Introduction
Understanding the socio-economic and cultural issues of a country needs a deep analysis of the history of the country from pre-historic times to the current day society. According to Bernhardson (67), in order to have a comprehensive understanding of a country’s history, it would be important to take detailed analysis of all the factors that have played off to make it to its current position.
This scholar says that if care is not taken, there are always chances that some of the most important facts may be ignored. Once this happens, then the analysis shall have lost its real meaning. This is because in every country, there would be something that is unique to it. It is always common to find that most of the cultural and economic practices of two countries from the same region are similar. Despite this similarity, always a small issue may bring a difference between the countries.
This difference should always be captured in order to bring out uniqueness of the country. It is with this knowledge that the researcher set forth to analyze the socio-economic and cultural factors between Uruguay and Argentina and how these factors compare in the two countries.
Uruguay and Argentina are two neighboring countries in South America. These countries have a lot in common, having been exposed to the external world almost at the same time. They both experienced similar colonization pattern, although Argentina gained its independence a few years ahead of Uruguay.
According to Bernhardson (90), when comparing two countries, it is important to bring out their similarities and differences in a clear manner as to enhance understanding. This scholar warns that when analyzing countries with near similar economic and social structure, the researcher should be in a position to pick differences in what appears to be similar because there must be some form on uniqueness in each country.
The researcher was keen on this warning because previous researchers have always stated that most of the South American states have many similarities in their socio-cultural practices. The researcher was therefore, keen to point out these similarities, while still making sure that the differences are captured in a clear manner. Also within the scope of this study is the sustained development between the two countries and the similarities and differences they have.
History of Uruguay
As was mentioned in the introductory section above, the first step towards understanding a country is to know its history. History of a country helps in bringing out the path the country has taken to reach its current position, some of the challenges it has faced in the process, and how it has been able to cope with these challenges in a manner that has defined its culture.
In order to have a clear understanding of Uruguay as a country in terms of its economic, social, cultural and sustained development, the researcher will give a brief history of the country. According to Lavrin (87), Uruguay was formerly known as the Republic East of the Uruguay, but latter changed this name to Oriental Republic of Uruguay. This scholar says that documents about this country before colonization are very scanty.
The only recorded history of this country before colonization was of the Charrua tribe. This tribe was later pushed south by Paraguayan Guarani. However, a rich documentation of this country during the European invasion, struggle for independence and after independence is in existence. In 1516, the first European settlers entered Uruguay. Spain was keen on colonizing this country, but met stiff resistance from the Indians who were living in parts of this country.
Lack of precious metal such as silver and gold slowed the rate of the colonizers grabbing this country because to them it lacked economic benefits. The Portuguese- keen to expand its territory in this region- also made a move to conquer this country by building a fort at the coastal region.
These two colonizers did not find this country economically viable, but the need to expand their territory and capture Brazil motivated them to capture this country. The onset of the 19th century would see British joining the two colonizers in a battle to gain control of this country.
However, after a series of battles between these colonizers, an agreement was reached and Britain and Portugal withdrew, leaving Spain to rule this country. The Spanish rule was soon brought to an end by a revolution led by José Gervasio Artigas at the battle of Battle of Las Piedras in 1811. An autonomous government was formed two years later, but the government had many wrangles. This created an avenue for the Portuguese to take control of this country in 1816 using only 10,000 troops.
The Portugal government handed over the country to Portuguese Brazil, and when the Brazilian Empire became independent in 1822, it retains Uruguay as one of its provinces. This led to a revolution where the Uruguayans demanded that they be declared independent.
This war lasted three years, until the British government fostered peace through the Treaty of Montevideo in 1828. This treaty gave birth to an independent Uruguayan state. When it was finally granted independence, this country was home to about 75,000 people. Despite this small population, the country became split into two political frontiers.
On one side were the conservative Whites with massive interest in agriculture. On the other side was liberal Colorado’s who had massive interest in general business. By 1879, the country experienced a mass immigration and development. Most of these immigrants came from Italy and Spain to practice livestock keeping. The twentieth century saw a series of revolutions between the Colorado and the Blacons. In 1973, the military took over the leadership of this country until 1985 when democracy was finally restored.
The country experienced serious economy contraction from 1999 to 2002, which led to massive loss of jobs and increase in poverty levels. This was caused by the reduced demand of cattle products in the international market. The country has been struggling to gain its footing economically, and with good results as it has managed to reduce government debt and increase employment. The country has also joined a few other nations is legalizing abortion, same sex marriage and use of cannabis.
History of Argentina
Argentina is one of the South American federal republics that were colonized by Spain. This country is officially known as Argentina Republic. It borders Paraguay and Bolivia to the north, Atlantic Ocean and Uruguay on the east, Brazil on the northeast, with Chile on its west. According to Selby (26), the name Argentina was derived from Argentum, a Latin name for silver.
There was a rumors that this country was rich in silver, hence the name, but the first Spanish settlers were disappointed to realize that there was no silver in this country. Unlike Uruguay, Argentina has a rich history dating back to the pre-colonization period. Richardson (56) says, “The history of Argentina can be traced back to those Paleolithic periods, with some traces of Neolithic and Mesolithic.”
The pre-colonial history of this country demonstrates that these people were hunters and gatherers. Scientists have also confirmed that people of this country also practiced advanced hunting, farming, and pottery. By the time the white settlers made an entry into this country, the locals had clearly defined cultural and economic practices. They also had a clear leadership structure that was based on chieftaincy.
The first Europeans to arrive in this country were a voyage of Amerigo Vespucci in 1502 (Behar 56). The Spanish would later make their first visit into this country in 1516.
It is worth noting that the invasion of Argentina not motivated by gold rush as was in other South American countries because there were no precious metals in its soils. Although Spain managed to conquer and rule this country, it faced many challenges, especially from other European nations such as France, which offered the locals military assistance to oppose the Spanish rule.
From 1776 when the United States gained independence, to 1810, there were a series of revolutions aimed at overthrowing King Ferdinand of Spain, especially the Peninsular Wars. According to Connolly (37), a series of rebellions brought down the colonial regime and Argentine Declaration of Independence was finally made in 1816. Soon after gaining independence, the country underwent a series of revolution because different political groups wanted to ascent to power.
The modern Argentine Nation can be traced back to the 1980s when the country changed its policies to encourage immigration. The whites, especially the British and French investors came to this country in mass from early 1880s. They were coming to invest into the agricultural sector.
