Introduction
Comparing crime rates in different countries can offer valuable insight into the effectiveness of law enforcement and the justice system in these countries. However, different legal traditions influence crime rates by affecting sentences, crime reporting, and legal definitions. The present paper will show how different legal systems in Germany, Saudi Arabia, and the United States affect crime rates and explain why it is problematic to draw conclusions based on this comparison.
Comparison of homicide rates
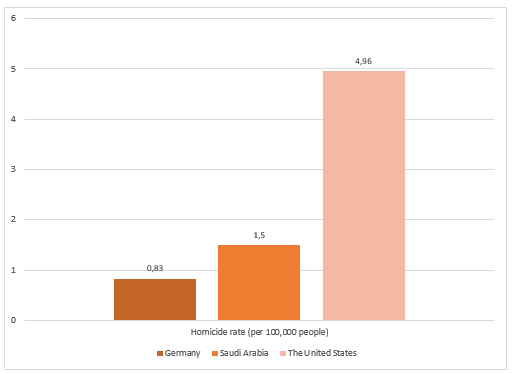
As shown in Figure 1, Germany had the lowest homicide rate in 2015, which may be due to the legal tradition used in the country (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime [UNODC], 2015). Germany uses a civil law system, which means that verdicts and punishments are based solely on the written law (Jehle, 2015). German legal tradition is also characterized by rigorous investigation processes (Jehle, 2015). This reduces people’s willingness to commit violent crimes, such as homicides. Overall, a country’s legal tradition, including laws and punishments, affects people’s decisions to commit a crime. This creates problems when comparing homicide rates in Germany, Saudi Arabia, and the United States, as these countries have very different legal traditions.
The second lowest rate of homicides in 2015 was observed in Saudi Arabia. The crime data in this country might be affected by its legal system, as Saudi Arabia uses Islamic (sharia) law, which is known for its severe punishments (Central Intelligence Agency, n.d.). For instance, Saudi Arabia has capital punishment and does not allow civilians to possess guns, which could influence the rates of serious crime, including homicide. The differences in legal systems make it challenging to compare homicide rates in Saudi Arabia to that of Germany and the United States, as Saudi Arabia laws allow for harsher punishments.
The United States had the highest number of homicides, which is largely influenced by its legal system. The country relies on common law, which involves referring to past judicial decisions to make a verdict. If a person was found not guilty of homicide in similar circumstances in the past, this could be used to issue a not guilty verdict. Moreover, the American legal tradition enables states to establish laws that influence punishment for homicide or create opportunities for people to access guns. Both the legal system and specific laws enacted by states can affect people’s decisions to commit violent crimes, as they lower the perceived risk of punishment.
Comparison of robbery rates
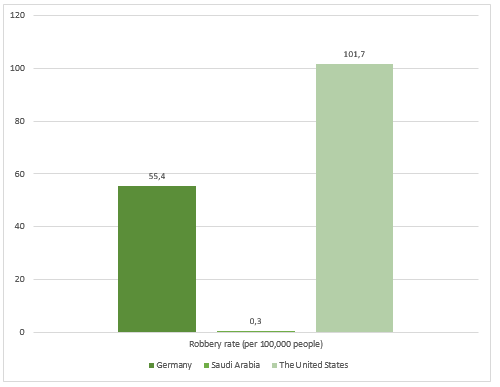
Figure 2 shows that Saudi Arabia had the lowest robbery rate in 2015, with 0.3 cases per 100,000 of the population (“Robbery rate,” 2015). This result could have been influenced by the country’s legal system. Sharia legal system is largely based on the Quran and the teachings promoted in Islam. As the vast majority of the population are Muslims, they are motivated by their religion to abide by sharia law. The connection between the primary religion and the legal tradition in Germany and the United States is not as strong. In addition, there is no official information about crime reporting rates for Saudi Arabia, which is why it is problematic to compare crime rates among these three countries.
