Smart cities are the pathway to the future. Dubai is amongst the leading metropolitan areas in the world to implement ambitious projects and strategies which would transform the way that private and public services are provided to the residents. A city can position itself on the global socio-economic landscape through the provision of smart technologies. Airports which serve as a key gateway and transportation to Dubai, are an essential priority to adopt smart technology to ensure safety and accessibility.
Dubai’s Vision
- The Dubai 2021 vision is a framework introduced to develop the city with a holistic and comprehensive perspective.
- It is a plan to deliver the aspirations of the city, society in order to set and achieve necessary goals for the growth of the urban environment.
- It is focused on improving the living experience of residents, their interaction with the environment, as well as economic and social services that are provided.
- Also, the plan is meant to improve and diversify the economy as the mechanism which drives city growth (Government of Dubai, 2016).
- One of Dubai 2021 key themes is “The Place: a smart and sustainable city” (Government of Dubai, 2016, p. 7).
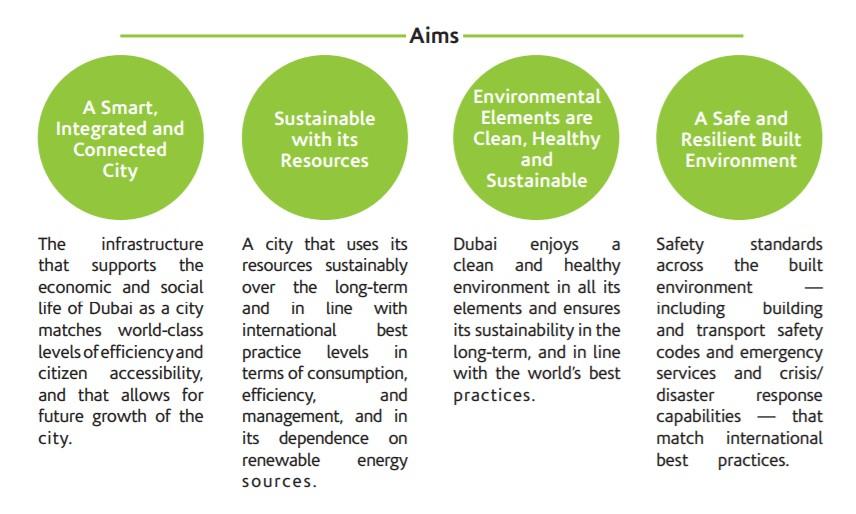
- It focuses on a smart, connectable, and integrated infrastructure and services. The infrastructure should ensure mobility for residents and tourists by providing access to economic and social centers in the city.
- Furthermore, Dubai’s growth should be sustainable, adhere to regulations, and seek to preserve natural resources.
Income Breakdown
- Dubai has radically redefined its economy in recent decades. It has used the strategic geographical location to become an important tourist destination and economic center.
- To survive the volatility of global oil prices and lowered demand, Dubai chose to diversify its economy. Oil production which used to contribute upward of 50% to Dubai’s GDP, now contributes less than 1% (“Dubai economy,” n.d.).
- Unlike most Middle Eastern cities, since 2003, company equity and real-estate share prices no longer depend on the price of crude oil. This has led for the seven major companies of Dubai’s real estate and construction sector to produce a 789 percent total return (Winkler, 2018).
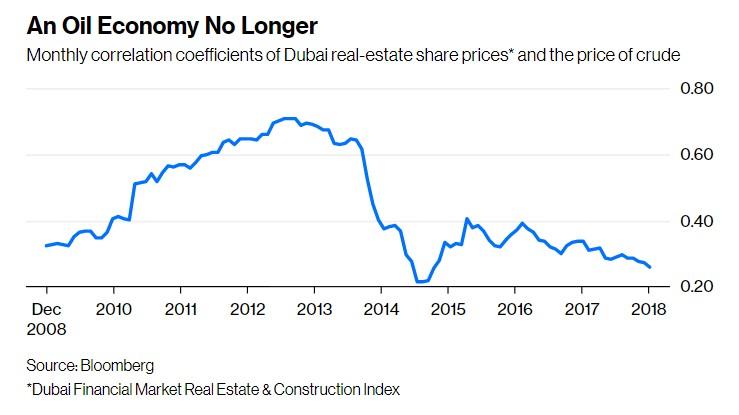
- In 2004, the Dubai International Financial Centre was built which propelled the city into a global hub for IT and finance. The city has become a major center for IT companies and services in the Middle East, serving as headquarters to leading global technology firms and media organizations.
- One of the sectors of the economy that Dubai is developing is tourism. It has seen significant success as tourist rates continue to increase year over year. In 2017, the city welcomed 15.8 million tourists, which is a 6.2 percent increase from the year before. Analysts expect the number to reach 20 million by 2020. Meanwhile, the hospitality sector is valued at $5.9 billion currently and is expected to reach $7.6 billion in 2022 (Mallinson, 2018).
Airport Rankings
- Airports have rankings assigned to them based on a variety of factors.
- Some rankings focus on architecture, infrastructure, and quality of service.
- Meanwhile, other rankings promote performance and passenger traffic.
- The prestigious Skytrax World Airport Award is handed out each year to top airports, most often based on quality and luxury rather than objective numbers. Dubai’s airports are not currently included in that list, led by Singapore Changi Airport (Hardingham-Gill, 2018).
- However, Dubai International Airport (DXB) holds the world’s top position for the largest annual traffic for international passengers.
- In the 2017 calendar year, DXB traffic reached 88.2 million passengers (averaging 7.35 million per month), an increase of 5.5 percent from 2016 (Gulf News Aviation, 2018).
