Abstract
Renewable energy has gained popularity in this century where people are concerned about the rate at which the environment is being polluted by the fossil fuels. Scientists, governments and the society in general have come together to help promote growth of the renewable energy. The main question that stakeholders do ask is whether this renewable energy can be developed to the levels where it can replace the fossil fuel.
Most industries depend on the fossil fuel, and so do cars and heavy machinery around the world. Governments have actively engaged in promoting renewable energy by attracting investors into this sector. Currently, renewable energy is more common in developed countries than in developing nations.
China and the United States are leading other developed countries in the generation and consumption of the renewable energy. The massive effort put by various stakeholders has seen a growth in production and consumption of renewable energy around the world. If the current trend continues, chances are high that renewable energy will be able to replace the fossil fuel.
Introduction
Renewable energy is the energy which comes from sources that are renewable such as wind, sunlight, rain, tides geothermal heat and waves (Boyle 2012, p. 112). There has been a massive effort made by governments and scientists to try and replace the fossil fuel with renewable sources of energy for both the industrial and domestic purposes (Simon 2007, p. 49).
The discussion of coming up with renewable energy can be traced back to 1973 when it was discovered that the fossil fuel could be depleted after a long period of use. However, the main concern during this time was the possible depletion.
The current concern is mainly the impact of the fossil fuel on the environment. Fossil fuel is the leading pollutant of the environment. Environmental blue print left after usage of the fossil fuel is a major concern in the society. According to Boyle (2012, p. 98), the fossil fuel forms one of the biggest threat to the environment.
The rivers and lakes will get polluted as the oil is washed off through runoff or effluent from the manufactures (Tiwari 2012, p. 46). The living organisms will get affected by this. The transportation of this product is also a threat to the environment.
The massive British Petroleum oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico in the United States is an example of how delicate the environment is when faced with the threat of pollution from fossil fuel (Sørensen 2011, p. 89). When the product is finally put to use, the gas produced by the machines and cars form a great threat to the environment.
It is, therefore, of great importance to ensure that the renewable energy is developed to help bring to an end the rate at which the environment is getting polluted (Shea 1988, p. 90). The efforts made by various governments have seen a rise in the use of renewable energy.
Energy from wind, water, geothermal, plants among others have been harnessed to help increase the production of energy that is friendly to the environment and is renewable. This research focuses on the economics of renewable energy.
Renewable Energy
There are a number of sources of renewable energy. Solar energy makes one of the fastest developing forms of energy. Known to be one of the traditional forms of energy, technology has been developed to help tap sunrays and turn it into electrical energy. This is made possible with the solar panels (Saunders & Chapman 2005, p. 27).
This energy can be used domestically for lighting, heating water, in the electronics and other domestic chores. This form of energy has also become very popular in schools and hospitals in regions that receive a substantial amount of sunlight throughout the year. This energy is still being used by farmers to dry their crops (Mukherjee & Chakrabarti, 2004, p. 67).
Grains dried in the sun are more nutritious than those dried using electricity. Wind energy is another form of renewable that has become very popular in the current world.
Traditionally used by sailors to propel their ships, wind is currently used to generate electric power for both the commercial and domestic purposes. Using the wind turbines, this energy can be tapped to generate enough energy to be used for domestic and commercial purposes.
Hydropower is another form of renewable energies that has become very popular in the current society. According to Chiras (2011, p. 115), water is 800 times denser than air, a fact which makes it a very reliable source of energy when in motion. The hydropower can be harnessed in a number of ways. Hydroelectric power is the most common and very reliable form of hydropower.
With the help of large dams, electricity is always generated by the use of large turbines which are moved by the moving mass of water. The dynamo technology helps in transforming the energy from kinetic to electric energy. This is then transported using high voltage electric wires to various points of consumption (Saunders 2006, p. 27). This form of renewable energy has proven to be the best in the industrial sector.
The recent development of electric trains means that the use of fossil fuels on the roads and rails may soon come to an end. Runoff river hydropower is another source of energy which taps the kinetic energy of the flowing water and transforms it into electric energy.
Biomass forms another source of renewable energy. Using the photosynthesis process, plants always tap the energy from the sun (Sayigh 2000, p. 78). When burnt, they release this energy.
Biofuel has also become very important renewable energy. Several countries around the world are trying to introduce cars that can use bio-fuel instead of the petroleum products. Other forms of renewable energy include geothermal energy and ocean-organic power.
Green Stimulus
According to Dabra (2013, p. 67), several governments have come up with Green Stimulus plans where these governments have committed themselves to support the development of the renewable energy.
In this movement, the governments have given their commitment to ensuring that clean energy technology is supported (Wengenmayr & Bührke 2013, p. 76). This effort is to ensure that there is a consistent reduction of the use of fossil fuels, while renewable energy is increased.
Literature Review
It has come out clearly that in the current society that renewable energy is the solution to the continued environmental degradation posed by the fossil fuels. This energy has no environmental footprints. This makes it a sustainable source of energy. It is a form of energy that the environment can sustain. According to Da (2013, p. 28), renewable energy has come a time when it is needed most.
The future of fossil fuel is not clear. Some of the sources of the fossil fuel are predicted to run dry after a period of 50 years. This means that the society has to look beyond the use of non renewable energy (Hazen, 1996, p. 114). This sentiment is supported by Kalogirou (2006, p. 98) who says that renewable energy is the best alternative form of energy both for the domestic and commercial use.
There has been a consistent rise in the rate at which investors get into this sector. The graph below demonstrates this.
