Introduction
Trade involves the supply of goods and services. For trade to be facilitated there must be a supply and a demand of goods and services. The amount of resources that individual and firms are willing and are able to commit in buying of goods and services produced in the economy are called consumer consumption.
It takes two angles, from a micro economics point where there is consideration of individuals and firms and from a macro economics when the entire society is considered. The remains after consumption is the saving that an economy, individuals, or firms will save (Carrick 33). This paper analyses the effects that tax cut can have on consumption and investment.
Consumption V/S Savings
The amount of income that a consumer gets at one particular point can be put in different use. It can be consumed or it can be saved. Income is the total amount of resources that individuals get. It is a product of all earnings. The following equation shows the elements of income (I);
I = savings(S) + consumptions (C)
I = S + C
Savings are utilized in various ways with the most common one being for investing in various projects of the economy.
So;
Savings (S) = Investments (I)
S=I
At constant income, if consumption increases, then savings will reduce and the rate of investments in the country will reduce. On the other hand, if consumption decreases, there is an increase in investments.
When an income of individual or firm increases, the effect on investment is dependent on the marginal rate to consume; if an increase leads to a proportionate increase in consumption, then the effect is the same to investment (Mishkin 12)
The diagram below show the connection between saving rate and consumer spending
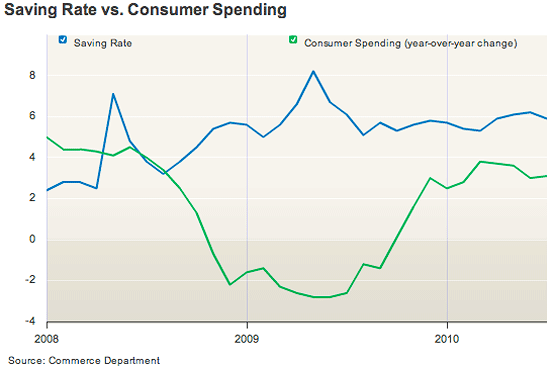
Factors affecting consumer consumption
There are different factors which affect the rate of consumption of an individual or firms; they include taxation, government expenditure, state of the economy and future expectations of the individual or firm.
The following table shows the rate of expenditure between 2005 and 2008 in the United States.
The valuation is as a result of:
Taxation
The government gets the greatest percentage of its income from taxes paid by tax payers in a certain country. Taxation is a policy whereby citizens or residents of a country contribute money for social services to the government through a well coordinated taxation policy.
Taxation affects the consumption rate of an individual as well as firms. During campaigns of 2008, Senator John McCain’s promised to reduce taxes as a way of reviving the economy but one wonders how the economy will grow if the government has no money. No one likes paying of taxes, however it is an evil that we have to live with (Straczynski 22).
Tax Cuts
Different countries adopt different taxation policies, however tax cut take the same route; it can result from raising the minimum amount that is taxable in an economy, reducing the percentage of taxation or even eliminating the entire amount of taxes. Some countries offer tax credits and remission to areas that they would like to give this percentage.
There are some cuts which are meant to cut across the entire economy and some are on a specific industry. Whichever the method, the end result is a reduced tax payable from the trader, individual or company. Governments play an important role in controlling how their country’s economy fair. In a broader perspective, they use monetary and fiscal policies for contraction or expansion reasons.
When regulations are made, they may hurt or benefit the economy in short term and long term. Tax cut is an expansionary fiscal policy adopted with the aim of reviving an economy.
Tax Cuts in the Past
There has been three times that tax cuts have been implemented by the government to facilitate economic growth, in all the phrases there has been success. In 1920’s, there was the Harding/Coolidge cuts, then in 1960’s there was president Kennedy cuts and the Reagan cuts of the 1980s. All the three cuts have proved to be successful. They have followed the same trends that facilitated revival of economies by ensuring that people are given a reason to invest and spend in their economy.
