Introduction
Motivation is very important tool in our daily business life. Motivation means to influence someone to do something willingly to achieve any goal or objectives. Motivation is the mixture of wants, needs and drives within the individual which seek gratification through the acquisition or object. Marketers continually ask what ultimately promotes the consumer to purchase their product. Clearly consumer motivations are complex, and marketers must work vigorously to uncover them. According to motivation theory, environmental stimuli may activate the drive to satisfy an underlying need. Theorists like Abraham Maslow and Henry Murray have elaborate models of the way physiological and social needs influence behavior. That means an influencer or motivator influence or motivate someone to do something willingly according to the motivator’s will in order to achieve goal.
According to Assael, et. al. (2007), “[m]otivation can be defined as the inner force that drives individual to reflect goal-directed arousal and it is important to note that motivation plays a very crucial role in the current society as it is the psychological power that influences an individual to work towards a desired goal”. The purpose of this essay is to describe the motivational theories and the affect of it on the buyer or consumer. In the modern marketing system a marketer always tries to motivate the customers to buy his products. Marketing means to gain profit through customer satisfaction. So to achieve customer’s satisfaction a marketer always tries to know the need of the consumer or the intension of the customer, then provide information about the essential goods and services that the customer looking for. And finally sell the goods or services to the customer.
It should be mention here that marketers do not only satisfy the customers demand, they create demand of a product after knowing the customer’s detail information. That means the marketers transform a customers need into a product. And here we find the best use of the motivational theories. Motivational theories help to classify the customers to understand their need and demand. All the customers are not in same status or class, so they are different in characteristics, behaviour, choice, income level and so on. Motivational theories here help to understand the need and demand of people according to their class. In this essay two famous theories will be discussed, one is Henry Murray’s theory (primary and secondary needs) and another is Abraham Maslow’s theory (a hierarchy of needs). In this essay we will observe how the theories effect on the consumer behaviour and how marketers use the practical use of these theories.
Henry Murray’s theory
Henry Murray’s theory of need, however, based on the consumer behaviour. Murray believed that stronger needs are expressed more often over time and lead to more intense behaviour. The main potent of Murray’s theory is that he believes that personality as being driven by the secondary needs such as Achievement, Dominance, Affiliation and Nurturance. The extent to which each of these needs was felt by an individual shaped their personality and behaviour (Heffner, 2002). American psychologist Henry Murray developed a theory of personality that was organized in terms of motives, presses, and needs. Murray described a needs as a, “potentiality or readiness to respond in a certain way under certain given circumstances” (Wagner, 2008). Henry Murray’s Theory was focused on 2 types of needs, which are physical needs and psychological needs. Murray identified needs as one of two types:
- Primary Needs: Primary needs are basic biological and psychological demands, such as the need for oxygen, food, water, sex and avoidance of pain. Physical needs aim to reach a satisfaction of basic physical processes. Primary needs which are biologically based. Some examples of such needs are food, water, air, sex, avoidance of pain.
- Secondary Needs: Secondary needs are acquired or learned, either derived from primary need or inherent on person’s psychology. For example- One can feel the thirst of Pepsi or one can feel the hunger of a Hot-dog (Murray, 2004, p.233). Secondary needs which are either derive from our biological needs or are inherent in our psychological nature. Examples of such needs are achievement, recognition, acquisition, dominance, aggression, autonomy affiliation, rejection, nurturance, play, and cognizance.
Now we will try to construct a practical aspect of this theory. Now a day’s people prefer the amusement parks. The need of the amusement park to satisfies the following variety of needs.
- Psychological need driven- Convenient to satisfy the philological need in leaser time.
- Preparation problem avoidance- people wants to pass their leaser time smoothly. They are unwilling to take the preparation problem to satisfy their need and try to full utilize their time.
- Socially Driven- People seek friendly environment to get variety of fun, food and drink to pass time. And people are more habitual to go to park.
- Experience Driven- To arrange the items of amusement by oneself causes many problems. And people get a variety of amusement in amusement park.
- Investment Driven – To prepare a self or family amusement system is costly. Besides this it is not possible to satisfy the variety of need of one’s family. So, people can get variety of need with a less cost in a park.
This practical example supports the Murray’s theory. As this motivation theory, needs don’t operate on their own to influence behavior. Rather, needs operate through motives. In simple terms, motives are thoughts and feelings that direct someone to enact behaviors which will satiate his/her need. According to Murray, people feel the need when it is motivated. Here the peoples are motivated form the variety of other environmental influencer. In another way motivation creates the need to the people. Here people motivated by amusement or refreshing need, which would ultimately direct to find something to get amusement or pleasure.
