What is Culture?
- Culture reflects the way people.
- Thus, we have cultural diversity among various cultures.
- We experience cultural diversity when different groups of people live in a similar social structure. These differences arise from various sources like:
- Ethnic;
- Gender;
- Racial;
- Socioeconomic;
- Language/Nationality;
- Religion;
- Handicap/Mobility;
- Education;
- Age;
- Educational qualifications.


Culture in Healthcare
There are various healthcare belief systems which:
- Classify and group health problems;
- Define the role of doctors or traditional healers;
- Identify causes of illnesses using specific models.

The Western Culture and Healthcare Beliefs
- Drugs have power over nature;
- Standardization of treatments for similar ailments;
- Medicines are from scientific discoveries;
- Find solutions to emerging illnesses;
- Act fast;
- Medicine comes from nature;
- Time heals everything i.e. wait and see;
- Every illness is unique;
- Have beliefs in treatments;
- Have diverse approaches to treatments such as consulting oracles, temples, and other shrines.


Cultural Competence for healthcare providers
Healthcare providers must be sensitive to ways in which cultures and beliefs influence healthcare provisions to patients.
Cultural competence refers to congruent practices, behaviors, and attitudes that professionals apply to work effectively in different cultures(Cross et al, 1989).
Cultural competence starts by:
- Self-assessment;
- Appreciating diversity;
- Controlling difference;
- Attaining the cultural knowledge of others;
- Adapting to various cultures.

Achieving Cultural Competence
Cultural competence is a learning process:
- Cultural Destructiveness;
- Cultural Incapacity;
- Cultural Pre-Competence;
- Cultural Proficiency.

Explanations for the model
- Cultural destructiveness: this acknowledges only a single culture and outlaws others.
- Cultural incapacity: it promotes separate ideologies (racism, prejudice, unfair practices etc).
- Cultural blindness assumes that people are alike, and one culture can substitute other cultures. It only serves the dominant group.
- Cultural pre-competence promotes learning and understanding, gaining new ideas, approaches, and considering needs of others.
- Cultural competence shows active consultation, commitment and applies wider varieties of practices.
- Cultural proficiency reflects a high-level of cultural differences appreciation, pro-active cultural engagement, and promotes learning of new cultures.


Where to start
- Healthcare providers should let patients know that they want to improve their health statuses.
- Healthcare providers must adopt the attitude of honesty and acceptance.
- Healthcare providers must engage patients directly.
- It is important for healthcare providers to have knowledge of the general culture.

At the individual level
- Identify one’s own culture;
- Challenge one’s own culture, beliefs, and assumptions;
- Develop empathy;
- Recognize differences in cultural beliefs.
In order to achieve these, the healthcare facility must change its:
- Policies;
- Administrative practices;
- Service delivery;
- Involve all stakeholders and communities.

Communication and Interaction
- Understand both verbal and non-verbal cues;
- Avoid stereotyping;
- Tolerate ambiguous situations;
- Adapt behaviors within a given cultural context;
- Encourage intercultural interactions;
- Be modest.

Behaviors to enhance Cultural Competence in healthcare delivery
- Recognize roles of cultural beliefs, attitude, values, actions, and behaviors on health conditions and treatments.
- Integrate cultural awareness into medical procedures and practices.
- Incorporate culture into all areas of healthcare provisions and other professional practices.

The need for an Interpreter
There are many immigrants in the US and some of them do not understand English. Hence, the need for caregivers to have interpreters.
Interpreter must meet some qualifications like ability to be:
- Comfortable in care facilities;
- Maintain confidentiality;
- Know/understand multiple languages;
- Understand conditions in the care facilities.

The Roles of the interpreter
The role of the interpreter to the patient must be clear. The interpreter should:
- Translate communications to both parties;
- Act as a culture broker;
- Advocate for the patient.
Advantages of Cultural Competence in Healthcare delivery
- Enhances equity in healthcare provisions;
- Eliminates cases of delay in gaining access to healthcare services;
- Improves health literacy among patients;
- Overcomes communication barriers and understanding between patients and care providers;
- Enhances safety of the patient and quality of healthcare;
- Improves the image of the healthcare facilities;
- Promotes better practices in the healthcare sector;
- On the other hand, cultural incompetent in healthcare provision has substantial risks to all stakeholders (Steele, 2010).


Overcoming communication barriers result into
- Clear expectation from the patient and the caregiver;
- Low cases of medical errors;
- Reduced cases of hospitalization rate especially in preventable conditions;
- Enhanced patient’s satisfaction;
- Provision of recommended treatment;
- Increments in follow-up cases.

Diversity Competency Model
This is useful in nursing. It main elements include:
- Drivers;
- Linkages;
- Cultures;
- Measurement.

Working together
- Different cultures working together.

References
Cross, T., Bazron, B., Dennis, K. and Isaacs, M. (1989). Toward a Culturally Competent System of Care. Washington, D.C: Georgetown University.
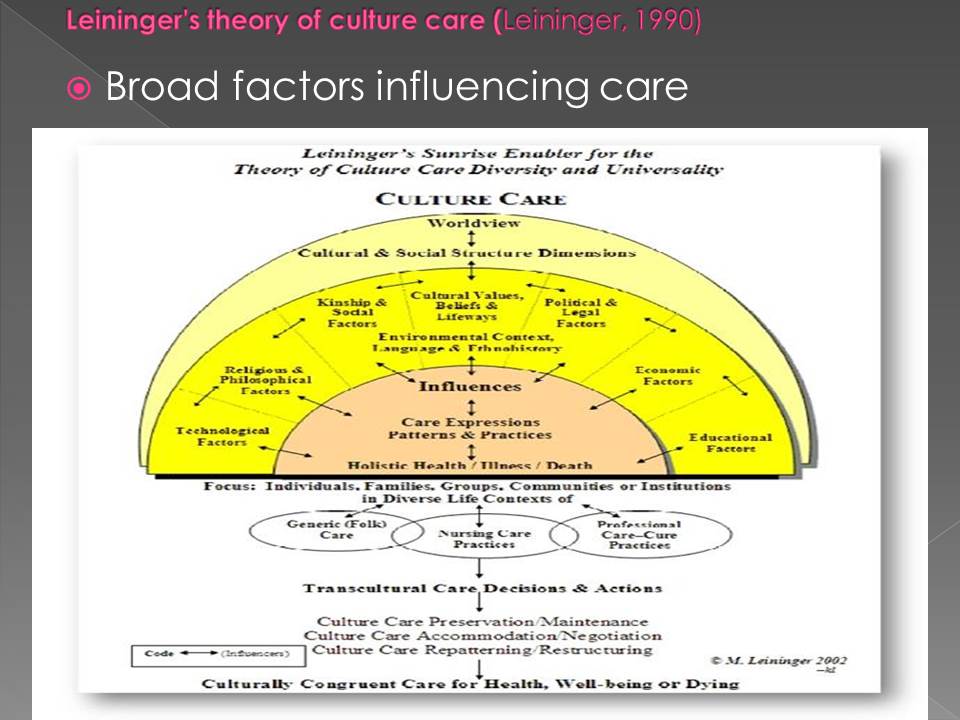
Leininger, M. (1990). Ethical and Moral Dimensions of Care. Detroit, MI: Wayne State University Press.
Steele, C. (2010). Whistling Vivaldi: And Other Clues to How Stereotypes Affect Us. New York : W. W. Norton & Company.