This massive immigration and investment saw the country emerge as one of the most industrialized nations in South America. The country’s economy grew rapidly through export of agricultural products. The population was also on the rise and this increased the market size.
President Juan Peron has been considered as one of the presidents of this country that helped shape the future of this country. Coming to power in 1946, this president introduced policies that motivated growth of the private sectors. He introduced peronism– a doctrine of leadership that denounced military interference in the political leadership of the country- into this country as a way of encouraging civilian rule.
Peronism generated a lot of debate among the military chief, a fact that made Juan to flee the country to Spain. The military would soon take over power and ban peronism and all its doctrines. There were a series of military coup and civil strife until 1983 when the military chiefs decided to allow for a civilian rule. The political environment had massive effect on the social and economic environment of this country.
Source of Income in Uruguay
The economy of Uruguay has experienced massive growth in the near past due to friendly policies that was introduced by the current regime. For a long time, Uruguay had majorly depended on livestock keeping as the main source of income. The main markets were Argentina and Brazil. However, this changed when the demand for livestock products fell in the world market. According to the report by Cortés (93), the Uruguayans remain the largest consumers of red meat in the world.
From 1999 to 2002, this country experienced massive economic problem, especially due to the reduced demand of its products in its main market. Argentina- the main market for its exports- was undergoing a serious economic crisis during this period, and this reduced the amount of their exports. Brazil also reduced the amount of their imports from this country. Because of this, the economy of this country shrunk by 11%, while the rate of unemployment rose by 21%.
Most of those people who relied on exports were rendered jobless because of this crisis. However, this country was able to recover from this economic shock by late 2003. Since 2004, the government has made deliberate effort to ensure that it stimulates the economic growth of this country. With the help from International Monetary Fund and other world agencies, the government of Uruguay borrowed money in 2004 and 2005 to stimulate economic growth and improve employment.
This has seen this country’s economy expand very consistently. According to Conesa (45), Uruguay was the only country in South America, which was not affected by the massive economic recession of 2010. This scholar says that it was strange that while the entire American continent was feeling the heat of the recession, Uruguay managed to expand its economy by over 10% and unemployment was reduced 5%.
It would be interesting to understand sources of income in this country that has made it gain a strong economic that could resist the inflation. The graph below shows economic growth and income inequality in this country since 1981 to 2010 in the urban centers. The graph above shows that the gross domestic product of Uruguay has been rising consistently from 1981 to 2010.
The growth of per capita income has been growing but in erratic manner. Hourly labor earnings have also been rising, but there has been a drop from 2008 to 2010. The following are some of the sources on income for the Uruguayans.
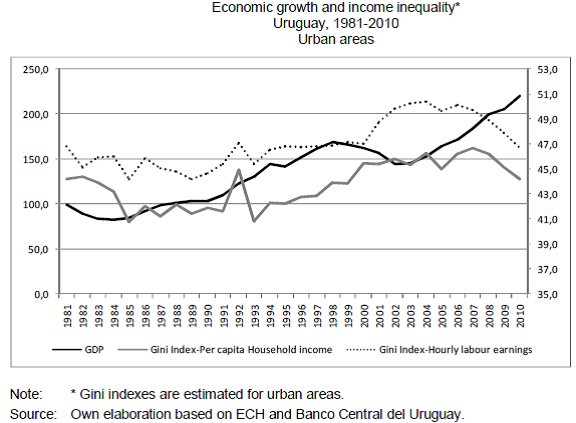
Source: (Lustig 83)
Agriculture
Uruguay has largely depended on agriculture as the main source of income for its populace. This sector remained the main source of income for the economy and for individual families until in the 1970s when it was overtaken by other sectors in the economy. One of the main agricultural practices that have been widely practiced is animal keeping.
During the immigration, most of the white settlers who came to this country were ranchers. They practiced cattle keeping for their meat and milk. The local population was not large enough to make a good market for these dairy products, and therefore these ranchers decided to export their products to neighboring Argentina and Brazil, which had huge markets.
Most of the exports were processed milk, cheese, meat and other animal products. These ranchers also kept sheep for their wool and meat. The climatic condition and geographic location of this country favored animal keeping. The locals found it easier to keep animals because there was plenty of grass for the cattle and the temperatures of this region were favorable.
A small percentage of the dairy products were sold in the local market, especially red meat. Prior to 1970s, this sector employed the highest number of Uruguayans either directly in the ranches, or indirectly in the transport sector or other related sectors of the economy. However, this changed in the 1980s and 1990s when there was a sharp drop in the demand for dairy products in the international markets.
This worsened as the two main markets of Brazil and Argentina started relying on the dairy products produced in their local countries. The economic recession that hit the world added to the injury of this struggling industry. The players in this industry realized that it was time to change tact.
They had to find another way of cushioning themselves from the deteriorating dairy products markets. Some considered changing from this sector completely to try other agricultural practices like farming. Others reduced the number of their cattle in favor of mixed farming. The most common crop in this country is rice. The country produces enough rice to meet the local demands and export others to some of the neighboring countries.
Wheat and corn farming is also practiced locally. Other common crops in Uruguay include sorghum, barley, oats, soya beans, sunflower, sugarcane, peanuts, potatoes, cotton, and flax. Most of the farmers in this country have adopted mechanization in farming as a way of improving their productivity. Although this sector is still a major source of income to many Uruguayans, it is no longer the leading economic activity in this country. It is estimated that agriculture accounts for about 10% of the total income in this country (Perry 118).
Tourism
Since gaining independence Uruguayan government had ignored tourism industry. Of all the sectors of the economy, this industry had no ministry responsible for its management and promotion. It was not until 1986 when the government decided to create Tourism Ministry to help attract tourists into this country. The government came to realize that this could be one of the leading economic sources in this country.
According to Frankema (48), the government of Uruguay started to develop infrastructure that could attract international visitors. The roads were improved, the sewer system changed and security was improved as a way to assure tourists that the government was determined to protect their interest when they come visiting. The government also tasked the ministry of tourism with promoting tourism by attracting international visitors. The beaches have been improved to offer tourists comfort and luxury when they visit.
This effort has done very little in attracting tourists from other continents, especially from the United States and other European nations. Graham and Eduardo (67) notes that over 85% of the tourists who visit this country on a yearly basis are from Argentina. Most of them have investments in this country, and therefore, they come to monitor their development.
