Human capital is a valuable organizational resource. A firm’s routine operations are dependent on its policies, especially those governing personnel issues. The implemented human resources (HR) procedures can impact the retention of quality staff with suitable skills to drive growth, quality, productivity, morale, and innovativeness. A significant emphasis is placed on employee recruitment, development through training, and motivation – competitive remuneration and incentives. HR procedures are also critical in addressing workplace issues. This paper presents a statement of management philosophy and recommends to the Deloitte Board of Directors HR policies and procedures that could help the consulting firm improve its human capital capacity across its business units.
Overview of the Organization
What the Organization Does and Its Organizational Structure
Deloitte is a leading management consulting firm headquartered in the UK. It comprises firms that operate under the Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited (DTTL) brand. It offers “business consulting, human capital development, risk and financial advisory, strategy and operations, and technology integration” to clients in diverse industries, including aerospace and technology (MarketLine, 2017, p. 10).
Core among its HR consulting services is talent, productivity, and change management. Its strategy and operations portfolio includes business model change, strategic alliances, and supply chain development (MarketLine, 2017). In the technology industry, the primary services offered by Deloitte are advanced analytics and information management.
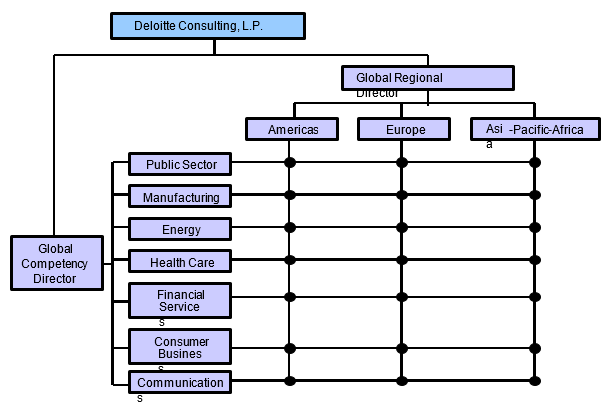
The firm’s organizational structure is built on two elements: geography and service line. It comprises a network of independent companies that operate under the same brand and standards. Under the member firm structure, firms are organized on a geographical basis or country, such as the US, Canada, and India (Deloitte, 2019). The structure gives competitive advantages locally, regionally, and globally.
The company has six service lines, which include “audit, consulting, tax and legal, financial advisory, risk advisory, and enabling areas” (MarketLine, 2017, p. 3). Deloitte, US, has a board of directors who include the CEO (Cathy Engelbert), the chairman (Mike Fucci), and several executives overseeing functions in one region who in turn report to the global director. A typical organizational chart for Deloitte is shown in Figure 1.
Organizational Operation and Task/Work Project Accomplishment
Deloitte operates using the member firm structure or model. Individual companies benefit from the expertise of others, brand reputation, and shared methodologies and can consult within the network (Deloitte, 2019a). The partners are organized based on the region of operation and are subject to domestic regulatory policies. They operate as independent companies that collaborate under the same brand, structures, and standards with a regional director (Deloitte, 2019a). Member firms have to adhere to Deloitte’s practices. They are required to uphold the brand reputation, align their strategies with those of DDTL, and follow a predefined set of professional standards and guidelines. Regional directors have to consult with Deloitte global on important decisions.
Given the network structure in Deloitte, tasks, or work projects are not accomplished in a linear, stepwise fashion. Instead, managers irrespective of position, rank, or location participate in planning, organizing, and controlling tasks (Armstrong, 2016). However, their participation in these functions is dependent on the project and opportunity available in its service lines. Planning involves laying down objectives for a task, while organizing entails identifying and assigning activities. Controlling encompasses monitoring work performance – a core function of HR.
Domestic or International
Deloitte is composed of firms that operate under the DTTL (Deloitte Global) international brand. Therefore, the company is an international organization with operations over 135 countries and regions such as the Americas, Europe, and Asia-Pacific (Deloitte, 2019a). In the US alone, Deloitte has 80 offices, including the one in Dallas. Member firms serve clients from a region in which they are located.
Competitors
Deloitte is a major player across most of its business units. In 2017, its revenue was $38.8 billion compared to PWC’s $37 billion (Deloitte, 2019a). Deloitte’s competitors include PWC, McKinsey & Company, EY, and KPMG. In auditing, PWC is considered a global leader while Deloitte comes in at number four. EY is a strong competitor in tax consultancy. Deloitte emerges as a top player in advisory services. Small, low-cost consulting firms operating in emerging economies, such as China, also eat into Deloitte’s global market share.
