Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is an internet based service that allows clients to use external IT resources from cloud service providers (Mitchell, 2012).
Cloud services are available as public, private or partner services:
- Public: Available on the open internet;
- Private: Existing on Private Virtual Networks;
- Partner: Based on relationships between the Provider and the client.

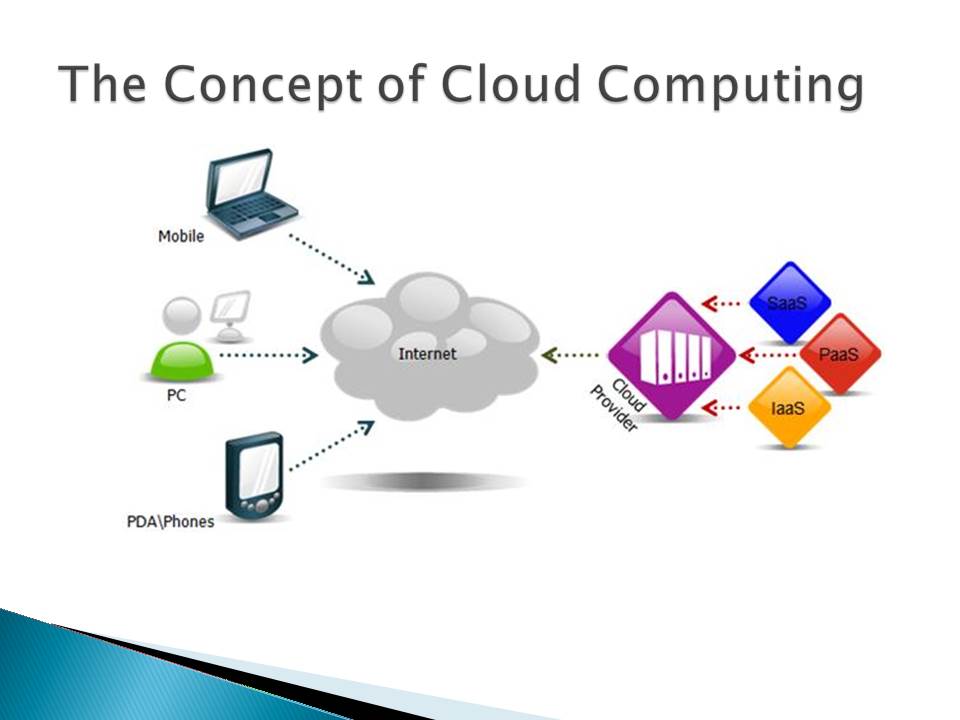
The Concept of Cloud Computing
Internet
- Mobile;
- PC;
- PDA/Phones;
- Cloud Provider:
- SaaS;
- PaaS;
- IaaS.
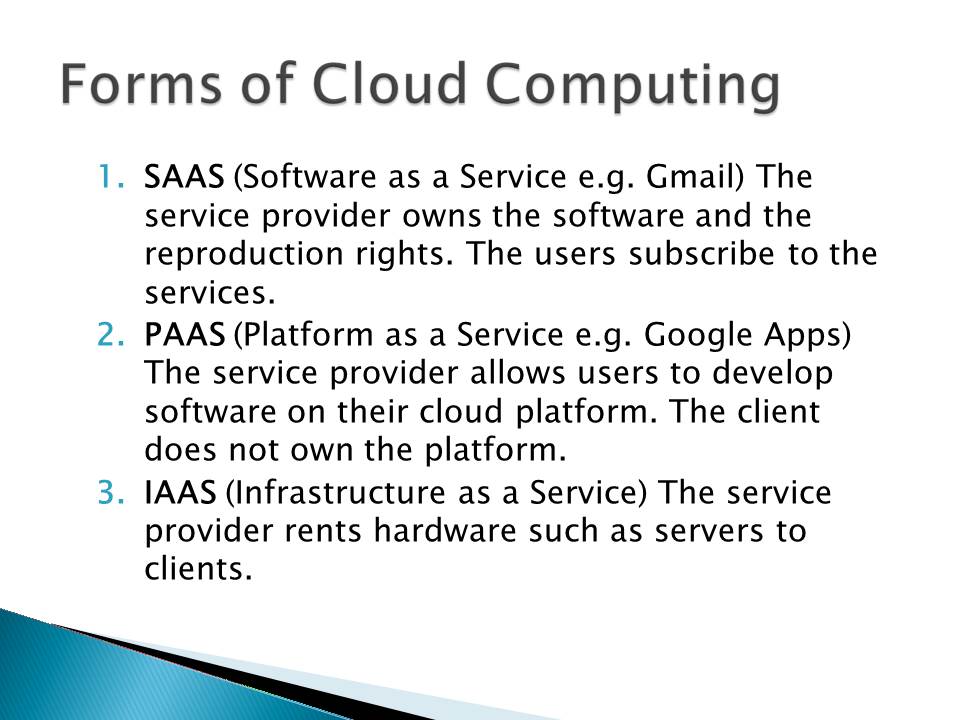
Forms of Cloud Computing
- SAAS (Software as a Service e.g. Gmail) The service provider owns the software and the reproduction rights. The users subscribe to the services.
- PAAS (Platform as a Service e.g. Google Apps) The service provider allows users to develop software on their cloud platform. The client does not own the platform.