Inasmuch as they come to tour the country and for the holidays their main drive is to monitor growth of their companies. About 10% of the tourists coming to this country are from Brazil. A few come from Paraguay and Chile. The country has not been able to attract tourists from other nations other than its immediate neighbors. This may be attributed to its limited flora and fauna. The country lacks vegetations and beautiful sceneries that can attract international visitors.
The wild animals that are found in this country are few, and are commonly found in other countries in other parts of the world. This has denied this country opportunity to attract international visitors because it is considered to lack what to offer to tourists. Moreover, Tanzi (29) says that this country do not have a five star hotel that most of the international customers prefer when they come to visit.
Most of the hotels in this country are owned by the Argentines and they are not of the standards that can attract the European and United States’ tourists. However, the government has made an effort to ensure that this grim face is changed in order to increase its attraction to the international tourists. The government has been keen to support investors in this industry through various incentives. If things continue in the same trend, then it is very likely that the tourism in this country will expand.
The industrial sector
The manufacturing industry in this country has been expanding consistently since the investors turned their focus from ranching. According to Behar (17), the industrial sector in Uruguay has massively expanded, especially the textile industry. When the demand for the dairy products dropped in the international market, the players in this industry focused on the production of clothes, shoes, and other products from the skin and fur obtained from the animals.
At first, there was a challenge in the production process because there was lack of technical skills and machines to enhance this production process. However, this industry gained stability when several investors and the government made a commitment to develop it. The government offered loans to the companies in this sector. These firms were then able to buy machines and other tools to make this process a success.
Between the periods of 1950s to 1970s, this country was able to produce enough textile products to meet the local demand. This production has improved, and currently this firm is producing enough to export to neighboring countries, especially in Argentina. The country has developed numerous entities that have been known to export their products to Brazil and other countries within South America. This has created sources of income to those who had lost jobs in the declining dairy industry.
According to Mooij (79), “The two largest autonomous entities were also the two largest companies in Uruguay: the National Administration of Fuels, Alcohol, and Portland cement, and the National Administration for the Generation and Transmission of Electricity.” The country does not export alcohol. The production of alcohol is meant for local consumption. Alcohol production has been a source of income for a number of citizens of this country.
Portland cement also employs a number of Uruguayan nationals. Generation and transmission of electricity is also another reliable source of income for some citizens of this country. The government has committed many resources to develop this sector as a way of increasing employment opportunities and reducing poverty levels. This has seen the level of absolute poverty drop to less than 2 percent in 2010.
Fishing
Fishing is one of the most developed industries in this country. According to Tulchin (110), Uruguay has had a long history of fishing even before the colonizers invaded it. For a long time, fishing has not been viewed as an economic activity in this country. Only a small percentage of Uruguayans depended on fishing as a source of income. Those who relied on fishing to earn their daily income were considered as poor people.
Most of those who went fishing did it for leisure. However, this is changing as the government tries to increase sources on income and fight poverty in this country. The fishing industry is gradually expanding as some investors have come to realize that this industry can also be tapped. Currently, commercial fishing is taking place in this country. Most of the fish harvested are for local consumption within the local market.
Health experts in this country have been warning against excessive consumption of red meat, which is readily available locally. Although majority of the citizens still consume red meat, a new trend is emerging where the locals are looking for alternatives other than red meat. Fish has been considered as the best option for those who want to stay away from red meat. This industry employs the anglers and those who handle this product until it is finally delivered to the consumer, either at the hotels or in the market.
According to Galeano (90), fishing is getting a new approach in this country. This scholar says that fresh water fishing has a long history in this country. Fishing is now considered as a sport in this country. Catching golden Dorado fish, especially at Salto, has gained a lot of popularity among the locals. This activity has been turned into a competition among the locals during weekends and holidays.
Some Uruguayans depend on this sport for their livelihood. Those who are able to catch the largest and highest number of golden Dorado fish are always rewarded. This leisure game is also attracting tourists. The coastal region has seen an influx of tourists who come to witness or participate in this game. Those who guide the tourists and the owners of the boats generate their earnings from this.
The service sector
The service sector is one of the main sources of income for the people of Uruguay and for the government. The service sector has expanded rapidly over the past few years and has already overtaken agriculture as the main source of income. This industry is big and the government has been able to invest in it extensively. One of the main sectors in the service industry that has developed includes the banking sector. The stated-controlled Central Bank of Uruguay was developed in 1967 to regulate the operations in this sector.
The growth of commercial bank was experienced from 1990s onwards. Some of the commercial banks such as Bank of Uruguay were started in1896 and it is still in operations. It is worth noting that there has been a limited penetration of the local banks into this country. Some of the world’s leading banks have been reluctant to enter this market. However, private investors have come into this industry and currently it is one of the major employers in the service industry.
Another service industry that has been considered as the main sources of income for the locals is the transport sector. This sector has employed a huge number of the locals. The government has invested in the transport sector by developing road and rail transport. Most of the youths are employed as drivers, loaders and various other tasks related to transporting people and products.
Entertainment industry has also gained momentum and now employs a good number of people. Acting is gaining popularity among the locals. A number of Uruguayans are generating their income through music and movies as artists, producers, or distributers. A number of informal sectors falling under the service industry have been able to offer employment opportunities to the locals.
Mining
It is a fact that Uruguay lack precious metals, a fact that made colonizers asserting their power into this territory. These colonizers never made attempt to promote mining because their exploration confirmed that there were no minerals locally.
When this country gained independence, mining was never considered as one of the possible sources of income because it had been confirmed that the country did not have precious metals. However, this industry started developing following the increased pressure to increase housing units, especially in the expanding urban centers of this country. Sand harvesting has become one of the sources of income for the locals. They harvest sand and sell it to the contractors.
Stones used in the construction of houses, roads, bridges among others also come from this industry. The recent funding done by the government to increase housing units and hotels along the coastal region of this country has been a boost in this industry. The number of those directly employed in this sector has been on the rise. However, environmentalists have complained that this sector has negative effect on the environment.
Forestry
Forestry is another source of income for a number of people in this country. Although Uruguay does not have large tracks of land dedicated to forests, individual famers have set aside part of their land to this industry. They grow trees and sell them to various customers who may need them for various activities.
Most of the buyers of the wood are carpenters who use wood to make various items sold locally. Paper manufactures and electric power supply companies also make a substantial market for the players in this industry. Although this industry has been employing more people, it is yet to get direct support from the government. Only a few foreign investors concerned with protecting the environment have made effort to support famers by providing them with seedlings.
