Despite the success that Coca Cola Company has achieved, there are some criticisms that the company has been associated with making it less reliable. These criticisms make it hard for the company to do effective marketing since there are some areas where people cannot take the drinks due to the criticisms on the same. For instance, some people believe that the Coca Cola products have some pesticides added to them. In addition, others believe that the products are extremely unhealthy for young children. These and other criticisms have made the marketing of the varied commodities a hard task (Roberts, 2009.).
The company at one point hired a psychologist to listen to the customer complaints, and he pointed out that many of the customers spoke as one does when discussing a deceased relative (Bellows 2008). In retrospective, some marketers believe that the failure of New Coke may have had something to do with the sensation transference, a human oddity first described by Louis Cheskin in the 1940s. Cheskin demonstrated that people would unconsciously associate imagery, sounds, tastes, aromas, and textures into their general impression of a product, even if such associations were unintended or inaccurate. These sensory inputs created a halo effect, which actually modifies flavour perception, so while Cola drinkers may have preferred the new Coke formula, they may have disliked the “taste” of the redesigned packaging. Even Gay Mullins– the man who tried to sue to restore the old flavour– showed a preference for New Coke when subjected to blind taste tests (Bellows 2008).
Contrary to the sales figures, many consumers viewed Coca-Cola as part of the American experience, an icon of modern culture. They were robbed of their cherished Coca-Cola without ever being asked for their opinion. Before the year was through, Pepsi held the market share in the Cola Wars.
Understanding the trends in the global food industry necessarily means the understanding of the constantly changing preferences of the consumers globally and appreciating the efforts put in by the global food industry in meeting such constantly changing demands. The process of transmitting food from the farm to the table is becoming increasingly complex, as there are many local, regional, national, and global agents involved in this entire process. It is actually a huge network(s). Although the fundamental motive that drives the global food industry is the changing consumer preferences, technology, existing and ever changing policies in the business environment, the connection that exists amid the members of the supply chain also are the reasons behind the global food market to constantly evolve. The amount of sophistication was involved in the global supply chain and the distribution channel has increased in the recent past.
Juran’s quality trilogy
Juran’s quality trilogy is applicable to Coca-Cola. By investing information technology, systems provided the company with an opportunity to increase productivity and lower the costs. Moreover, Juran’s quality trilogy is associated with enhanced profits for the company because it helps the company gain competitive advantage. Information technology is considered as the enabler of Juran’s quality trilogy, and is increasingly used to measure, understand, and enhance an organization’s level of sustainable quality. In addition to this, information technology helps facilitate the application of quality function deployment, as well as the development of a real-time collection of data in terms of “customer satisfaction, internal process controls, critical business systems, and other measurement systems that are needed to support Juran’s quality trilogy” (Hill, 2008).
Information technology systems are composed of sophisticated communications and computational tools; the data storage systems could be the key to the success of Juran’s quality trilogy. However, previous studies have showed that the use of information technology on a Juran’s quality trilogy environment necessitated significant changes in organizational culture. Information technology may be harnessed to support the leadership role of the top management, help in the dissemination of Juran’s quality trilogy values, and manage information pertaining to quality which, in turn, facilitates the application of Juran’s quality trilogy and promotes the advantages of it. The leadership of senior managers has an important impact on operational performance. Organizations that have top management leadership generate products that are higher in quality than those firms that have low levels of commitment form senior managers. In this light, information technology is able to provide support to management leadership that generates quality performance (Segal-Horn & Faulkner, 2010).
In addition to this, it must be recalled that Juran’s quality trilogy values customer relationships. With the use of information technology, Juran’s quality trilogy organizations are able to touch base with customers dwelling in remote places. In the same way, studies have shown that customers themselves are willing to manage the relationships themselves, using new technologies. Information technology can be used in administering customer surveys, and perform complex analyses of consumer needs targeting on certain consumers and products. Hence, IT also supports customer relations that have been found to have positive effects on operational performance.
Another way in which information technology may harness the support to Juran’s quality trilogy is through supplier quality management, wherein the common issue is the selection of suppliers according to quality of their raw materials rather than price. Again, information technology may be used to support supplier relationships by enhancing communication links. For instance, Juran’s quality trilogy may be used in placing orders, communicating product specifications, confirming invoices and paying for suppliers. On the other hand, the Internet may be used in searching for new suppliers. Evidently, information technology may be used in supporting supplier relationship that is expected to enhance operational performance.
It is not possible to apply Crosby’s Zero Defect concept to Coca-Cola because the company serves over 1.3 billion daily. This is a huge production, which will not miss a defect.