Factors Critical to Success in this Organization
The integration of communication technology into Deloitte’s systems is a significant success factor. I believe that new software and advanced analytics can improve employee efficiency and day-to-day operations at the firm. Additionally, adopting a web video technology (teleconferencing) in its offices would support communication, allowing executives in different locations to exchange ideas and make decisions. The approach would also reduce operational costs. Implementing a non-hierarchical organizational structure would ensure that the staff in member firms are connected to Deloitte’s business strategy and executive management.
Organizational Culture
Deloitte strives to give a distinctive culture and approach to work. It has a program dedicated to innovation by urging its staff to think differently during occasions like the iSpace (Deloitte, 2019b). Another aspect of the culture at Deloitte is striving to have an impact on clients, employees, and society. It also focuses on developing expertise and network necessary to offer technical/business leadership to its diverse clients.
How Information is communicated
Communicating information at Deloitte can be understood based on its organizational structure. In terms of geography, member firms in Texas would report to the Dallas executive director. One channel of communication is the hierarchical reporting lines established between the office and service line managers and partners. However, sometimes analysts or consultants can work directly with senior management (Deloitte, 2019b). Thus, information from stakeholders can be communicated promptly to the directors through interdependent structures.
Working for this Organization
People would aspire to work for Deloitte for three reasons. First, the company offers excellent opportunities for learning and career development – mentoring, coaching, and formal training – that would enable one to realize his/her dreams (Deloitte, 2019b). Second, Deloitte fosters teamwork and diversity that are critical in acquiring cultural competency. Third, the company is a reputed brand with standardized work procedures globally, competitive pay, and enticing rewards.
Policies
Statement of Management Philosophy
The management philosophy statement presented would inspire talent and help Deloitte, Dallas, achieve higher performance. The suggested vision statement for the firm is to foster creativity and innovation required to deliver excellence across its business units. The hiring mission statement is establishing workplace conditions ideal for talented staff in member firms to grow in their career and excel in their work. The core HR values proposed for Deloitte, Dallas, are hiring the best talent irrespective of their background, nurturing cultural diversity, and emphasis on collaboration as a competitive strength.
The Rationale for Policies and Procedures
To realize the organizational goals of improved productivity, quality, innovativeness, and staff morale, and profitability in 2019 and beyond, Deloitte needs to adopt relevant HR policies and procedures. The rationale is to develop generalized guidance for specific personnel issues, including recruitment, promotion, development, and dismissal (Armstrong, 2016). Therefore, HR policies inform decisions about a firm’s workforce, while procedures specify precise actions or responses.
For Deloitte, Dallas, creating a family-friendly workplace is critical to talent attraction and retention in a highly competitive environment. Promoting work-life integration through the provision of a telecommuting option has been shown to increase productivity by up to 13% (Tajlil, 2014). Deloitte should also integrate corporate social responsibility commitments (energy-efficient offices) into its HR policy to capture the imaginations of environmentally conscious staff (van de Wetering & Wyatt, 2011).
However, implementation barriers to the adoption of such policies must first be overcome. Relevant strategies include adequate supervisor support for the procedures, their universal availability to all employees, negotiability, and effective communication to promote acceptance (Ryan & Kossek, 2008). Fulfilling these attributes signals a firm’s support for diversity and inclusivity.
An organizational policy on sexual harassment can help Deloitte, Dallas, take appropriate steps to investigate complaints and take action against the perpetrator and counsel the victim. The rationale for having such a policy is that the failure to address harassment can lead to reduced productivity, low job satisfaction, and loss of talent (Boxall & Purcell, 2016).
A relevant legal issue includes institutional liability for failure to provide reporting systems or illegal discrimination (in case of dismissal of the complainant) under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act (Boxall & Purcell, 2016). The organization must define what constitutes sexual harassment, reporting procedures, and disciplinary measures for first and repeat offenders (Johnson, Widnall, & Benya, 2018). Medical and psychological support services should be made available to victims.
A clear promotion policy is also essential to Deloitte. According to Armstrong (2016), distinct procedures and criteria for promoting a worker should be anchored on job performance and goal achievement. Deloitte’s promotion policy should be fair and impartial. Summary dismissal should be procedural. An investigation is required to establish grounds for removal, and the employee should be given a chance to respond to the alleged misconduct (Armstrong, 2016). He/she may be suspended after a fair process to avoid violating the employment law. Wrongful termination claims may be made based on anti-discrimination laws or a breach of contract.