Source of Income in Argentina
Argentina is the third largest economy in South America. When the country gained independence, the local leadership was concerned of how to fight poverty among the Argentines. It was clear that the country’s resources were under control of the external forces. According to Fischlin (39), the colonizers were reluctant to leave this country even when it was declared as an independent state.
This scholar says that the ability to empower the locals was challenged by the constant leadership wrangles by different factions. Although these factions were committed to empowering the locals, greed for power serious affected economic growth of this country. A series of coups have made it difficult for successive governments to make a step towards economic growth. These governments’ focus was how to retain power by avoiding possible military takeovers.
Due to government instability during the early years, economy experienced a number of challenges. This instability continued until 1946 when Juan Momingo Peron took over power through a democratic election. He introduced Peronism- a doctrine that was meant to empower the civilians and promote economic growth locally- to this country. Under his leadership, the country experienced a substantial economic growth as many companies were put up to promote development in various sectors.
Currently, Argentina is classified as one of the upper-middle income economies in the world by various organizations, including the World Bank (Davis 71). This scholar also says that the gross domestic product of this country and its per capita is higher than most of its neighbors.
The World Bank has classified this country as one of those with the highest human development index in South America. Although the economy of this country has been affected by the recessions, especially in the late 20th century, it has remained strong over the years. This is attributed to high literacy in its population, and the rich natural resources. The increasing export of its agricultural products has also given it an edge over other competitors in the market.
This country is among the G-20 economies, and is classified as one of the emerging economies in the world. The government has promoted the private sector as a way of promoting economic growth. Inasmuch as the government has faced criticism from various quarters as being corrupt having been ranked position 100 out of 178 most corrupt countries by Transparency International, the country has seen growth in various sectors of the economy.
The table below shows the trend of investment in this country over the years.
Investment, 1980-1998 (Constant Prices 1980)
Source: (Davis 91)
The above statistics shows that there has been a consistent decline in public investment as a percentage of gross domestic products since 1980 to 1998. The total gross fixed investment as a percentage of gross domestic products declined from 1980 to 1991 when this percentage started to rise until 1998.
The following are some of the main sectors that have offered employment to the Argentines.
Agriculture
Agriculture has been one of the main sources of income among the Argentines. This country has been practicing crop farming even before attaining independence. For a long time, faming was considered as a source of income to peasant farmers. Enough attention was not given to faming when investors came to this country after independence.
However, this changed when the government realized that it had to import agricultural products in order to sustain its increasing population. Anton (73) says that Argentina is one of the South American countries that are endowed with various natural resources, including land. Large tracks of land were put under farming and mechanization was embraced in order to improve productivity.
Government made direct efforts to support crop farming in this country by zero-rating tax on farm inputs to reduce cost of production. The government also eliminated tax on most of the farm products, a fact that attracted investors into this industry. Currently, this country is producing enough to export to other neighboring nations. Rice, corn, wheat, barley, beans, and sugarcane are some of the main crops that have been earning the Argentines a lot of income.
Just like its neighbor Uruguay, Argentina has embraced ranching as one of the sources of income. The government has supported development of this sector in order to reduce the level of importing dairy products such as milk and red meat from its neighbors. Huge market in this country has motivated investors to enter this sector. The skins and fur from the slaughtered animals also find their ready market in the textile industry, which has been expanding over the years.
Some of the products from animals are used in making various other products such as cooking oil. This sector has employed a large number of Argentines at various stages of production. Their income from this sector has been stable despite the recession that this country has gone through in the past. With the increasing support from the government, this sector is destined to be one of the leading sources of income for the citizens of this country.
Tourism
Argentina’s tourism sector is very advanced and this is attributed to its natural assets in various cities. Tourists are also attracted to the country because of the rich cultural practices that is unique to this country. According to the report by Bernhardson (58), in 2010, this country received about 5.3 million visitors most of whom come from the United States and Europe.
This makes it the leading tourist destination in South America, beating the neighboring Brazil. In fact, this country is considered having the second highest number of international tourists in the entire Latin America. In this year, it is estimated that this country received about US$ 4.93 from tourism. Some of the most popular destinations in this country include Buenos Aires, Iguazu National Park, Bariloche, Los Alerces National Park, and Los Glaciares National Park among others.
This industry employs a massive number of people directly and indirectly. The tour guides fully depend on tourism as their source of income. With the increasing popularity of this country as a tourist’s destination, the number of people getting into this job has been on the rise.
This industry has also been a major boost to the hotel industry, which also employs very many people. Other professionals such as drivers and security agents also draw their source of income. To the government, tourism has been one of the main foreign exchange earners, besides export goods.
The industrial sector
The industrial sector in this economy is very advanced. According to Bernhardson (37), manufacturing sector is the largest sector of the economy, accounting to 19% of the country’s gross domestic product. This massive development was witnessed in the late 19th century and early 20th century when the government offered direct support to manufacturing firms. Successive governments have given this sector a lot of attention that led to this great growth.
The industrial sector employs the highest number of Argentines either directly or indirectly. Lavrin (78) says that, “Leading sectors by production value are Food processing and beverages; motor vehicles and auto parts; refinery products, and biodiesel; chemicals and pharmaceuticals; steel and aluminum; and industrial and farm machinery; electronics and home appliances.” According to this scholar, this country produces enough home appliances and electronics to meet the local demand.
Other major manufactured products in this country include cement, glass, plastic, and tires. The country also produces textiles, apparel, furniture, leather, and tobacco products. The main destination for these products is the local market. However, some of these products are exported to some of the neighboring countries. The country is also considered as the main exporter of cobalt-60, an isotope that is used widely in cancer therapy (Lavrin 71). The country also depends on the production of laptops servers as its source of income.
Fishing
The Argentine sea has been a source of income to people living along the shore. Fishing is not given as much emphasis as it is in the neighboring Uruguay. However, a few people have been keen on earning their income from fishing. It is estimated that there are over a thousand fish species in this sea. There is a ready local market for the produce from this lake. However, this industry has received minimal support from the government either directly or indirectly through the players.
The service sector
The service industry is also very much developed as compared to its neighboring countries. The government has given massive support to the banking industry as a way of motivating other sectors of economy. The central bank of Argentina has developed policies that many have considered as friendly to the commercial banks. The banking sector of this country has attracted a number of international banks.
