access to its consumer bases (Choudhry, 2022). Despite this general similarity in services, product lines, and operational scale among the country’s top four or five banks, competition is fierce. Customers are easily persuaded to switch to a competitor by more attractive offers, as their switching costs are cheap. Having a high-net-worth contact keeps their banking with the institution. Therefore, we can infer that JP Morgan Chase’s competitive rivalry is a potent factor shaping the competitive landscape and, by extension, the bank’s approach to the market.
Analysis of JPMorgan Chase provides information about its strengths, weaknesses, opportunity, and threats that make it become the best competitor of Citibank. Weaknesses and strengths are internal, while opportunities and threats are external. SWOT Analysis is a tried-and-true management paradigm that allows a company like JP Morgan Chase to compare its operations and performance against its rivals (Krzyzewski, 2022). JP Morgan Chase is one of the top names in banking and financial services. Table 2 below shows the SWOT analysis of JPM org bank.
Table 2: SWOT analysis of the JPM org Bank
BNP Paribas
In practically every market today, firms must contend with fierce rivalry. However, having an advantage over the competition does not guarantee that the company will be able to maintain its position in the market. A regular review of the market’s volatility is needed to inform the firm about the need to enhance service quality and secure dominance over rivals’ goods and services (Hromylo, 2022). As a result, BNP Paribas Group has implemented successful strategies that give it promising prospects to develop its products and services for its customers to compete with its rivals.
Conclusion
BNP Paribas is often regarded as one of the most successful companies in its industry. BNP Paribas can preserve its position as the industry’s preeminent financial institution by scrutinizing and updating the SWOT analysis in great detail, as shown in Table 3. The SWOT analysis is a highly interactive process that requires effective communication between many different departments inside a corporation (Giovannelli, 2018). These departments include management, advertising, finance, planning and control, and long-term planning.
Table 3: SWOT analysis of the BNP org Bank
References
Aliapoulios, M., Ballard, C., Bhalerao, R., Lauinger, T., & McCoy, D. (2021). Swiped: Analyzing ground-truth data of a marketplace for stolen debit and credit cards. In 30th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 21) (pp. 4151-4168).
Autio, E., & Thomas, L. D. (2018). Tilting the playing field: Towards an endogenous strategic action theory of ecosystem creation. In World Scientific Reference on Innovation: Volume 3: Open Innovation, Ecosystems and Entrepreneurship: Issues and Perspectives (pp. 111-140).
Choudhry, M. (2022). The principles of banking. John Wiley & Sons.
Giovannelli, E. (2018). Long term rental in the automotive industry: digital tools and strategies to create a lead generation campaign. Varius Project case study.
Gupta, M. D. (2018). Minor project report (Doctoral dissertation, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University).
Hromylo, D. (2022). Involvement of the Economy in International Trade (on the basis UKRSIBBANK) (Doctoral dissertation, Private Higher Educational Establishment-Institute “Ukrainian-American Concordia University”).
Krzyzewski, M. (2022). The Sport Business Handbook. Human Kinetics.
Lenferna, G. A. (2018). Divestment as climate justice: Weighing the power of the fossil fuel divestment movement. In Climate Justice and the Economy (pp. 84-109). Routledge.
Liang, C. C., & Nguyen, N. L. (2018). Marketing strategy of internet-banking service based on perceptions of service quality in Vietnam. Electronic commerce research, 18(3), 629-646.
Mattioli, F. (2020). Dark finance: Illiquidity and authoritarianism at the margins of Europe. Stanford University Press.
Megargel, A., Shankararaman, V., & Reddy, S. K. (2018). Real-time inbound marketing: A use case for digital banking. In Handbook of Blockchain, Digital Finance, and Inclusion, Volume 1 (pp. 311-328). Academic Press.
Mosteanu, N. R., & Faccia, A. (2020). Digital systems and new challenges of financial management–FinTech, XBRL, blockchain and cryptocurrencies. Quality-Access to Success Journal, 21(174), 159-166.
Wewege, L., Lee, J., & Thomsett, M. C. (2020). Disruptions and digital banking trends. Journal of Applied Finance and Banking, 10(6), 15-56.