Critical analysis on Murray’s Theory
Here all the needs are individually important but they are interrelated and one has effect on the other. By this theory, Murray shows that people first derives by the basic need but the preference or the demand derived by the acquired or learned knowledge, either derived from primary need or inherent on person’s psychology. For example: one may feel hungry. To satisfy his hunger one needs food. When one goes to a shop for food, surely they will find that the food preference is not same with each other. The food preference differs from culture, income, one’s status, psychology, etc. To understand the consumer psychology or behaviour Murray’s need theory plays an important role. But the fact is this theory gives the information about the need of the customers. Do not exactly mean the demand of the consumer. Consumer buying behaviour is very much complex and we find that the preference comes from the amalgamation of these needs.
So from this theory we can know the reason of consumer’s motivation or how we can motivate the customers. But to know the consumer behaviour it is not so much helpful. Rather the research on consumer’s income, culture, technology, demographic condition will be more helpful to understand consumer’s behaviour. All the business is growing up centering the customers. Manufacturer are very much concern with their customer behaviour. Marketing means now profitable relationship with the customers. Most of the marketing companies are now researching on consumer behaviour. Here the need theory has a great use. Again sometimes one need influences another and sometimes one need make contrast with another need. So it has a great impact on the consumer buying behaviour, choice and preference. Suppose the need for Aggression may conflict with the need for Nurturance when overly controlling behavior drives away friends, family, and romantic partners. On the other hand need of Recognition may influence the need of Achievement.
Beside this “Murray contended that environmental forces played a significant role in the exhibition of the psychogenic needs. He called the forces “press,” referring to the pressure they put on us that forces us to act. He further argued for a difference between the real environmental forces, alpha press, and those that are merely perceived, beta press.” (Heffner, 2002)
This also proves that the need theory singly cannot estimate the consumer need or motivate customer. There are other factors that are influencing consumer’s behaviour.
Abraham Maslow’s Theory
Human motivation, management training, and personal development theories are developed by Abraham Maslow through the Hierarchy of Needs model in 1940-50’s of USA. The most popular and well-known approach to human motivation is based on the research of the psychologist Abraham Maslow. He presented the idea that there is a hierarchy of needs in man, ranging from the lower-order physiological drives (e.g. thirst, hunger and rest), through safety needs (e.g. shelter, protection and security) and affective needs (e.g. affection, friendship, love and acceptance), to the higher-order needs for self-esteem (e.g. prestige, success and accomplishment) and self-actualization (e.g. self-fulfillment and enriching experiences).
The lower-level needs are considered to dominate the higher-level needs. That is, consumers must satisfy lower-level needs first, before they begin to pursue higher-order needs. According to Maslow the highest level of need is related to self-actualization, i.e. the desire to live up one’s full potential and to maximize the use of skills and abilities. However, this need for self-actualization only becomes activated if all four of the lower-level needs have already been satisfied. Maslow postulated that there exists a deprivation of soma human needs which induces the need to gratify it and that process of need gratification is activated to satisfy the hierarchical needs (Wahba & Bridwelt 1976. p. 515). In Maslow’s theory there are five consecutive needs that motivate a person chronologically. They are Self-Actualization, Esteem Needs, Social Needs, Safety Needs and Physiological Needs. Indeed, Maslow’s ideas surrounding the Hierarchy of Needs concerning the responsibility of employers to provide a workplace environment that encourages and enables employees to fulfill their own unique potential (self-actualization) are today more relevant than ever.
Diagram: Maslow’s Hierarchy of need
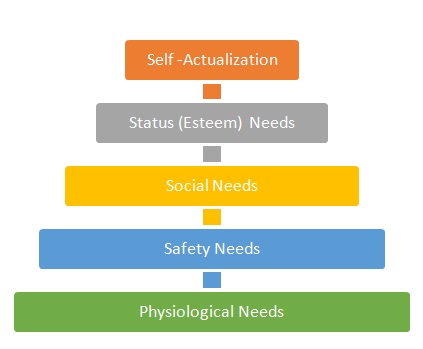
From the above discussion it is found that how step by step the need theory motivates a people and changes his behaviour. Here we find the practical implication of Masslow’s theory. However, the major problem with Maslow’s theory is lack of empirical and theoretical evidence to support its basic assumptions (Wahba & Bridwelt, p.514). Here we just find the direction of the need and how a consumer can fulfil the need. And it does not show any specific direction of choice as stated in Henry Murray.
Critical analysis on Abraham Maslow’s theory
Maslow’s theory has a great importance to motivate people step by step. Thus it is still popular to many firms and businesses. It considers the stage of people’s status and shows his needs and demands as well as the way to motivate him. Specific criticisms of Maslow’s hierarchy theory include its acknowledged strength of being sufficiently generic to cover most lists of human needs, means that the concepts are too general. Whether needs conform with Maslow’s proposed prepotency hierarchy has been questioned and even Maslow questioned the hierarchy upon which his theory is based. Another hierarchy-related criticism is that it cannot be tested empirically as there is no way to measure precisely how satisfied one need is before the next higher need becomes operative.