The government has been using the commercial banks to manage inflation and to motivate investment. The banking sector is another major employer in this country. Most of the graduates prefer working in this sector because it is considered as very prestigious. Transport sector also employs a good number of people in this country. The informal sector also employs a good number of Argentines. The government has also been able to generate income from taxing these firms.
Mining
Argentina is one of the countries in South America where mining has not been given a lot of importance. However, the private sector has been keen to develop this industry, especially due to the rising need for power. As was stated before, the country’s industrial sector has been growing over the years.
However, the country was at one time forced to import electricity from Brazil. Investors have come to develop this sector specifically to meet the local demands. Geothermal has been developed to reduce the country’s dependence on external sources of power. Just as in Uruguay, mining in this country involves harvesting of sand and stones to help develop infrastructure in this country.
Comparison between Source of Income in Uruguay and Argentina
The above analysis has given a detailed analysis of the sources of income in Uruguay and Argentina. In this analysis, some similarities and differences have come out. The following are some of the similarities brought out.
- Both countries depend on agriculture as one of the main sources of income
- Ranching is a well-established source of income and was introduced by white settlers in both countries
- The industrial sector is the main source of income in both countries.
- The governments of both countries have been promoting tourism, which is another major source of income in both countries.
The above similarities may be attributed to the fact that both countries are neighbors and experience a similar environmental pattern. Despite the above similarities, a number of differences in source of income in both countries are evident. The following are some of these differences.
- The industrial sector in Argentina is developed, while that of Uruguay is still developing.
- Although both countries export various products to the international market, the amount of Export of Argentina is larger than that of Uruguay.
- The tourism sector in Argentina has attracted visitors from Europe and the United States, while that of Uruguay has only attracted regional visitors from neighboring countries.
General Overview of International Organization in Uruguay and in Argentina
The foreign policies in Uruguay have helped it develop close ties with the international society. According to Selby (49), Uruguay has been keen to promote international relations with its immediate neighbors and other nations overseas.
Uruguay is a member of World Trade Organization, the United Nations, International Labor Organization, World Food Program, UNESCO, World Health Organization, among other international organizations. This country joined International Organization of la Francophone, making it the first South American nation to join this organization.
This country was among the non-aligned countries during the first and second world wars. One of the issues that have affected this country is emigration. It is estimated that more that 19 percent of its citizens are living abroad. Majority of those who emigrate from this country are young individuals, making it vulnerable due to the aging population. This country has a stable military (the army, navy, and air force), but has never been forced to use it against its neighbors in the recent past.
Argentina on the other hand, has had its own issues with its foreign policies and international relation. Soon after gaining independence, this country received criticism from the former colonizer of using its strategic Buenos Aires port to facilitate smuggling. In response to this claim, the government developed a policy that would grant it more autonomy.
This country has also had a policy granting it an autonomous alignment to the United States, but this was changed by president Nestor Kircher in 2003. Although there has been accusation, from other countries, that Argentina is selling arms to Ecuador and Croatia despite attempt to bring peace the government has been keen to avoid any military confrontation with its neighbors and other foreign nation (Selby 82).
Trade between this country and international society has been growing at an attractive rate. It is important to note that although Uruguay and Argentina share a number of issues in their international relation policies their policies also have many differences.
Overview of Commercial and Logistic Sources in Uruguay and Argentina
According to Conesa (61), the commercial sector is always depended on the logistical issues within a country. This scholar says that it is not possible for the commercial sector to prosper when means of transport is not adequately developed.
It is because of this that the governments of Uruguay and Argentina have been keen to develop the transport sector. Developing this sector always has a direct impact on the growth of the commercial sector. As was mentioned in the sections above, these two countries have large industrial sectors that have supported their economies.
Both countries depend on exports in order to advance their economies and increase job opportunities. These commercial activities can only be a success if a country has a developed infrastructure. The domestic players as well as the exporters rely on goods roads, rail, air, and sea transport to achieve their goals in the market. It is therefore, important to analyze these four sectors of transport in these two countries in order to determine how well these countries can support commercial activities.
Sea Transport in Uruguay
It was mentioned in this research that the main destination for most of the exports from Uruguay is Argentina. These two countries have close trade ties. Although these two countries do not share borders because of the water body between them, they have had very close trade corporations. Uruguay exports its red meat to Argentina. In exchange, this country buys electronic products, especially home appliances from Argentina.
This close exchange of goods needs a good sea transport. Most of the products that these countries exchange are bulky and cannot be transported by air. Uruguay also has close trade corporations with other South American states such as Paraguay. Recently, there has been a close trade corporation between China and Uruguay. Although Uruguay is yet to find a way of making its exports to China, more substantial, Chinese products are finding their way to Uruguay at an unprecedented rate.
These commercial activities can only be made a reality of there is a developed sea transport within the country. The government has developed a number of ports that can handle cargo leaving this country to international markets. These ports also handle goods from the international markets into the country. Montevideo is the main port that has been handling cargo from this country leaving for the international market, and those that are being imported.
Fray Bentos, Paysandú, Nueva Palmira, La Paloma, Carmelo, Juan Lacaze, Conchillas, Salto, Colonia Del Sacramento, Punta Del Este, Piriápolis, and Mercedes are some of the major ports and harbors in this country that has supported international trade. The government of Uruguay manages these ports, although the government has allowed the private sectors to have joint operations with the government in some of them.
Air Transport in Uruguay
Air transport is very important for the Uruguayan tourism industry. According to Lustig (59), the government of Uruguay has been struggling to develop tourism industry for a very long time. This country has not been able to attract tourists from the United States and Europe.
Although some scholars have attributed this to less developed hotel industry of this country, others claim that air transport into, and out of this country may be another reason for this. Uruguayan airports do not have straight routes to some of the major international airports in the United States and Europe.
This forces tourists who wish to travel to this country from these European countries to pass through Argentina or Brazil and then connecting to Uruguay. Some tourists end up spending their time in Brazil or Argentina without making it to this country because of this. It is very unfortunate that this country do not have a national airline. Private investors own the airline companies operating within this country. Most of these investors are foreigners from Argentina, Brazil and other European nations.
The government has launched a massive plan that would see a number of the airports in this country improved to meet the standards that would allow them to have direct routes to major cities in the world. Lustig (73) observes that Angel International Airport, Villa Independecia Airport, Artigas International Airport, and Santa Bernardia International Airport are some of the main airports in this country trusted with the international flights.