Smart Technologies
- Smart technologies affect people’s lives, professional industries, and the function of services in cities. Recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) can help with an array of operational tasks.
- Dubai International Airport should focus on adopting AI as part of its technological infrastructure. It can be used for everything from improving efficiency to communication with passengers, answering any potential questions they may have.
- Some AI platforms, developed by major tech giants such as Apple and Google, have conversational capabilities. Therefore, these AI-powered bots can contextualize and personalize services depending on the request (Hippold, 2018).
- Another smart technology which has significant potential is known as beacon technology.
- These are relatively low-cost pieces of hardware that can be attached to practically any hard surface.
- They run on batteries and have low environmental impacts.
- Using a Bluetooth connection, it can transmit to any electronic device.
- It helps to receive a signal while a person is indoors, which is usually difficult with walls blocking cell phone reception.
- Furthermore, facilities can use beacons as a system of organization, sending information and enhancing the experience (Danova, 2014).
- The beacon technology can be used for everything from navigation and payment services, to issuing announcements and warnings in the airport.
- Finally, the Dubai airport can adopt comprehensive smart information technology systems into its network.
- One of the largest corporations that offer this service is SITA.
- The technology it seamlessly integrates into the airport infrastructure ranges from airport operations such as safety and security to passenger communication and processing.
- The technology can also be used for operational communication with aircraft, cargo management, and baggage processing (SITA, n.d.).
- This type of smart technology can effectively manage day-to-day operations as well as large-scale projects and processing.
Accessibility
- Airports worldwide are evolving and adapting to accommodate the needs of its passengers, particularly those with disabilities.
- The range of disabilities can be managed through innovative technology implemented in the airport.
- Resourceful initiatives in the industry can make air travel and time at the airport a manageable and enjoyable experience.
- Dubai International should focus on adapting some of the assistive technologies that have had success in other global airports, thus being able to improve its quality of service.
- Assistive technology is any product, service, feature, strategy, system, or device that is focused on enhancing the abilities or functional capacity of any person with a physical or cognitive impairment or disability.
- It is meant to overcome limitations for physical and social participation.
- Assistive technology has a wide variety of uses, including helping with daily activities, establish communication, enable the use of digital devices, structural modifications, and control of public environments.
- Furthermore, it can provide physical postural support, reduce visual or hearing impairments, and provide mobility solutions for transportation.

- Assistive technology is a powerful tool to provide autonomy to people with disabilities, as well as ensuring welfare and social inclusivity (Campese, da Silva, da Silva, Figueiredo, & Menegon, 2016).
- Airports worldwide have implemented various technologies, devices, and mobile phone applications for passengers with disabilities.
- An application was introduced by the Edinburgh Airport, which allows creating a personalized profile, outlining their needs and request assistance from the airport’s specialized service so that any mobility issues can be addressed (Gallagher, 2018).
- Canada’s Toronto Pearson also introduced an app which has specific guides for people with special cognitive needs. Several airports in the United States, have introduced smart-glasses which offer guidance. These smart glasses can live stream what the passenger views to the company agent, which directs the patient via audio (Grey, 2018).
- Other services to aid passengers with impairments include providing identifying lanyards, introducing assistance security lanes, providing easily accessible information, and enhancing staff disability training (Whitehead, 2018).
- It is critical to focus on improving disability-friendly services and accessibility in the Dubai airport.
- More adults with disabilities are choosing air travel each year, spending approximately $17.3 billion annually (Grey, 2018).
- However, airports and air travel remain some of the biggest accessibility barriers for these individuals.
- Better service to disabled passengers should be a collaborative effort between airlines, airports, and private service providers.
- This will improve the quality of assistance and increase the level of support.
- In turn, this will increase passenger satisfaction, directing more traffic through the Dubai airport and increase its rankings on the list of best airports in terms of quality and safety.
Conclusion
Dubai has set a vision for itself to become a global and smart city by 2021. As the city’s economy becomes more business and tourist-oriented, it is critical to modernize the Dubai International Airport as it becomes a gateway hub to the city. Smart technology can greatly improve service quality and efficiency of the airport. It is particularly important in accommodating and addressing the needs of passengers with disabilities. By doing so, Dubai fulfills its vision by integrating smart technology as well as providing a safe and accessible environment to its residents and visitors.
References
Campese, C., Da Silva, T. N., Da Silva, L. L., Figueiredo, J. P., Menegon, N. L. (2016). Assistive technology and passengers with special assistance needs in air transport: contributions to cabin design. Production, 26(2). Web.
Danova, T. (2014). Beacons: what they are, how they work, and why Apple’s iBeacon technology is ahead of the pack. Business Insider. Web.
Dubai economy. (n.d.). Web.
Government of Dubai. (2016). Dubai plan 2021. Web.
Gallagher, R. (2018). New app for disabled passengers to use at Edinburgh Airport. Web.
Grey, E. (2018). Smart environments: how airports use tech to welcome special needs passengers. Web.
Gulf News Aviation. (2018). Dubai airport retains position as world’s no. 1. Web.
Hardingham-Gill, T. (2018). World’s best airports for 2018. Web.
Hippold, S. (2018). Use AI to make cities smarter. Web.
Mallinson, H. (2018). Dubai to welcome 20 million international tourists by 2020 as tourism in UAE skyrockets. Express. Web.
SITA. (n.d.). Airports. Web.
Whitehead, J. (2018). How airports are improving travel for passengers with hidden disabilities. The Independent. Web.
Winkler, M. A. (2018). Dubai’s the very model of a modern Mideast economy. Bloomberg. Web.