Introduction
In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), water security and consumption are frequently discussed issues to ensure their sustainable development and regular access. Although recent progress provides the citizens of the region with a chance to live under normal and favorable conditions, there are still some extreme emergencies and unpredictable situations when water may be in increased demand. Therefore, the UAE Security Strategy 2036 promotes the idea of the creation of desalination plants as one of the dominant technologies in the UAE (Official Portal of the UAE Government, 2019). In this paper, the location and names of several UAE desalination plants will be identified to clarify the details of their work and cost in general and discuss its advantages and disadvantages in particular. Despite its high costs, energy consumption, and dramatic environmental impact, desalination contributes to a supply of fresh drinkable water in the UAE, which makes this process proven and effective.
Desalination Plants in the UAE: Locations and Names
The UAE is one of the countries with limited natural water resources. To predict and avoid water-related problems in the country and make sure enough freshwater sources are available, desalination plants are established. For example, in Dubai, there are the Jebel Ali Power Plant and Desalination Complex that includes six stations and AL KAFTAN with reverse osmosis desalination systems. In Abu Dhabi, there are Shuweihat Asia Power Company and Al Taweelah plants with the possibility to produce about 100 million imperial gallons of water per day (Official Portal of the UAE Government, 2019). In Fujairah, there is a Kalba desalination plant that provides the population with water regularly. Regarding their location and the direct connection to the Persian Gulf or the Arabian Sea, several desalination plants can be found in each state. In total, at this moment, in the UAE, there are about 70 major desalination plants that produce about 14% of drinkable water worldwide (Official Portal of the UAE Government, 2019). These solar-powered constructions are funded by private organizations and global initiatives to fight against drought.
A Desalination Plant: Work and Cost
Regardless of the location of a desalination plant, each of them usually has a similar infrastructure and placement. It is better to locate the plant on the coast close to an ocean or a sea that serves as a sustainable natural resource. Then, several tunnels and reservoirs are required to process water and unite the parts into one whole system. As soon as the water reaches an intake tunnel, it is transported to screening and filtration reservoirs. Then, as shown in Figure 1, salt and other impurities of the seawater are removed by the reverse osmosis systems, making water drinkable. In the majority of cases, desalination plants prefer to use reverse osmosis technologies.
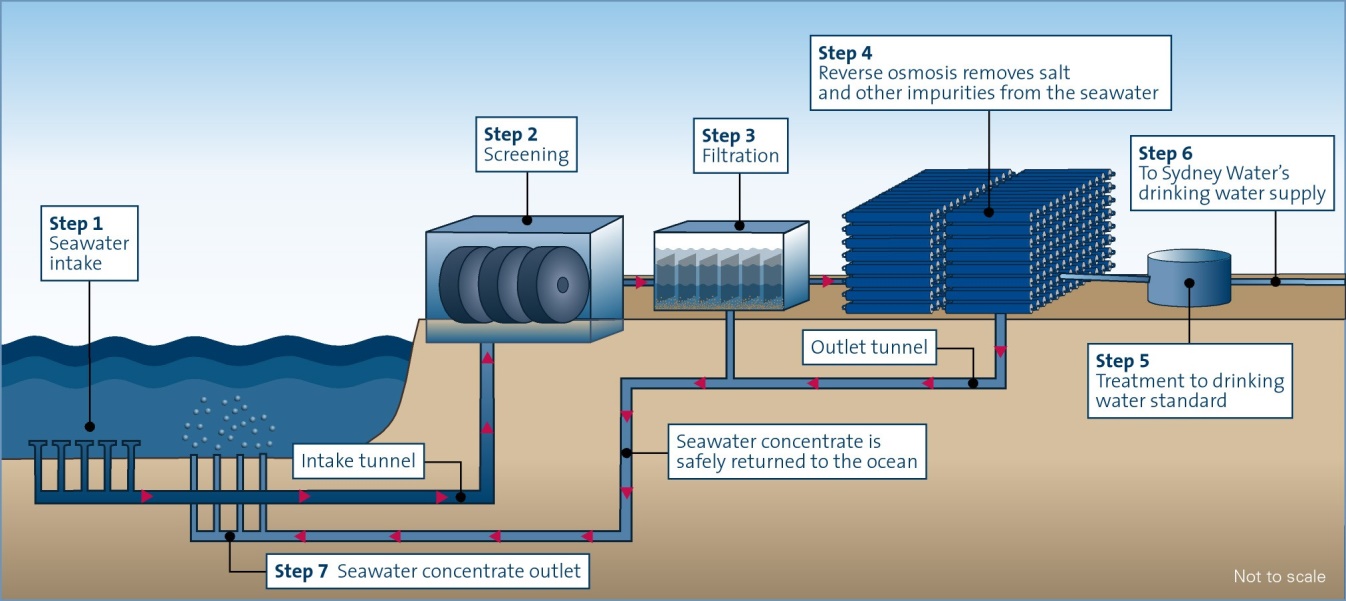
Costs of desalination processes change with time in the UAE. Wang (2018) defined reverse osmosis as expensive and energy-intensive and offered membrane distillation with low-grade heat or forward osmosis systems with two liquids driving water as available alternatives. At this time, the UAE finds it normal to spend millions of dollars on building operating desalination plants and meeting their desalination capacities. For example, in Abu Dhabi, one organization wants to invite several international companies and spend between $600 million and $1 billion to reach its capacity of 200 million gallons per day (“Abu Dhabi invites bids for giant water desalination plant,” 2018). The private sector is ready for such financial and economic costs to find a solution to drinkable water access.
Advantages of Desalination
The method of reverse osmosis for desalination is proven as effective as it creates fresh resources of drinking water that is an evident advantage of the process under analysis. The technology that is necessary for desalination is not complex, meaning that many plants can allow it nowadays. Another significant benefit is the possibility to use oceans and seas as the major resources, with about 50% of water being back after processing. Therefore, environmentalists should not be afraid that desalination plants devastate natural resources. Finally, all the plants are safely located without polluting residential areas and disturbing people. Special industrial zones are properly chosen by private agents for their further activities.
Disadvantages of Desalination
In addition to several benefits of desalination, it is necessary to remember its shortages. For example, many organizations find it expensive to build a plant, and people do not afford the established prices. In addition, much energy is required to maintain all the processes. Finally, greenhouse gas emissions are present as well as at any plant on the globe. Despite the existing needs for a desalination plant, its negative environmental impact, and air or water pollution matter.
Conclusion
In general, the UAE shows rather good results in the establishment and promotion of desalination plants to make sure that enough freshwater supplies are available to local people. Many working plants in the regions process millions of liters of water daily. People enjoy the opportunity to drink fresh water and not harm their health. However, financial and environmental aspects have to be recognized and solved with time. Desalination with reverse osmosis technologies is a good opportunity for countries with limited natural resources to survive and improve their quality of life.
References
- Abu Dhabi invites bids for giant water desalination plant. (2018). Web.
- Official Portal of the UAE Government. (2019). Water. Web.
- Sydney Desalination Plant. (n.d.). Infrastructure. Web.
- Wang, H. (2018). Low-energy desalination. Nature Nanotechnology, 13(4), 273-274. doi:10.1038/s415650-018-0118-y