A host of other airports also exists to help handle the domestic and international flights. The government has committed itself to improve the status of the current airports in this country based on the guidelines of IATA instead of increasing their number. The security at these airports has been maintained, but customers have complained before of the service delivered by these airports.
Road and Rail Network in Uruguay
Road and rail transport has been important in promoting movement of goods and people within the borders of this country. The rail and road transport has also been important in promoting trade between Uruguay and Brazil, the only country with which it shares a border. The manufacturing sector has the local market as its main destination. These products are always delivered through road and rail transport.
The country has well developed road network that covers most of the cities and the rural areas. However, the rail network has not received much attention from the government as would be expected. The effort to develop the road network has been much stronger as compared to the effort put to improve railways transport. The first railway line to be developed in this country was in the 17th century by the colonial government. Since the country attained its independence, little has been done to promote rail transport.
Recent reports have indicated that the government is heeding to the pressure from various stakeholders to privatize this sector as a way of reviving it to ease transport pressure on roads. This in turn helps improve other commercial sectors of the economy. Road penetration into various parts of this country has been on the rise.
The macadamia roads are common even in the rural set-ups in this country, a fact that has made movement of raw products and finished goods to the company and to the market respectively, very easy. Road transport has kept the industrial sector very active. According to Perry (72), the road network within this country and those that link it to its neighbor Brazil has facilitated improved commercial activities within this country. It is estimated that roads in this country are about 77,732 kilometers in total length.
Sea Transport in Argentina
Argentina has a well-developed sea transport that enables it to export its manufactured goods to foreign markets, and import products that are insufficient within its borders. For a long time, this country had not developed its industrial sector and imported most of the industrial goods from Europe, the United States, and China. However, this changed when the government gave focus to the local industrial firms.
Currently, Argentina produces several industrial products such as home appliances, electronics, among others. Some of these industrial products are exported to the neighboring countries. The commercial relationship between Argentina and Uruguay has been very close, with a number of Argentine investors coming to invest in Uruguay. There is a massive exchange of goods between these two countries. However, these two countries do not share a land border.
This means that road and rail transport cannot be used to facilitate trade. These two countries depend on water transport to move their goods from one country to the other. The coastal strip of this country is estimated to be about 1600 kilometers stretch.
According to Perry (39), some investors have developed shallow-draft river craft along this coastal strip to facilitate quick movement from Argentina to Uruguay, Paraguay, Chile, and other countries sharing a marine border with Argentina. The shallow-draft river crafts are specifically meant to transport passengers.
The shipping industry has grown over the years with the expansion of the commercial activities between this country and its neighbors. Bulk ships, container ships, cargo ships, roll-on roll-off ships, liquefied gas tanker ships, chemical tanker ships, petroleum tanker ships, and combined passenger-cargo ships are some of the main ships used at the ports of Argentina (Cortés 47). This scholar says that Argentina has about 11,000 kilometers of navigable waters. This makes it one of the countries with the largest navigable waters in the world.
The cargo freight using these waters was estimated to be about twenty-eight million metric tons as at December 2010. Some of the most active ports and harbors in this country include Bahía Blanca, Comodoro Rivadavia, Buenos Aires, La Plata, Mar del Plata, Río Gallegos, Concepción Del Uruguay, and Necochea. These ports have facilitated movement of goods from Argentina to other parts of the world, and from other parts of the world to Argentina.
Air transport in Argentina
Air transport in Argentina has been developing very fast. The increasing number of tourists has propelled this development into this country. Argentina is one of the most attractive tourist’s destinations in South America. Most of these tourists come from the United States and Europe. This has stimulated growth of international airports in this country.
Air transport has been instrumental in the development of trade between Argentina and international community. Every province in this country has an airport in order to facilitate movement of tourists and other businesspersons in this country. Although considered more expensive than other means of transport, air transport is gaining popularity even among the locals because of the speed and convenience.
Buenos Aires remains the most active airport in this country, especially for the international travels. However, other major airports coordinating regional movements include Córdoba, Mendoza, and Rosario airports. These three airports were developed to ease the pressure on Buenos Aires due to the increasing international travels into and out of this country.
The national courier for this country is Aerolíneas Argentinas, which is one of the largest airline companies in this region. However, international airlines such as British Airways, Virgin Atlantic, and Air France always make frequent visits to the international airport of this country.
Road and Rail Network in Argentina
The road and rail transport in Argentina is very developed, and always active throughout the year. One of the most conspicuous transport means when one gets to any of the Argentine cities is taxi. This may be attributed to the high number of tourists who visit this country throughout the year.
Within the cities, there are large buses that help in the movement of people from one place to the other in order to facilitate running of commercial activities. Long distance buses also exist to help travelers moving from one city to another or one province to another. Most of the Argentines prefer the use of Buses to airplane because of the relatively low cost of road transport. Large tracks are used to transport goods from the ports to their destinations or from various companies to the market or the port.
Rail transport has also helped improve commercial activities in this country. According to Cortés (48), suburban trains are vital in connecting Buenos Aires city with other cities in this country, especially the Greater Buenos Aires area, a fact that has helped in moving bulky goods into the market. The commuter trains also help a lot in enhancing movement of people within the cities and from one city to another.
It is estimated that about 1.3 million people use commuter train every week. Although the government has been able to phase out some of the diesel-power train and replace them with electric trains, some cities in this country still depend on diesel-powered trains for their movements. The capital Buenos Aires is the only city that has an Underground metro train in this country. However, plans are underway to expand metro system to other cities.
Comparing the Infrastructural Development between the two countries
The above discussion has given a detained infrastructural development between Uruguay and Argentina based on their transport system. From this analysis, it comes out clearly that both countries have developed sea, air, road, and rail transport. The governments of both countries have realized that the only way to promote commerce in their countries is to improve transport system, which would facilitate movement of goods and people.
However, there are some striking differences between the two countries in their transport system. Uruguay only has Brazil as the neighbor it shares a land border with in South America. However, its main trading partner is Argentina. This has made sea transport the most important transport system when it comes to international trade in this country.
However, this is not the case in Argentina. It is also clear that air transport is more developed in Argentina as compared to that of Uruguay (Aloian 45). The Argentine government has also been able to improve its rail services and currently, Argentina has more trains that are electric then Uruguay. The volume of trade within Argentina is by far larger than that of Uruguay. While Uruguay depends on the region market for its exports, Argentina has been able to reach out for the markets beyond South America with its products.
