What is Biodiversity?
Biodiversity is the variability of life across all the living organisms found on earth. Within the ecological research, biodiversity forms the basis to which all the living organisms exist, especially about each other. A rich diversity means the capacity of the natural environment to have many living organisms to thrive (What is biodiversity?, 2016). The availability of many living organisms within an ecosystem enhances the capacity of nature to recuperate from climatic change.
The importance of biodiversity
Biodiversity is important because a rich blend of living organisms within an ecosystem allows the facilitation of processes such as purification of air, water, and soil. Whereas the natural environment loses too much of its diversity, chances are that the indigenous species and varieties of plants and animals would deplete. This affects the quality of air and water, thereby limiting the quality of life for humanity, plants, and animals (What is biodiversity?, 2016). Besides, the knowledge on biodiversity helps scholars to identify and understand the correlations between the different life forms on earth, thus inspires scientific research on improving the quality of biodiversity.
How biodiversity is measured
Biodiversity is measured in terms of attributes that explore the quality of nature; richness and evenness of the living organisms within an ecological niche. Whereas richness implies the quantities or clusters of genetically related individuals, evenness represents the proportionality of the functional groups found within an ecological niche (Principles of vegetation measurement & assessment, 2016). According to Purvis and Hector (2000), most vegetation surveys express richness in terms of the number of species or varieties found within an ecosystem. An ecosystem with low evenness, virtually, indicates that a few varieties or species are found in an ecosystem.
Extinction and what is causing it today
Extinction indicates an evolutionary process, which gradually leads to the deterioration of species of living organisms. When living organisms become extinct, they face a series of genetic heritage loss. Through evolution, species may change into other organisms in the process of adapting to gradual environmental alterations (The extinction crisis, 2016). Natural extinction is a biological process, which might not be misconstrued to mean a negative process that might be accepted as such. Changes in the natural environment might be unavoidable, and the living organisms tend to adapt to those changes to survive; this process is responsible for the extinction.
The Endangered Species Act
Passed in 1973, the Endangered Species Act is important legislation for conserving and protecting the species under threat as well as their habitats. By providing the international community with monetary aids and incentives to advance and maintain biodiversity, the Act offers a mechanism for safeguarding nature (Biodiversity, 2016).
Some of the most and least diverse species in my local area
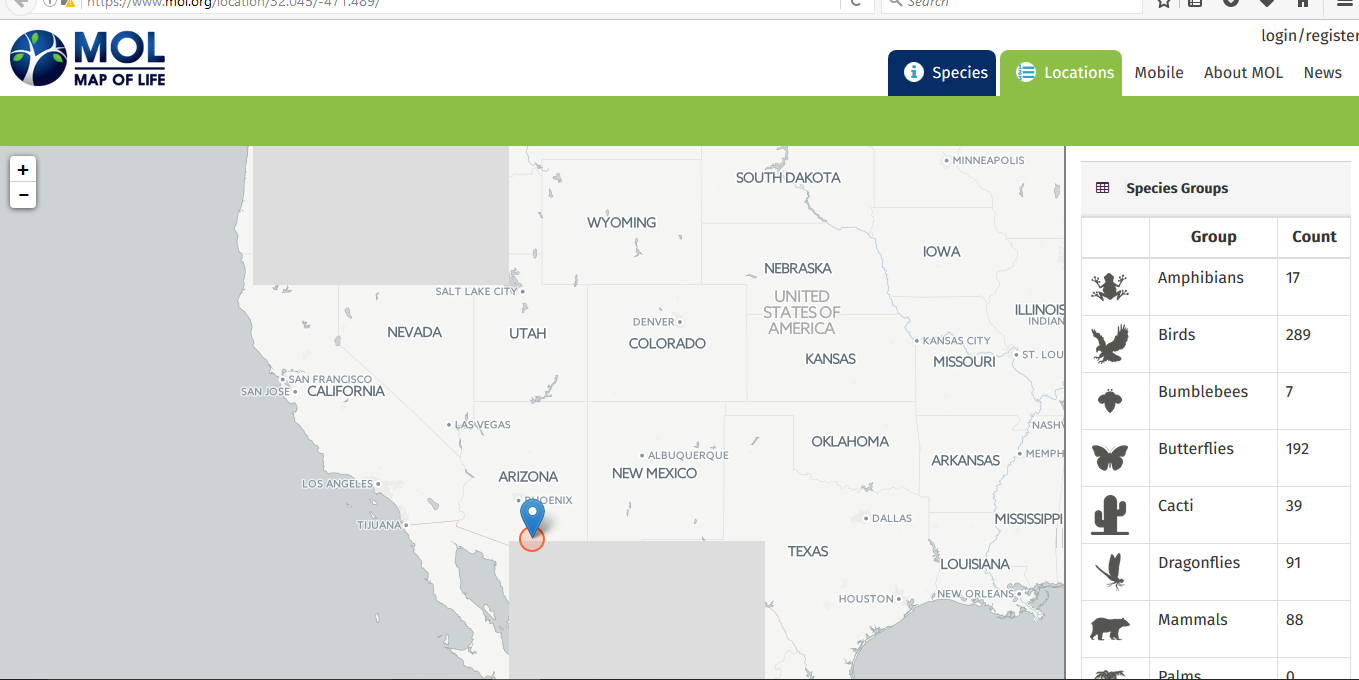
Some of the most diverse species in my local area are birds, fish, and butterflies, while some of the least diverse species are palm plants, coral reef, amphibians, algae, cacti, and crustaceans. In my local mapping provided here below, species are grouped in terms of their richness and vastness within the map of the lie.
What I can do as an individual to help slow the loss of biodiversity
As an individual, I can do several things to help slow down the loss of biodiversity. Among these are practicing cover cropping, diversifying my garden, enhancing consumer consciousness, limiting pesticide use, and lobbying the government to lead the fight against habitat loss.
References
Biodiversity. (2016). Web.
Principles of vegetation measurement & assessment and ecological monitoring & analysis. (2016). Web.
Purvis, A. & Hector, A. (2000). Getting the measure of biodiversity. Web.
The extinction crisis. (2016). Web.
What is biodiversity? (2016). Web.
Where in the world are frogs? (2016). Web.