- IAAS (Infrastructure as a Service) The service provider rents hardware such as servers to clients.
Top Reasons for Cloud computing
Need for robust Enterprise Resource Management (ERM) systems that can function beyond the reach of the company’s network.
The cloud allows company employees to access information for decision making from a distributed network.
Need for better data security and enhanced data availability to support spatial operations.
Cloud service providers can commit resources to data security better than what a company can do internally.
The need to cut back on IT infrastructure costs.
Accessing services via the cloud eliminates the need to pay for software licenses or the need to buy storage infrastructure.

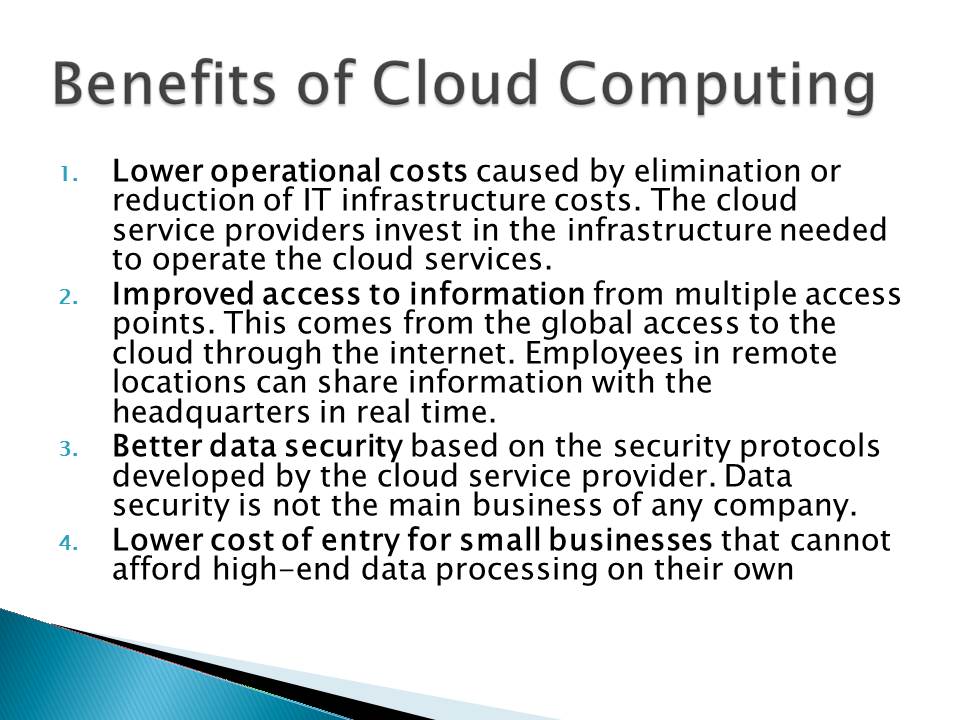
Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Lower operational costs caused by elimination or reduction of IT infrastructure costs. The cloud service providers invest in the infrastructure needed to operate the cloud services.