Cultural Similarities and Differences between Uruguay and Argentina
Culture is one of the defining factors of a given community. The world is increasingly being globalized and the world society is slowly adopting a similar culture that is universal. Graham (67) calls this convergent of culture globalization or westernization. Various societies around the world are being exposed to the western culture backed by capitalism that has already engulfed the world.
For these reason, it is true that some cultural practices that were unique to these two countries have been influenced by the western culture. South American states have tried to remain closed states in a bid to avoid the massive influence that the United States had on other countries around the world.
It was important that their governments took measures to avoid the massive westernization that grew when the United States became the only superpower in the world. To an extent, this has helped them retain some unique cultures, but the truth is that this culture is fast being eroded by western culture. These two South American countries have a number of similarities and differences in their culture as discussed below.
Cultural similarities between Uruguay and Argentina
As mentioned previously, these two countries come from South America, and they share a marine border. This is a clear indication that traditionally, these two regions shared a lot in common because of constant contact they had with each other.
The cultural practices of these two countries were also influenced by the slave trade that was very popular in this region before it was finally brought to an end. In order to bring an understanding into the cultural practices in these countries, the research will focus on some of the striking similarities in both countries.
Gander power
Gender inequality has been an issue in both countries since they gained independence. The cultural practices in both countries have given men power over women. Until 19th century, women were not expected to engage actively in leadership issues and in the corporate world.
These societies were highly patriarchal, with women expected to play a passive role whenever she was in the presence of men. Westernization has fought this notion, with various gender-based organizations criticizing governments for its reluctance to empower women. It is in this twenty first century that women in both countries have gained full liberation from dominance by men. However, it is still apparent that men still have an upper hand and this is because of the historical cultural practice that was common in this country.
Sports
Sport is one of the most important recreational activities that define culture of a society. According to Tulchin (113), by determining the recreational activities of a particular region, it may be possible to explain some of the behavioral patterns of a particular group. One of the sports that have been common in these two countries is football. In both Argentina and Uruguay, football is the most favorite game, especially for men.
Women also like football, but men’s football has been given priority. Both countries have been able to win World Cups more than once since it was started. There has been an argument that football must have originated from this region, though it has been modified in various ways to acquire its current form.
Religion
Religion is one of the cultural practices that bind together the society and shapes morality in both countries. There are scanty documents describing the religious practices in the two countries before the colonization. However, when the colonizers came, Christianity was introduced into this region, and it has remained the main religious practice.
Most of the Uruguayans and Argentines are Christians. In both countries, the Roman Catholic is the main religious denomination. It has over 60 percent of the total residents in the two countries. There are a few protestant churches in both countries, with a negligible percentage being Jews.
Cultural differences between Uruguay and Argentina
Despite the above differences and the fact that the two countries are geographically located in the same region in South America, there are a few differences in cultural practices. One of the differences in cultural practices that have become very conspicuous is the architecture. The Argentines have embraced the western architectural designs, while the Uruguayan architectures leans more towards the Chinese architecture.
This may be attributed to the fact that the Chinese contractors have been very common in Uruguay than in Argentina. Although cinema is a common leisure in both countries, Argentina has more developed theaters, and their film industry is much advanced. Red meat is more popular in Uruguay than it is in Argentina. While it is true that wine taking is a common practice in both countries, it is more common among the Argentines than in Uruguay.
Environmental Concerns in Uruguay and Argentina
According to Tulchin (83), Uruguay is one of the countries that are highly endowed with natural resources in form of biodiversity. This nation has rich environmental ecosystems that are characterized by various forms of biodiversity. The researches show that this nation has very fertile soils that can support the life of many food plantations.
Among the food, crops that are planted largely in this country include wheat, rice, corn and many others. This indicates that a large part of Uruguay’s economy is supported by agriculture. A part from the fertile farmland soils, the country is also known to have several waterways that enable the country to harvest hydroelectric power, support fisheries, industries, and agriculture.
However just like many other nations, Uruguay is has many environmental issues that poses a threat to the economic development in this nation. Like in many nations, these environmental concerns emanate from the failure of the country to link the environment’s food production ability with sustainable management of the related resources. Uruguay experiences a lot of water and air pollution. Water pollution results from the nation’s industries and mining activities.
Pollution of water poses a serious threat not only to human healthy but also to the fishery resources. Water pollution has posed serious and negative impacts to the biodiversity in Uruguay. This research continues, points out that many plant and animal species are endangered, and some have become extinct because of water pollution. Some of the species that are reported to have been threatened to extinction include turtle, tundra, and crocodile species.
Air pollution has healthy impacts to many life forms in this nation. Air pollution just like water pollution emanates from the unregulated mining and industrial activities. Water and air pollution have high impacts to the environment of this nation which if the polluted is not curbed, it is yet to affect the nation.
Just like Uruguay, Argentina also has a number of environmental problems that raise a lot of concern. Argentina’s environment is characterized by availability of all forms of biodiversity.
Like many other nations, this country faces a lot of environmental degradation, which poses serious impacts to different life forms in the nation. The environmental concerns in Argentina include deforestation, soil erosion, water pollution, and air pollution among others. Tulchin (40) says that the nation of Argentina is growing rapidly in population and the industrial activities are expanding rapidly.
This researcher points out that the increase of population puts pressure on the available water sources resulting to water shortage. In addition, the industries also harvest lot water from the water bodies adding up to the problem of water scarcity. What complicates the whole matter is that the industries release the untreated wastewater with chemicals to the water streams making water from such bodies to be unhealthy for drinking.
Deforestation is also high in Argentina. It is a common knowledge that forests acts as habitants for many life forms including animal and plant species. Once these forests are cleared, it is understood that the biodiversity is also lost. This leads to several plant and animal species becoming extinct and others endangered.
Some of the animal species that are greatly threatened include the crocodile species, some birds’ species, deer, tundra and goose species. It is reported that more than 25 mammals are endangered and close to 200 reptiles threatened in Argentina. Forests play a crucial role in the process of rain formation. They are preserved as good water catchment areas.
Therefore, deforestation affects the rain patterns which results to water issues on shortage. It is also worth noting that tree roots helps in holding the soil particles together. This is vital as it helps in preventing soil erosion. Once tree vegetation is removed, the soil is left bare and prone to the agents of erosion. This nation is also faced with air pollution problems. This results from high emissions from industrial activities. This again poses a health problem to human beings and animals.
Comparing the environment in Uruguay and Argentina, there are similarities in the environmental concerns raised. In both countries, the environment highly degraded. The two countries have similar environmental concerns that emanate from the inability of the nations to observe sustainable development.