Implementation challenges can affect the effectiveness of HR policies and procedures. Efforts must be made to address these barriers. Carr and Simon (2014) state that obstacles to policy adoption can be overcome by adequate engagement of the implementers. Addressing constraints beyond the control of employees and capacity building at all management levels can also promote adherence to HR procedures.
Actual Policies
The specific HR policies recommended for Deloitte, Dallas, are included in the appendix.
Implications and Conclusions
Good HR policies have an impact on employee satisfaction, retention, and turnover. The HR activities of Deloitte, Dallas, are based on global best practices, which makes it an attractive employer. However, there is room for improvement in employee recruitment, motivation/satisfaction, and development, focusing on line supervisors. The HR policies developed for this firm are meant to address these areas. A family-friendly work environment is associated with productivity gains and employee satisfaction (Armstrong, 2016). Facilities such as flexible work hours, daycare centers for breastfeeding female workers, and telecommuting options will result in a more satisfied staff.
Employee empowerment through training and development will enhance individual skills to perform in one’s current role. It will also increase one’s chances of earning a promotion and reduce turnover. On recruitment, a graduate trainee program can help identify and hire talent that would drive the organization’s growth. The conclusions that can be drawn from Deloitte’s HR policies are that the integration of standards and procedures reduces turnover and increases competitiveness, and a rewards system increases employee retention.
Recommendations and Impact on the Organization
The rationale for selecting the policies included in the appendix is to offer a generalized guide for dealing with issues of recruitment, promotion, development, and dismissal. Additionally, the procedures are meant to create a fair and inclusive workplace and a distinctive culture to achieve Deloitte’s goals. The impact of the recommended policies on the organization is significant. A family-friendly environment will increase job satisfaction and productivity (Armstrong, 2016). Clear policies on sexual harassment, promotion, equal opportunity employment, and dismissal will avoid high litigation costs associated with discrimination or wrongful termination lawsuits. Further, they will prevent workplace conflicts related to unfair criteria for promoting employees.
Plan of Communication for Implications
The above implications of the proposed HR policies will be communicated to the staff and management. The communication options that will be used are a handbook detailing the policies and procedures, electronic and print newsletters, e-mail, and meetings. The aim is to reach geographically dispersed Deloitte staff since the organization is a multi-unit entity with operations in different locations. A feedback channel will be established to allow the audience to seek further clarification. Evaluation of the communication plan will involve a survey of the audience to determine its success.
References
Armstrong, M. (2016). Armstrong’s handbook of strategic human resource management. London: Kogan Page.
Boxall, P. & Purcell, J. (2016). Strategy and human resource management. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Carr, E. R., & Simon, D. (2014). Conclusions – Engaging critical perspectives in development policy and implementation. Third World Quarterly, 35(3), 524-527. Web.
Deloitte. (2019a). Network structure. Web.
Deloitte. (2019b). Life at Deloitte: Our culture. Web.
Johnson, P. A., Widnall, S. E., & Benya, F. F. (Eds.). (2018). Sexual harassment of women: Climate, culture, and consequences in academic sciences, engineering, and medicine. Washington, DC.: The National Academies Press.
MarketLine. (2017). Company profile: Deloitte Consulting LLP. London: MarketLine.
Ryan, A. M., & Kossek, E. N. (2008). Work-life policy implementation: Breaking down or creating barriers to inclusiveness? Human Resource Management, 47(2), 295-310. Web.
Tajlil, M. H. (2014). A framework for promoting women’s career intentionality and work-life integration. Career Development Quarterly, 62(2), 254-267. Web.
van de Wetering, J., & Wyatt, P. (2011). Office sustainability: Occupier perceptions and implementation. Journal of European Real Estate Research, 4(1), 29-47. Web.
Appendix: Actual HR Policies for Deloitte, Dallas
- Family-friendly policies – flexible work schedule, job sharing, an option to work part-time, and telecommuting.
- Sexual harassment policy – sexual harassment cannot be justified, rules against such conduct, reporting procedure (via the supervisor or email) and disciplinary actions on offenders, including dismissal.
- Promotion policy – employees shall be promoted based on performance and conduct. The criteria for promotion include experience in the position, performance after two consecutive evaluations, and skill requirement in the new role.
- Dismissal policy – the employee can only be dismissed for unacceptable conduct and after the pre-dismissal hearings. He/she may appeal the decision.
- Equal opportunity employment policy – staff recruitment will be based on talent and skills, not one’s religious, racial, and socioeconomic ethnic or gender.