- Improved access to information from multiple access points. This comes from the global access to the cloud through the internet. Employees in remote locations can share information with the headquarters in real time.
- Better data security based on the security protocols developed by the cloud service provider. Data security is not the main business of any company.
- Lower cost of entry for small businesses that cannot afford high-end data processing on their own.
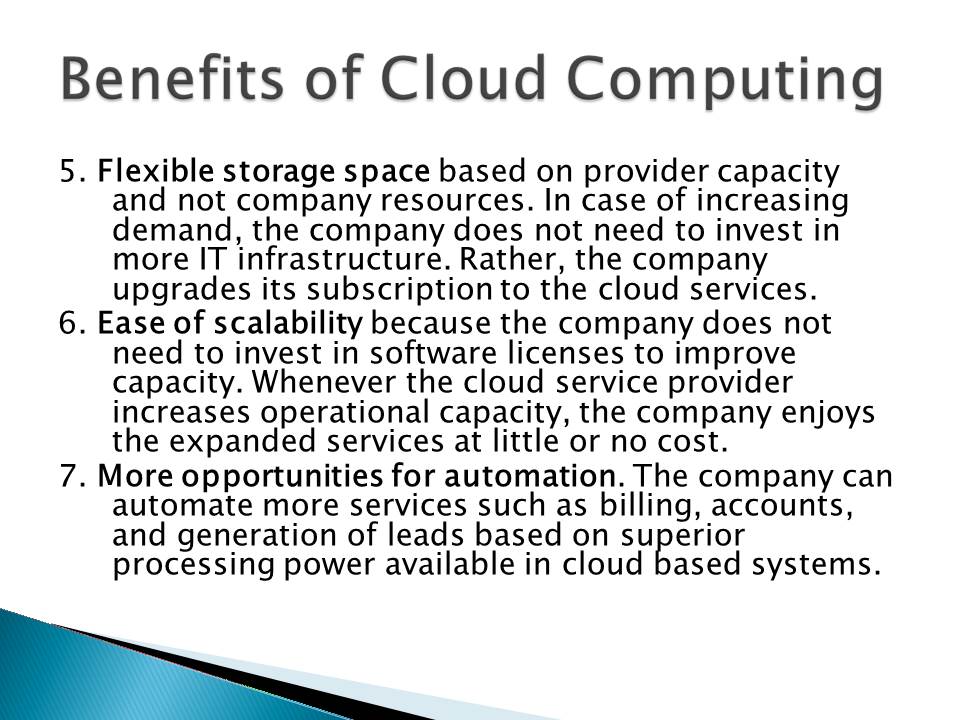
- Flexible storage space based on provider capacity and not company resources. In case of increasing demand, the company does not need to invest in more IT infrastructure. Rather, the company upgrades its subscription to the cloud services.
- Ease of scalability because the company does not need to invest in software licenses to improve capacity. Whenever the cloud service provider increases operational capacity, the company enjoys the expanded services at little or no cost.
- More opportunities for automation. The company can automate more services such as billing, accounts, and generation of leads based on superior processing power available in cloud based systems.