Sustainable development is necessary for the prosperity of any nation that desires to grow. This researcher argues that a nation and its citizens should not develop at the expense of the environment. In both Uruguay and Argentina, water and air pollution is common. Tulchin (75) says that this kind of pollution can only be curbed in Uruguay only if industrial activities and mining can be regulated.
The seriousness of water pollution in Uruguay has provoked the nation to collaborate with various authorities with an aim of trying to reduce the levels of pollution. However, as indicated earlier on, much is still to be done for these efforts to yield fruits. While this is the case in Uruguay, air pollution in Argentina mainly arises from the industrial emissions in the environment and from the motor vehicles. To a smaller percentage, this pollution is caused by mining activities around Esquel town, Chubut province in Argentina.
The two countries as a result of the environmental degradation have severed suffered the loss of many animal and plant species. Although the animal species that have been endangered and become extinct differ, some common species have been threatened in both nations. These include tundra, and crocodile species. Unlike Uruguay, much has not been done to address the environmental issues in Argentina.
Sustainable development in Uruguay and Argentina
The above discussion has demonstrated that both Uruguay and Argentina has experienced healthy economic development in the past years. Although these two countries suffered from political anarchy immediately after gaining independence, they were able to gain political stability, a major ingredient in achieving sustained development. Both countries have been able to fight extreme poverty with a lot of success.
The percentage of those staying in object poverty in Argentina and Uruguay is way below the world average. Income distribution may not be as even as would be expected, but the governments of these countries have developed mechanisms through which those staying in object poverty can be helped by the state to get access to basic needs.
Various measures can be used to determine sustained development in a country. In Argentina, the economy has been consistently growing and the International Monetary Fund has classified it as the middle emerging economies. Fischlin (48) says that there was a time when Argentina was considered as the richest country in Latin America. However, this was interfered with when the government became corrupt in various ways. This slowed the economic growth.
However, it gross domestic product has been on the rise despite the economic challenges it faced during the recession that hit the world. On the other hand, the economy of Uruguay has remained strong. Government has invested in various sectors of the economy in order to stimulate sustained development in the country. The government of this country has also tried to avoid overreliance on exports and foreign aid. This explains why the country was not affected by the 2009/2010 world economic recession that hit the world.
The government of Uruguay has also developed foreign policies that would encourage foreign investment. This has seen more Argentines come to this country to invest in the hospitality industry. Through this, the government has been able to reduce the rate of unemployment to less than 4%, a fact that has been of help in the struggle to achieve sustainable development.
Conclusion
Uruguay and Argentina are countries that share marine border in South American content. The two countries have had a cordial relationship with each other since they gained independence from Spain. Given the fact that they are in the same region, the two countries share a lot in various field.
The discussion above has given a systematic analysis into the economic, social, and cultural practices in both countries and how they compare. From the above discussion, it is apparent that Argentina has a larger economy than Uruguay. This is attributed to the larger size of Argentina as a country and its rich natural resource endowment. However, both countries have been able to fight poverty among their citizens. In both countries, the rate of unemployment is below 4 percent, a sign that living standards is above the world average.
This analysis has also demonstrated that both countries rely on each other for trade, with most of the exports from Uruguay finding their market in Argentina. However, it has come out that tourism sector in Argentina is much developed as compared to that in Uruguay. Socially, both countries share a lot. Football is the main sport in both countries. The two countries have had over 1000 players from each country playing in other countries, especially in Europe.
The music and foods eaten in these two countries compare very closely. Christianity is the main religion in both countries. This is because of their geographical closeness. From this analysis, it is clear that Uruguay and Argentina share many cultural, social, economic and environmental issues. The difference that comes out is due to difference in geographical size and leadership.
Works Cited
Aloian, Molly. Explore South America. St. Catharines: Crabtree Publishers Limited, 2007. Print.
Anton, Donald. Environmental Protection and Human Rights. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2011. Print.
Behar, Jaime. Cooperation and Competition in a Common Market: Studies on the Formation of Mercosur. Heidelberg: Physica-Verlag, 2000. Print.
Bernhardson, Wayne. Argentina: Uruguay & Paraguay: Includes the Falkland Islands and Chilean Patagonia. Hawthorn: Lonely Planet Publications, 2008. Print.
Conesa, Eduardo. The Argentine Economy: Policy Reform for Development. Lanham: University Press of America, 2007. Print.
Connolly, Michael B, and Melo J. De. The Effects of Protectionism on a Small Country: The Case of Uruguay. Washington: World bank, 2004. Print.
Cortés, María. Trade between New Zealand and Latin American Countries. Colombia: Universidad del Valle, 2005. Print.
Davis, William. Warnings from the Far South: Democracy Versus Dictatorship in Uruguay, Argentina, and Chile. Westport: Praeger, 2006. Print.
Fischlin, Daniel. Eduardo Galeano: Through the Looking Glass. Montréal: Black Rose Books, 2000. Print.
Frankema, Ewout. Has Latin America Always Been Unequal? A Comparative Study of Asset and Income Inequality in the Long Twentieth Century. Leiden: Brill, 2009. Print.
Galeano, Eduardo. Open Veins of Latin America: Five Centuries of the Pillage of a Continent. New York: Monthly Review Press, 2002. Print.
Graham, Carol, and Eduardo Lora. Paradox and Perception: Measuring Quality of Life in Latin America. Washington: Inter-American Development Bank, 2009. Print.
Lavrin, Asunción. Women, Feminism, and Social Change in Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, 1890-1940. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2010. Print.
Lustig, Nora. Coping with Austerity: Poverty and Inequality in Latin America. Washington: Brookings Inst, 2005. Print.
Mooij, Marieke. Consumer Behavior and Culture: Consequences for Global Marketing and Advertising. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications, 2011. Print.
Perry, Guillermo. Poverty Reduction and Growth: Virtuous and Vicious Circles. Washington: World bank, 2006. Print.
Richardson, Hazel. Life in Ancient South America. New York: Crabtree Pub. Co, 2005. Print.
Selby, Anna. Argentina, Chile, Paraguay, Uruguay. Austin: Raintree Steck-Vaughn, 2008. Print.
Tanzi, Vito. Income Distribution and High Quality Growth. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1998. Print.
Tulchin, Joseph. Garland. Argentina, the Challenges of Modernization. Wilmington: SR Books, 2002. Print.