Furthermore, Maslow’s theory does not take into account heroic and altruistic behavior as other theories can do, nor incorporates other important needs such as dominance, abasement, play, and aggression (Witt & Wright 1992) that are included in Murray’s classification. William James (1892/1962) and Mathes (1981) have given a proposal on the hierarchy that has three levels of human need. The hypothesized levels of James are material (physiological, safety & security), social (belongingness, esteem need), and finally spiritual. On the other hand three levels of Mathes that he has proposed are physiological, belongings, and self-actualization, he expressed security and self-esteem as unwarranted (Maslow, 2004, p.226). This statement expresses the importance of the theory as well as criticizes. The real fact is the theory was given on the basis of that time. But time has gone a long way and the theory may face little change or problem.
“One of the many interesting things Maslow noticed while he worked with monkeys early in his career was that some needs take precedence over others. For example, if you are hungry and thirsty, you will tend to try to take care of the thirst first. After all, you can do without food for weeks, but you can only do without water for a couple of days! Thirst is a “stronger” need than hunger. Likewise, if you are very very thirsty, but someone has put a choke hold on you and you can’t breathe, which is more important? The need to breathe, of course. On the other hand, sex is less powerful than any of these. Let’s face it, you won’t die if you don’t get it!” (Maslow, 2006).
Here, the study finds that the consumer behaviour is affected with some other external factors. So, to understand the consumer behaviour we have to think some other factors. Let see what we find from the statement below.
“Though Maslow’s hierarchy makes sense intuitively, little evidence supports its strict hierarchy. Actually, recent research challenges the order that the needs are imposed by Maslow’s pyramid. As an example, in some cultures, social needs are placed more fundamentally than any others. Further, Maslow’s hierarchy fails to explain the “starving artist” scenario, in which the aesthetic neglects their physical needs to pursuit of aesthetic or spiritual goals. Additionally, little evidence suggests that people satisfy exclusively one motivating need at a time, other than situations where needs conflict.” (Maslow, 2004)
So it has been found that there are some other factors that are influence or motivate the consumer. These factors are more vital then the need statement. The need theory is not enough to understand the consumer behaviour. But in many cases the need theory factors plays important role to motivate customers.
Conclusion
Need theories are important tools to understand customers need and demand. But the theory alone does not understand the consumer need. Beside this the need theory is actually helpful to motivate the employee, entrepreneur, business man, etc. Now a day’s buyers are buying behaviour is very complex. They take a buying decision considering many other factors. The best way to know the consumer behaviour and to motivate them is to know consumers culture, income level, attitude, market condition, etc. Witt and Wright (1992) suggest at the theoretical level expectancy theory enables many of the existing concepts in the study of consumer motivation to be incorporated within a single theoretical framework i.e., need theories such as Maslow and Murray but the emotional aspects of consumer motivation, for example as in case of tourist motivation, the needs which instigate the desire to travel in the first place, the decision making involved in choosing whether to do on holiday and, if so, where is not provided in the models provided by Maslow or Murray.
So in conclusion it can be said that even if the need theories are highly criticized for lacking strong empirical support one should not forget that both the above theories were derived from clinical learning and practice. So they may not have correlations between each other as any study will look for, but are causal models. Moreover their validity lies in their acceptance in management practices especially is explaining consumer motivation and other allied areas of marketing like advertising and positioning of products. Hence these theories cannot be rejected for their lack of empirical support as they provide huge assistance to explain human personality and their behaviour.
References
Alan Chapman review and other material. (1995-2008). Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Abraham Maslow original Hierarchy of Needs concept. Web.
Heffner, L. Christopher. (2002). Personality Theory. In Chapter 7: Trait Theory. All Psych and Heffner Media Group. Web.
Huitt, W. (2004). Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, Citation: Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Educational Psychology Interactive. Valdosta, GA: Valdosta State University. Web.
Maslow, Abraham. (2004). A hierarchy of needs, Motivation, personality and Emotion. In Chapter 8. Part-3.
Maslow, Abraham. (2006). Biography. Web.
Murray, Henry. (2004). Primary and Secondary needs, Motivation, personality and Emotion. In Chapter 8.
Wagner, Van Kendra. (2008). Murray’s Theory of Psychogenic Needs. about.com. Web.
Wahba, A., & Bridgewell, L. “Maslow reconsidered: A review of research on the need hierarchy theory.” Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 15, 1976, pp. 212-240.
Witt, C. & Wright, P. Tourist Motivation: Life after Maslow. In P. Johnson and B. Thomas (eds.), Choice and Demand in Tourism, (pp. 33-55). London: Mansell, 1992.