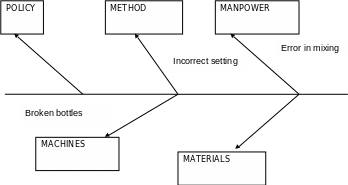
Fishbone diagram for Coca Cola’s bottling plants
Coca-Cola production process is composed of five business resources: man, machine, method, material and environment. Man is the human resource designated to run the process. Machine is the equipment used so that raw materials may be converted to finished goods. Methods are the techniques used in assessing the different phases during the material conversion. Materials are the unfinished elements that are brought together so that they may be converted by the process into an output. Finally, there are certain conditions in the environment that allow the conversion from input materials to output materials. Cause and effect diagrams can be used in solving problems related to this process. Cause-and-effect diagram simply refers to a simple aid that is in a form of a fish fishbone designed to help in logical determination of various possible causes of unsatisfactory results of the project.
As a quality control instrument, it is perceived that the possible cause of the problem would release some effects which can then be used to indicate why a given process within the project’s life cycle goes out of control at a given point. Often, the effects that are released by the possible cause are divided into two categories; the main and secondary causes. This diagrams are used when implementing projects, especially when evaluating the performance of a plant. The plant problems may be complex, affecting production from physical resources to human resources. Every customer expects that they would get quality products and quality service from their suppliers or manufacturers.
Those companies who are able to meet this demand build their customer base over time as people become loyal to them. Others lose their customers because they do not meet the quality expectations of their buyers. Most people have had encounters with poor quality, such as a new vacuum cleaner that worked only once then permanently conked out; airlines losing their passengers’ luggage and university courses that turned out to be different from published curricula. A consumer’s experience with poor quality could even be worsened by the seeming indifference of an employee assigned to manage customer complaints. Successful companies are aware of how important customer-defined quality is to their businesses; hence, they consistently raise their quality standards in order to gain competitive advantage. It is important to note that making quality a priority requires companies to place the needs of their customers first.
Prioritizing quality means that customer expectations must be met or even surpassed, and this can only be achieved if employees closely interact with one another so that they are able to accomplish collective goals. The diagram will be used to evaluate the causes of Coca-Cola failure to deliver quality products to their customer (Hill, 2008). The following diagram shows how a plant of the company will use it.
First, it necessary is to evaluate the mean of the sample against the intended process target. The mean will show how far or near the process target a given set of data. The second step is to evaluate the variability of the individual values that comprise the mean. The variability in results can help a lot in maintaining or controlling quality.
The objectives of effective quality control plans are to identify and resolve problems that are alien to the process design. The resulting actions needed to achieve these goals must be reinforced with a high degree of statistical certainty, and must be data and design driven. Quality control samples and evaluation are meant for the manufacturing operator who needs to make a decision during sample analysis. Decisions should be simple without a set of complicated rules that reflect all possibilities that are theoretically possible, but are generally outside of the process design range.
Process evaluation decisions indicate the current state of sample data, as well as the historic performance of the process. The objective here is to control both the within-lot variability as well as the between-lot variability.
We have identified no link between quality programs and financial budget provisions. Therefore, it is suggested that financial benefits of managing quality be measured in full and financial reporting systems linked to other systems.
Coca-Cola has a method of evaluating and monitoring technology application but this needs to be improved. The process will also be improved and assessed regularly. Customer satisfaction should be assessed as well as people’s satisfaction. The customer must examine regularly these parameters as well as the impact of the business on society. It is important for the company to realize that self-appraisal is an indication of commitment.
As a supplier of soft drinks, Coca-Cola product is differentiated in terms of its content and ingredients as compared to other beverages in the industry such as juices and other energy drinks. Instead of expanding its product line or directly competing with other drinks and brands, it has made a niche market for itself. Also, for giants like Coke, manufacturing drinks is not a difficult task whereas other bottlers may also open up small bottling plants and manufacture their own concoction to be sold in national stores and supermarkets, thus supplier power in the industry in generally low with many players entering the market due to low input costs and many alternatives available. Coca-Cola source majority of their products from the local markets and use bottling operations in local countries to cut down the costs.
Conclusion
In the Coca Cola Company, the work of the manager is easy despite some few challenges. They have a good marketing structure across the world. They have also diversified their products. After diversification, they did a lot of advertising on the new product to ensure that it would become accepted in the market. Despite the few challenges like criticisms, the marketing structure that they have is beneficial. They have been criticized, for instance, to produce beverages that are harmful for human consumption. There are some regions where people cannot take coca cola company’s beverages because of the beliefs they have. This becomes a challenge to the manager as to the overall marketer in the company.
Reference List
Bellows, A. 2008. ‘The American gustatory crisis of 1985’. Web.
Hill, C. 2008. Global business today: Globalization. Boston, MA: Irwin/McGraw-Hill.
Roberts, J., 2009. ‘Can Coca-Cola double sales within 10 years. New markets hold the answer’. Web.
Segal-Horn, S. & Faulkner, D., 2010. Understanding Global Strategy. Hampshire: Cengage Learning.