In Germany, the robbery rate was 55.4 per 100,000 people in 2015 (“Robbery rate,” 2015). German legal tradition is based on civil law, which means that there are strict definitions of different crime types and the punishments for committing them. Thus, if a person has committed a robbery, they will be found guilty and face a punishment, which increases the risk associated with committing a crime. This could lead to lower crime rates, as people will be more reluctant to commit a crime. When comparing data from Germany to U.S. crime rates, it is problematic to make any conclusions because the two systems might have different definitions of robbery, which would affect crime data.
The United States had the highest rate of robberies, with 101.7 robberies per 100,000 of the population (“Robbery rate,” 2015). The common law system used in the country could affect this figure by decreasing the perceived risk of punishment. Also, the U.S. legal system offers various opportunities for inmates to achieve an early release. Given that the country also has a high rate of recidivism and relatively short prison sentences for robbery, this could also contribute to a high incidence of robberies (Hall, Harger, & Stansel, 2015). Before comparing crime rates in the U.S. and other countries, it is thus critical to account for recidivism and parole options granted by law.
Comparison of assault rates
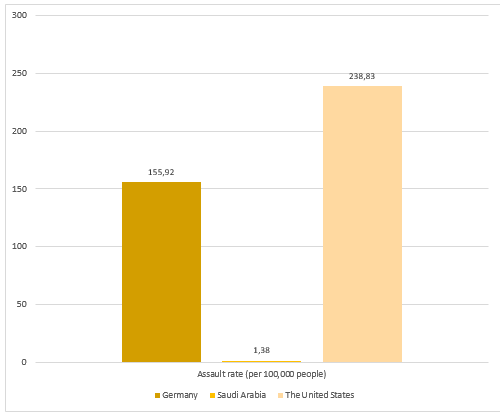
With regards to assault rates, Saudi Arabia is in a favorable position compared to both the United States and Germany. The legal system in Saudi Arabia could have an influence on assault rates in a similar way that it affects robbery rates. On the one hand, the sharia law that is practiced in Saudi Arabia rests on religious premises, and thus Muslim people living in the country have greater motivation to follow the law. On the other hand, the legal tradition in Saudi Arabia also involves more severe punishments, which increases the perceived risks associated with committing an assault. However, when comparing the three countries, one should also review the legal definitions of assault and take into account the possible issues with crime reporting.
As evident from Figure 3, Germany has lower assault rates than the U.S. (UNODC, 2015). The civil law tradition that is applied in Germany could have a negative influence on assault rates, as it increases the risk of punishment following an offense. In addition, the German legal system has enhanced procedures for probation and supervision, which helps to reduce recidivism and leads to reduced crime rates. In comparing data on assault rates in Germany and the U.S., it is problematic to draw conclusions due to the possible differences in legal definitions of assault and crime reporting standards.
Assault rates in the United States are higher than in Saudi Arabia and Germany, which might be because of the common law tradition. By definition, common law involves referring to previous court decisions before issuing a sentence. This could lead to lighter sentences for those who committed an assault, which influences people’s perception of risk associated with assaulting someone. Furthermore, stand-your-ground laws in some states also improve people’s rights to self-defense, thus reducing the possibility of being punished for a physical assault. Overall, the existing differences in legal traditions and laws make it harder to compare assault data in the chosen countries.
Conclusion
The three chosen countries vary greatly in their legal traditions, which affects their crime rates. Saudi Arabia laws include more severe punishments, which makes the perceived risk associated with committing an offense higher. Germany, on the other hand, uses a civil law system and an enhanced probation process to reduce first-time offenses and recidivism. In the United States, the common law system sometimes allows for lighter sentences, while states’ self-defense laws also contribute to violent crime. In order to conclude on the success of the legal systems in these countries, it is critical to take these differences into account.
References
Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). (n.d.). Field listing: Legal system. Web.
Hall, J., Harger, K., & Stansel, D. (2015). Economic freedom and recidivism: Evidence from US states. International Advances in Economic Research, 21(2), 155-165.
Jehle, J-M. (2015). Criminal justice in Germany. Web.
Robbery rate. (2015). Web.
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). (2015). Crime data. Web.