The idea of diffusion innovation theory was credited to Everett Rogers. The theory examines the process through which an innovation spreads through a social system via a given communication channels (Rogers, 2003). It scrutinizes how new ideas and technology are adopted majorly through a social system. This theory has been used since its inception when it was published in 1962. Everett Rogers put more exploration on how innovations are deeply adopted. He proposes four main criteria which influences spread of any idea in the social system. The four are named as innovation, communication channels, social system and time (Valente, 1995). Innovation is a new idea either by technological innovation, a practice or just an object. For instance, innovation would mean new way of doing things for instance in education, ne methodology of teaching or lecturing. This may involve even anew software or hardware created that helps in the teaching process.
Communication channels are the means by which the idea or the message on innovation is spread across in the social system form one individual to another. For instance, in the current technology, people can use face book, tweets or just presenting the innovation at a given conference. The third way which facilitates an idea is time factor. Time is the duration or the period required for the adoption of the innovated technology (Valente, 1995). Lastly the fourth way that diffusion innovation can be facilitated is through social system. Social system is a group of people who are interrelated and are engaged to solve or achieve common goal. People at the social system may be divided to form various categories which describe how fast they adopt any given innovation.
In the social system, the first category is the innovators. They form about 2.5 % of any social system. They are the youngest and the people who take risk in the group. They form higher social class. In this, there are positive and negative traits. Positive traits are able to interact with different other innovators while negative traits normally liable for risk taking.
The second category is the early adopters who are about 13.5% of the social population. The groups have got higher number of opinion leaders with advanced education and higher social status. It also has positive and negative traits. The third is Early Majority who makes about 34% of the social system. They make part of the social system that is difficult to adopt the new innovation. They will only adopt after Innovators and Early adapters. They too have got positive and negative adapters. In a learning organization, this is the group requiring training in order to adopt the new technology. This is the inquisitive group that may have untapped wisdom though they lack relative authority.
Large Majority form about 34% of the social system. They are slow in adopting new technologies and will do after Early Majority. It has got positive and negative traits. Positive traits are more vocal and inquisitive about the value of innovation. Negative traits have got low social status and financial standards. Laggards are part of the social system which forms about 16% (Rogers, 2003). They are the last in adopting any innovation in the social system. They also have positive and negative traits. The negative traits are geared towards rejecting change.
A Curve showing the diffusion of innovation capturing all the discussed factors is as shown bellow (Rogers, 2003).
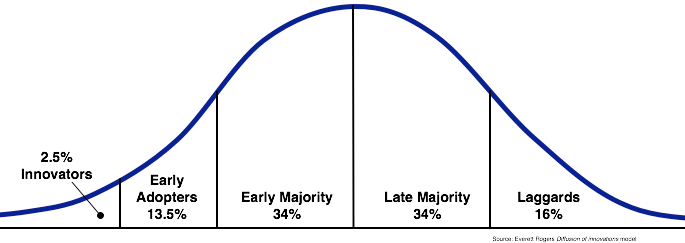
This curve shows that many people adopt innovated technology at different rating. The main purpose as professionals is to understand the levels and make the people adopt the changes appropriately. The nature of adoption will depend on the nature of the social system in focus.
References
Rogers, E. (2003). Diffusion of Innovation. New York: Free Press.
Valente, W. (1995). Network Models of the Diffusion of Innovations. N.J: Hampton Press.