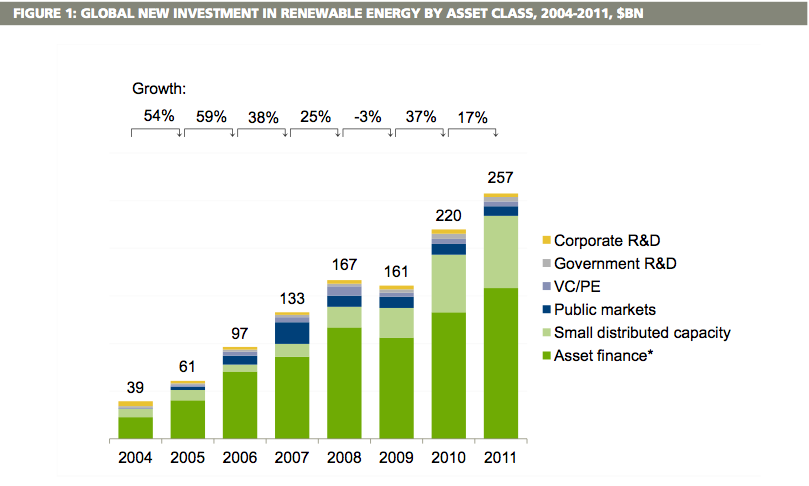
Source: (Kalogirou 2006, p. 69)
The figure above shows the rise in the levels of investment in this sector. Different forms of renewable energy have attracted a number of investors. According to Johansson (1993, p. 57), solar energy has attracted the highest number of private investors followed by wind. The following graph demonstrates this.
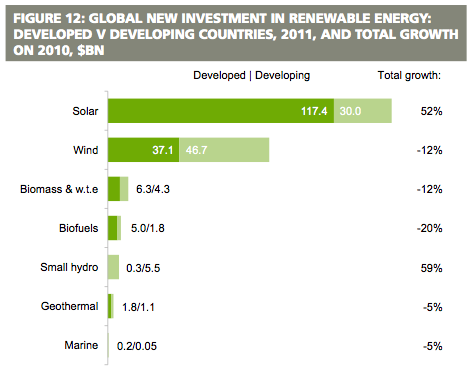
Source: (Lund 2010, p. 84)
The world has come to appreciate the importance of renewable energy and this is witnessed in the level of investment in this sector (Sunen 2007, p. 89). Europe has the highest number of investors in this industry followed by China and then the US. The graph below shows this.
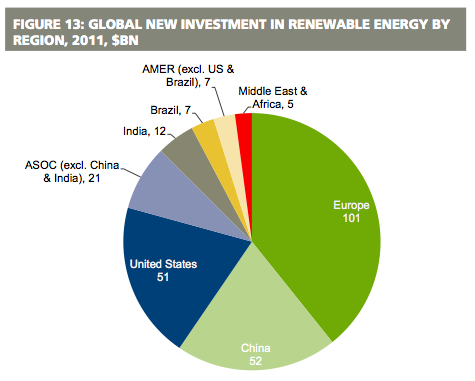
Source: (Maczulak 2010, p. 118)
Methodology
Every research method applies a specific research method (Michaelides 2012, p. 17). In this research, the researcher plans to use quantitative research methods to arrive at specific conclusions. The researcher will use both the primary and secondary sources of data for the purpose of analysis. The primary data will be collected from the field using sample population which shall be selected using stratified sampling.
Questionnaire will be used in collecting primary data. The researcher will maintain ethics in this research. The secondary data will be collected from the available literatures on renewable energy. The researcher will use SPSS version 20 in analyzing primary data. The analyzed data will be presented in graphs and tables for simplicity and clarity.
List of References
Boyle, G 2012, Renewable energy: Power for a sustainable future, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Chiras, D 2011, The homeowner’s guide to renewable energy: Achieving energy independence through solar, wind, biomass, and hydropower, New Society, Gabriola.
Dabra, M 2013, The renewable energy processes, Cengage, New York.
Da, R 2013, Fundamentals of renewable energy processes, Wiley, New Jersey.
Hazen, M 1996, Alternative energy: An introduction to alternative & renewable energy sources, Prompt Publications, Indianapolis.
Johansson, T 1993, Renewable energy: Sources for fuels and electricity, Island Press, Washington.
Kalogirou, S 2006, Artificial intelligence in energy and renewable energy systems, Nova Science Publishers, New York.
Lund, H 2010, Renewable energy systems: The choice and modeling of 100% renewable solutions, Academic, London.
Maczulak, A 2010, Renewable energy: Sources and methods, Facts on File, New York.
Michaelides, E 2012, Alternative energy sources, Springer, Berlin.
Mukherjee, D & Chakrabarti, S 2004, Fundamentals of renewable energy systems, New Age International (P) Ltd, New Delhi.
Saunders, N 2006, Renewable energy, Raintree, Chicago.
Saunders, N & Chapman, S 2005, Renewable energy, Raintree, Chicago.
Sayigh, A 2000, Renewable energy: Renewables: the energy for the 21st century: World Renewable Energy Congress VI, 1-7 July 2000, Brighton, UK, Pergamon, Amsterdam.
Shea, C 1988, Renewable energy: Today’s contribution, tomorrow’s promise, World-watch Institute, Washington.
Simon, C 2007, Alternative energy: Political, economic, and social feasibility, Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Lanham.
Sørensen, B 2011, Renewable energy: Physics, engineering, environmental impacts, economics & planning, Academic Press, Burlington.
Sunen, B 2007, Renewable energy conversion, transmission, and storage, Elsevier/Academic Press, Amsterdam.
Tiwari, G 2012, Advanced renewable energy sources, RSC Publishing, Cambridge.
Wengenmayr, R & Bührke, T 2013, Renewable energy: Sustainable concepts for the energy change, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.