Introduction
An enzyme is a substance formed by a living thing that functions as a catalyst to trigger a certain biological reaction. Enzymes reduce a reaction’s activation energy, which is necessary for a chemical reaction to occur (BIO-RAD, 2022). They achieve this by attaching to a substrate and holding it in a way that permits the reaction to happen more effectively. Biofuels are a type of sustainable energy made from biological sources. The most popular biofuels are biodiesel, biogas produced from organic wastes, and corn-based ethanol (Jean-Charles, 2022). The simplest way to obtain biofuels is by fermenting crops with high starch or fat content into ethanol, which can then be blended with gasoline to power vehicles. By maximizing the carbon cycle on the earth, biofuels contribute to a decrease in the carbon footprint of transport systems and other industries by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The enzyme cellobiase, often found in mushrooms, is broken by the cellulose’s glucose-glucose linkages. The synthesis of biofuel and ethanol now heavily depends on both cellulose and cellobiase (Jean-Charles, 2022). To make the cellulose conveniently available to the cellobiase, once it is added, the biomass is chopped into shreds and processed with heat and chemicals. The role of cellobiase in the experiment is engaged in the last stage of the conversion of cellulose to glucose (McMillan, 2017). The hypotheses assert as follows: the reaction rate with enzymes is more rapid than without enzymes, high temperature above optimum denatures enzymes, and low temperature below optimum deactivates the enzymes (Jean-Charles, 2022). Other hypotheses claim that pH changes and enzyme concentration also modify the layout of an enzyme’s active site. Lastly, enzymes speed up the reaction rate under optimal conditions.
Material and Methods
Each step was carried out following the instructions provided in the BIO-RAD Biofuel Enzyme Kit Manual (BIO-RAD, 2022). Cellobiase, in this case from shitake mushrooms, was first removed to experiment. Shitake mushrooms weighing approximately 2 grams were put into a mortar along with 4 ml of extracted buffer 10ml, according to the protocols (McMillan, 2017). The mushroom and buffer were then crushed into a slurry using a pestle. Four 1.5 ml micro-centrifuge tubes were filled with the semi-homogenized mushroom/buffer solution (BIO-RAD, 2022). These tubes were put into a micro-centrifuge, which rotated at a higher speed for three minutes to obtain a pure solid mushroom particle, then cellobiase was placed in a clean micro-centrifuge labeled “extract.”
After the isolation of the enzyme, it was possible to evaluate how temperature and time affected the enzyme’s activity hence detecting the enzymatic activity. The temperature labels for three test tubes were placed on them: 40ºC, 60ºC, and 80ºC. Each tube contained 1.2 ml of 0.1 M citrate buffer, 1.5 mm p-Nitrophenyl glucopyranoside, 1.2 ml of the substrate, and 0.3 ml of distilled water before being rapidly vortexed to mix up the constituents (McMillan, 2017). The remaining test tubes were filled with 4.5 ml of 0.1 M NaOH and labeled with the proper temperature and time (2, 5, 10, and 15 minutes).
The three tubes holding the buffer/substrate solutions were pre-warmed in their designated temperature tap water baths for around 2 minutes. Each tube was filled with 0.3 ml of a mushroom extract containing cellobiase, mixed thoroughly, and placed in the appropriate tap water bath. Then a timer was set up to keep track of reaction speed. 0.5 mL of the reaction solution was taken from each test tube in the tap water baths and put into the 12 designated stop reaction tubes that contained NaOH at times specified on the labels. The tubes were then vortexed. The reaction solutions were carefully transferred to the designated “stop” tube at the specified temperature and reaction duration.
Since p-nitrophenol absorbs light at 405 nm, that wavelength was utilized. Finally, each “stop” tube’s absorbance was measured and recorded.
Results
These tests aimed to investigate the behavior of enzymes and how temperature variations impact their activity. Studies on how temperature influenced cellobiase activity showed that the enzyme’s performance peaked at 60ºC. The amount of p-nitrophenol generated over time by cellobiase at 60ºC was much higher than that of products made at 40ºC or 80ºC, as seen in Figure 1, which supports this assertion. The experiment demonstrated that 60ºC was the most optimum for enzyme activity of the three temperatures evaluated.
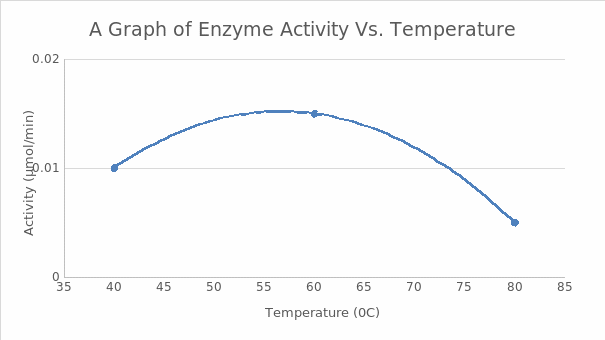
Figure 1 above shows a graph of the number of products against time at different temperatures.
Discussion
The experiment investigated how temperature affects the activity of enzymes. All the hypothesis is accepted because the data collected indicates that temperature significantly influences an enzyme’s work. Every enzyme has a certain temperature range where it is most active. The optimal temperature to break down cellobiase in this situation was around 60ºC. The reaction rate at 60ºC is rapid, and enzyme performance is greatly impacted if temperatures stray from this optimal range of 60ºC. There is a slow reaction rate at 80ºC since the enzyme are denatured by the high temperature (Jean-Charles, 2022). Enzyme activity is suppressed below 40ºC; hence the reaction rate in this condition is low. The most plausible explanation for this occurrence is that molecules have less kinetic energy at lower temperatures.
The future directions concur that enzyme activity decreases as soon as temperatures rise over the ideal temperature. The most plausible explanation for this phenomenon is that as temperature rises, molecules obtain more and more kinetic energy and start to vibrate erratically. Since protein structure is essential for activity, as the temperature rises, the quaternary and tertiary structures of the enzyme start to denature, entirely minimizing its capacity to operate. Therefore, for any enzymatic activity, it must take place at an optimal temperature.
References
BIO-RAD. (2022). Biotechnology ExplorerTM. Biofuel Enzyme Kit. Catalog Number 166-5035EDU. Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
Jean-Charles, F. (2022). Biofuel Enzyme Reactions. PowerPoint Slides.
McMillan, V.E. (2017). Writing Papers in the Biological Sciences 6th Ed. Bedford/St. Martins, Boston, MA.