Introduction
Although people promise to live happily in marriage, that is not the case in most marriages in the UAE (Magdy, 2014). For example, Dubai was shown to have about 3 daily cases of divorce in 2012, a figure that could imply a total of 1,129 divorce cases annually. It is even more worrying for Emiratis, who have been shown to contribute to 30% of divorce cases in the UAE (Pathak, 2013). Ten factors influence couples with regard to divorce trends in the region.
Infidelity is one of the major reasons why many marriages are ending. Poor communication has led many married people to misunderstand each other and terminate their marriages. Loss of jobs in the UAE has been contributing to high divorce rates, because couples cannot make ends meet. Spouses who have religious and cultural differences have high chances of separating in the region (Wikipedia, 2014). Pathak (2013) has also shown the following factors to be responsible for divorce:
- The use of social media.
- Sexual incompatibility.
- Financial negligence.
- Child rearing matters.
- Unrealistic expectations.
- Lack of marriage support systems.
The topic was chosen because it is essential to understand more about the factors that are threatening the marriage institution in the UAE.
Conjecture
The following list of questions would be used to explore the topic further:
- In the UAE, why do people marry? Do they plan to get married for the purpose of procreation or companionship?
- What is the age difference of the most people at the time they get married in the region?
- What roles do partners play in preventing divorce cases? Are they actively or proactively engaged?
- Could external factors such as the interference from in-laws be blamed for termination of marriages?
Hypothesis
Cultural differences, religious variations, age brackets and other factors contribute differently to divorce rates in the UAE.
Peer review
In order to gain insights about divorce issues in the UAE, I shared my thoughts and ideas with family members. They were instrumental because they gave comments regarding termination of marriages from their experiences. During courtship, lovers hardly have sufficient time to learn about the expectations of each other. They are either too busy with their occupations or they do not view expectations in the future as significant reasons that could negatively impact their marriages.
Thus, people marry and they learn about each other after a few months and/or years. Upon realising that a partner has different expectations and perceptions with regard to marriage, many spouses start behaving differently because they feel incompatible. Frustrations in life start emerging and spouses might choose diverse ways of ending them.
These could be being unfaithful, practising childcare negligence and being financially negligent. Ultimately, couples consider terminating their marriages because they cannot solve issues. Termination of marriages has different effects on spouses and children (Amato, 2000)
Methodology
The study would be carried out following clear steps in order to obtain results that would be relied upon in making conclusions. Four major steps would be adopted. First, a sample will be identified through sampling methods. Second, data will be collected from study participants through the use questionnaires. Third, the collected data will be analysed to obtain important results. Finally, conclusions will be made about the population based on the study findings.
The study will use the following factors as the independent variables: age brackets of marriage partners, religious variations, cultural differences, and other factors. Divorce rates will be the dependent variable. The study will not use a control group because it would be expected that there would be no perfect marriages based on religion, age differences of spouses and cultural variations. Thus, the independent variables will be used as the fixed variables because they will not be influenced by other factors.
Data will be collected using detailed questionnaires, which would aim at obtaining respondents’ information about marriage aspects, including age, religion, culture, and other essential factors. Three possible outcomes will be expected from the study. First, the study results might indicate that divorce cases are mainly caused by cultural differences.
Second, the study might reveal that spouses terminate their marriages due to cultural variations. The study findings could also indicate that divorce cases are mainly caused by age-related factors that affect marriages in different age brackets of spouses.
Evidence
Data representation
Data collected were organised and the results were presented in the form of graphs.
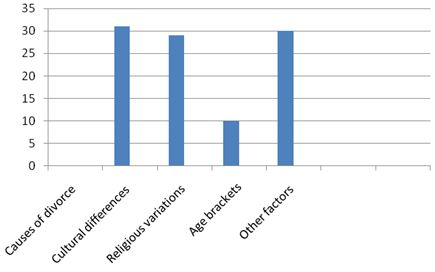
Figure 1. A figure showing a summary of factors that contribute to divorces in the UAE.
Data analysis
The data analysed in the study provided important findings with regard to divorce issues. The four independent factors showed different levels of contributions to termination of marriages. Cultural differences were the leading factors that make married people separate. This could be because the UAE is open to the rest of the world and people from all regions of the world could meet and marry. These people characterised by distinct cultural variations, which influence spouses to end their marriages.
The cultural difference variable was closely followed by other factors (30%) while religious variations and age brackets were placed in the third and fourth positions respectively. Other factors are those issues that were not captured by the questionnaire and they could be infidelity, loss of job, financial negligence, and childcare negligence, among others. The hypothesis that was formulated in the study was supported by the study findings.
Conclusion
Based on the results, it can be concluded that divorce cases in the UAE are mainly caused by cultural variations of spouses. The other three main aspects that lead to termination of marriages include religious differences, age brackets and other factors.
Reflection
The study was characterised by some strengths and limitations. Some of the strengths included the following: flexibility with regard to scheduling, cost effectiveness, relatively high chances of objectivity, ease of quantification, and ability to test a hypothesis. Some of the limitations of the study included low level of validity and a high probability of misinterpreting emotions from respondents.
It was difficult to make a decision about the specific type of data collection tool to be used in the experiment. In addition, it was not easy to decide about the specific sample size and how the sample could be identified in the population. In order to improve the results of the study in the future, a bigger sample size, more independent variables and statistical tests should be used.
References
Amato, P. R. (2000). The consequences of divorce for adults and children. Journal of marriage and family, 62(4), 1269-1287.
Magdy, S. (2014). Reasons your marriages are insecure in UAE!. Web.
Pathak, S. (2013). 10 reasons why UAE marriages fail – Rising divorce rate among expats and Emiratis worries counselors. Web.
Wikipedia. (2014). United Arab Emirates. Web.