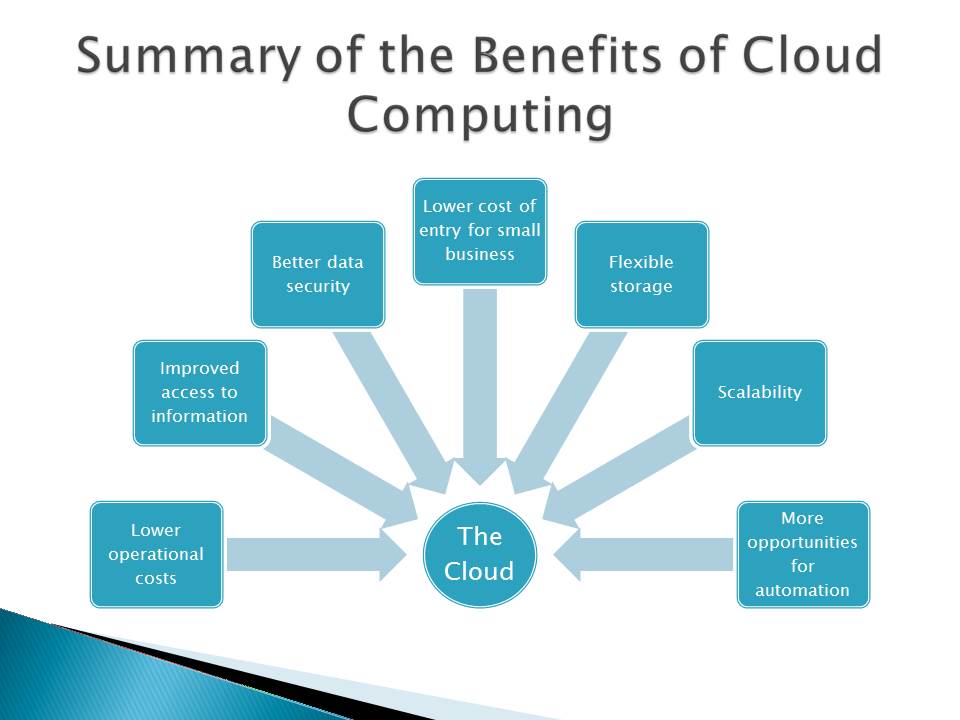
Summary of the Benefits of Cloud Computing
The Cloud:
- Lower operational costs;
- Improved access to information;
- Better data security;
- Lower cost of entry for small business;
- Flexible storage;
- Scalability;
- More opportunities for automation.
Cloud Computing Challenges
Loss of confidentiality because of committing data to third party servers. These servers are accessible to the cloud service providers hence they can access the data.
Risk of data loss in the event of catastrophic destruction of the provider’s servers. This can happen in case of physical destruction or cyber attacks.
Little or no protection from third party access to confidential data. The cloud service providers may need to allow government agencies and other regulators to access their servers, leading to exposure of client information.
Inability to audit data security protocols provided by the cloud service provider. The company has no way to confirm the efficacy of security measures in use.
Few options for disaster recovery in the event of catastrophic damage to cloud servers. The company can lose its entire data collection if there is no backup away from the cloud service provider.
Reduced control over business strategy dependent on the cloud services. The company cannot do anything beyond the scope provided by the cloud service.
Loss of capacity to develop custom solutions to handle organizational needs. Outsourcing storage and processing takes away the company’s capacity to develop local solutions.
Lack of say in data management protocols used by cloud services providers.


Issues to Consider when Implementing Cloud Computing
Legal issues
- Laws governing the sharing of information may limit the company’s capacity to use cloud services because storing client information in third party servers can qualify as data sharing.
- Risk of suffering breaches because of legal action against the cloud service provider by third parties. If the cloud provider faces legal demands to open their data warehouses to scrutiny, company information will leak out.
Information management system
- The company needs an information management system to manage data posted on the cloud. There is need to control the flow of data from local servers to the cloud.

Recommendation
Adopt a phased approach to cloud computing starting with data that is not mission critical:
- Cloud computing will help reduce operational costs because cloud service providers invest in hardware and software.
- It will also help to increase operational dynamism because of the availability of extra processing capacity for the company at little extra cost.
Implement the cloud computing initiative with the advice of a cross-departmental committee.
Develop strategic options to respond to legal, technological and security threats associated with the use of the cloud.


Reference
Mitchell, K. F. (2012). Cloud Computing: White Paper. Maryland: University of Maryland.