Modern world is based on numbers. Mathematics and statistics are the main sciences which support the modern world. Economics, politics, countries’ studies are fully subordinate from numbers and calculations. Every economical document, every country affair is supported by statistics. Population and business companies are the main consumers of statistical services. Statistics is not the exact science, and some deviation is possible.
Statistic is “a value, usually a numerical value, that describes a sample. A statistics may be obtained from a single measurement, or it may be derived from a set of measurements from the sample” (Gravetter & Wallnau, 2006 p. 6). To provide the statistical measurement a lot of information (data) should be collected, then analyzed and only then the statistical methods are used to interpret this data and make conclusions. There are a lot of methods, which statistics uses to make conclusions. Descriptive statistics is one of them. Descriptive statistics are “statistical procedures used to summarize, organize, and simplify data” (Gravetter & Wallnau, 2006 p. 6).
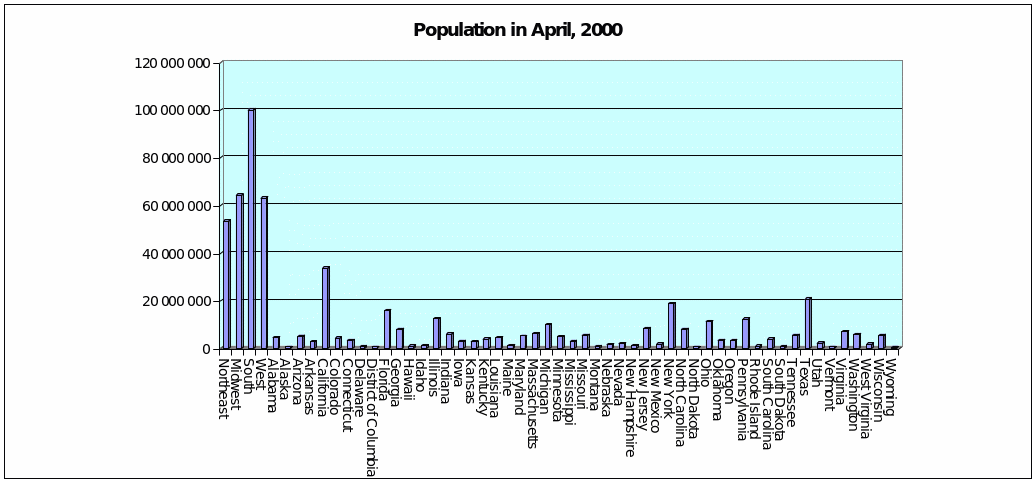
Descriptive statistics is used to organize and interpret the data. Let us give the example of the descriptive statistics on the information about the development of population in the states of the USA from April, 2000 till the July, 2008 (Table 1). This is the data analysis of the population growth (reduce) of the population in the states of the USA, which are organized in the table. There are some other ways to organize descriptive statistics, such as diagrams and graphs. The other type of the descriptive statistics, that is bar graph, may be seen on Table 2.
Statistics is used everywhere. Business is not an exception: accounting, finance, marketing, production and economics are not the only spheres where people use statistics. Statistics is very important in sales analysis, as the company should follow the information what type of the product is in great demand and which one is in abundance on the market. People’s interests can also be seen from the statistics, as “brand managers can review the scanner statistics and the promotional activity statistics to gain a better understanding of the relationship between promotional activities and sales” (Anderson, 2007 p. 5). Good gathered data, which reflects the dynamics of customers’ interests to this and that product for the last 5 – 10 years, may help managers to create the strategic plan of the company for the next 5 – 10 years with the reference to customers’ interests.
The information about sales may also be put in the EXCEL table or the graph, which is very convenient. The first column may contain the sales rate in 1999, the next in 2004, and the last in 2009. In this case the information may be seen how one and the same product was sold in different years. The given information is not enough to make up a strategic plan of the company, but a lot of conclusions may be provided from the statistical data of sales.
As it was mentioned above, statistics is not an exact science, so some possibility for chances exists. “To be able to draw logical conclusions from data, we usually make some assumptions about the chances (or probabilities) of obtaining the different data values. The totality of these assumptions is referred to as a probability model for the data” (Ross). In other words, probability shows in which case and with what rate this event may either occur or not. Probability is closely connected with the statistics as one event has the probability to occur in the situation when the other supportive event takes place. (Lipschutz, 2000)
It is certain that different probabilities may mislead the business decisions. Managers may take up wrong decisions focusing on the wrong data, or misunderstand the statistical issues. There are at least 3 outcomes of every business decision, 0 the probability is irrelevant, 1 it is sure to occur, and a lot of other situations may happen if the rate of probability between 0 and 1. (Spiegel et al, 2002) While making a decision a human factor is very important.
Considering the type of probabilities that can be encountered during a person’s employment, it should be mentioned that a lot of factors may influence the person’s chance to be employed in this or that company. There are two main probabilities, whether the person will be taken to the job, or not. The other probabilities deal with the chances whether the employee will be taken on the position he/she requires, or the other one. The situation with the probability of the salary is also the same, whether the person will get the salary he/she wants, or the offer will be to accept the lower salary.
These probabilities may be either used by the employee or not. There are a lot of circumstances, which should be taken into consideration. The first, and the main, in my opinion, is the experience and skills of the employee. If the employee has great experience in the field or on the required position, so it should be unacceptable for him/her to take up the lower position or to accept the low salary. The employer should also take into consideration these probabilities and to offer lower salary to the person with little seniority and lack of experience. The information about previous work of the employee should also be focused on by the employer.
So, statistics is very important discipline in the business and other sciences and field of people’s lives, such as population counting. Statistics is not exact science, so the notion of probability should be taken into consideration, as one event may either occur or not in different conditions.
Reference List
Anderson, D. R. (2007). Statistics for business and economics. Cengage Learning EMEA.
Gravetter, F. J. & Wallnau, L. B. (2006). Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences. Cengage Learning.
Lipschutz, S. (2000)..Schaum’s outline of theory and problems of probability. McGraw-Hill Professional.
Ross, S. M. (2004). Introduction to probability and statistics for engineers and scientists. Academic Press.
Spiegel, M. R., Schiller, J. J.& Srinivasan, A. (2002).Probability and statistics. McGraw-Hill Professional.
Table 1