Effects of Tax Cuts
In cases of a tax cut, then the people will have more funds to use, their disposable income will increase. Disposable income increase means an increased consumption. In the recession period, consumption in the economy leads to an aggregate demand of goods and services. Spending will induce money in the economy, which in turn will affect the economy positively.
If expenditure is facilitated, then chances of recovery are higher. Businesses on the other hand will have adequate resources for business expenditure (in terms of investments). In all economies personal Consumption Expenditures, account for the largest amount of government revenue; thus when facilitated it is likely to lead to a quicker recovery from recession.
Local Investments and Foreign Direct Investments
One of the hindrances of foreign investments is high taxes especially if the company is a foreign company. If taxes rates are reduced, then investors will be attracted by the favorable tax t-rates and invest in the economy. Investments increase the rate of country development, there is an increased employment, a larger tax net is created and increased consumer choices.
Local investors are also to benefit from tax cuts since they will feel attracted to invest in their own economy since the taxes they are paying is manageable. The overall will be an economy that can meet its own demands in terms of employment, products and services.
International Trade
The world is undergoing an era of globalization where different countries are involved in trade among each other. As economies expand and trade with each other with assistance of improved technology, the world is becoming a global village. Economies are joining efforts to develop an economic, political or/and social block as they prepare to play a role in the global environment.
When trading a country with a comparative advantage is likely to dominate the market since it is able to produce more goods at relatively low prices. When calculating the cost of production, there are fixed cost and variable costs. This will set the price that the commodity will be sold whether in the national or international market. When tax rates are reduced, then the cost of these products are reduced; they can then compete more favorably than the same good from countries which has no tax cuts.
Negative Effects of Tax Cuts
Government use taxation money to finance its projects; if the finances are reduced, then priority areas will be undertaken first. One of the areas that are likely to suffer is government participation in businesses directly. This is likely to come in terms of privatization as they fetch for money to finance deficit created by reduced taxes or it may be through not involving in trade. When it sells public companies to individuals, then there is a facilitated competition (Ludvigson 45).
Personal Opinion
Taxation is a macroeconomic tool that is utilized by the government to ensure that its controls the economy. It gives the government revenue to invest in different sectors of the economy and provide social amenities. When making a decision of whether there should be a tax cut or not, the government should analyze the conditions of the situation. When tax cuts are administered, there is an increased spending in the economy and the resultant will be facilitated trade which on the other hand leads to larger tax base.
In my opinion, tax cuts can revive an economy however its effectiveness and efficiency is only in the short term. They also need to be implemented timely since there are times that they can yield good results (Wilcox 21). There are times that they can injure an economy and make it worse.
Conclusion
The amount of resources that individual and firms are willing and are able to commit in buying of goods and services produced in the economy are called consumer consumption. It takes two angles, from a micro economics point where there is consideration of individuals and firms and from a macro economics when the entire society is considered. Consumer consumption affects savings and investments in a country. Tax cuts can benefit an economy however it can also injure it.
Works Cited
Anon. Average annual expenditures of all consumer units and percent changes, Consumer Expenditure Survey, 2005–07. Web.
Carrick, James. “Consumer Spending Review.” Credit Control 29.1 (2008): 48. MasterFILE Premier. EBSCO.
Lahart, Justin. Consumer Spending Grows Modestly. 2010. Web.
Ludvigson, Sydney C. “Consumer Confidence and Consumer Spending.” Journal of Economic Perspectives 18.2 (2004): 29-50. EconLit with Full Text. EBSCO.
Mishkin, Frederic S. “Consumer Sentiment and Spending on Durable Goods.” Brookings Papers on Economic Activity 1 (1978): 217-232. Business Source Complete. EBSCO.
Straczynski, Stacy. “Consumer Spending Jumps 1.3 Percent in Aug.” Sales & Marketing Management 161.6 (2009): 136. MasterFILE Premier. EBSCO.
Wilcox, James A. “Consumer Sentiment and Consumer Spending.” FRBSF Economic Letter 2008.19 (2008): 1. MasterFILE Premier. EBSCO.