Statistics of CHF
- Approximately 5.1 million people in the US have CHF (CDC, 2013);
- In 2009, one death from nine deaths resulted from CHF;
- Nearly a half of people with CHF die within five years after diagnosis;
- CHF costs the US $32 billion every year;
- There are about 550,000 new cases of CHF every year;
- People aged above 65 years are prone to the condition;
- There will be many cases of CHF because of the aging baby boomers;
- CHF affects people of all ages, including children.

Definition: CHF
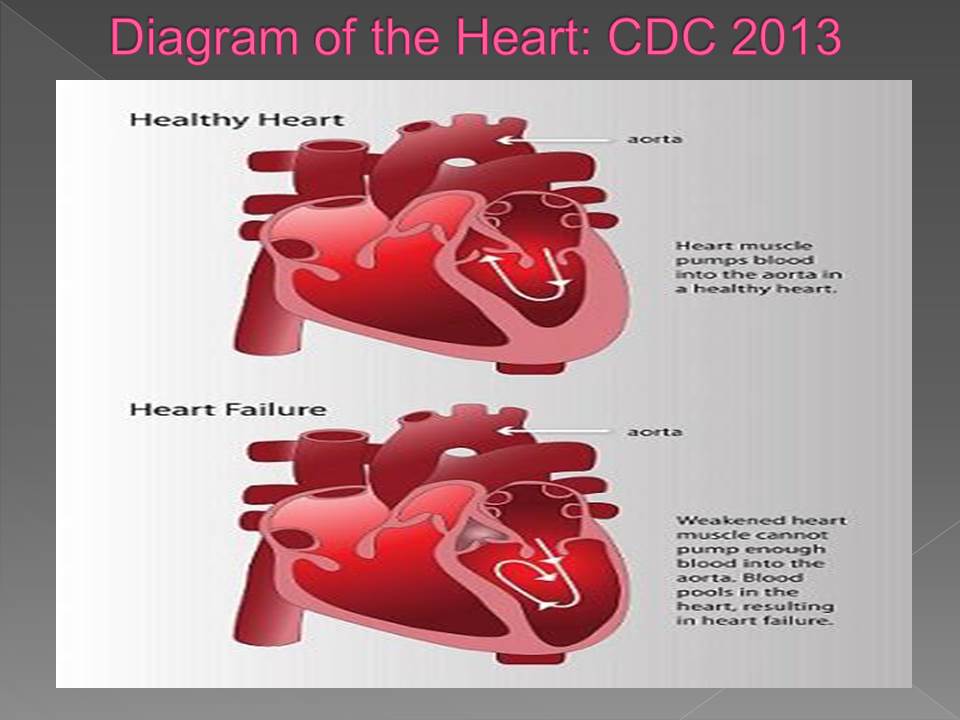
CHF is a condition that occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the entire body (CDC, 2013).
CHF can take the following forms:
- Left side heart failure – failure in the left ventricle;
- Right side heart failure – failure in the right ventricle;
- Systolic heart failure – failure in the ventricle to contract (systolic dysfunction) during pumping (Hildebrandt, 2006);
- Diastolic heart failure – failure in the ventricle to relax (diastolic dysfunction) because of stiff muscles.
Diagram of the Heart: CDC 2013
Causes of CHF
- Diseases (coronary artery disease) that narrow blood vessels and cause weaknesses in heart muscles;
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure;
- Heart attack, leaky or narrowed heart valves, and arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms).
Symptoms
- Shortness of breath, cough, fatigue, faintness, enlarged feet, liver, and abdomen;
- Weight gain and loss of appetite;
- Irregular breaths or heart beats (palpitations).

Risk Factors
High blood pressure, coronary heart disease, heart attack, diabetes, irregular heartbeats, smoking tobacco, kidney diseases, congenital heart defects, age, and lifestyle.
Complications
- Cardiac Cachexia (unintentional rapid loss of weight);
- Impaired kidney functions;
- Congestion or fluid buildup;
- Arrhythmias (Irregular beatings of the heart);
- Angina and heart attacks.

Test and Diagnosis
- Analysis of medical history for risk factors like high blood pressure, smoking, obesity;
- Diagnosis of physical signs, such as enlarged heart, abnormal breathing, swelling, fluid retention;
- Laboratory tests involve brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), blood sugar, sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes, thyroid function, complete blood counts;
- An electrocardiogram (ECG) or EKG test;
- Chest x-ray;
- CT scan;
- Angiography;
- Echocardiography;
- Exercise stress test.

Treatment and Drugs
- ACE inhibitors in cases of diabetes;
- Biventricular pacers (BVPs) for abnormal health rhythms;
- Angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs);
- Beta blockers;
- Restrict dietary;
- Diuretics;
- Aldosterone inhibitors;
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy (pacemaker);
- Implantable cardiac defibrillators (ICDs);
- Exercise training;
- Surgery (Health Central, 2013).

Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Stop smoking and excessive consumption of alcohol;
- Reduce salt intake;
- Stay active;
- For overweight patients, it is advisable to lose weight;
- Lower the level of cholesterol;
- Get adequate rest.
Preventative care
- Stay active;
- Manage high blood pressure;
- Control stress;
- Avoid certain herbs and supplements;
- Eat healthy food.

Coping and Support
- There is no know cure for CHF;
- Adhere to medication;
- Consult a physician before using any supplements or herbs;
- Surgery may be necessary for certain cases of CHF;
- Visit a physician regularly or have emergency number nearby;
- At the end-stage heart failure, discussion about palliative care and comfort with the family is critical for the patient (Emanuel and Bonow, 2011).

References
CDC. (2013). Heart Failure Fact Sheet. Web.
Emanuel, L., and Bonow, O. (2011). Care of patients with end-stage heart disease. In O. Bonow, D. Mann, P. Zipes & P. Libby (Eds.), Braunwald’s Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine (9th ed.) (p. 34). Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier.
Health Central. (2013). Heart Failure. Web.
Hildebrandt, P. (2006). Systolic and nonsystolic heart failure: equally serious threats. JAMA, 296(18), 2259- 60.