Economic inequality entails disparities existing in the distribution of wealth and individual income. Uneven income negatively affects poor people while giving an advantage to the wealthy population. It is responsible for the widening wealth gap between the rich and the poor in society. Schaeffer (2020) revealed that 20% of families earned more than half of the entire income in the U.S in 2018. This explains that the highest-earning families control the economy since most of the resources belong to them. The top fifth household earners acquired more than $130,000 accounting for 52% of the entire income in the U.S. The prevalence of income inequality is higher in the U.S compared with the G7 countries (Kraus et al., 2017). This paper describes the economic inequality, socially optimal outcomes, and government interventions to support socially preferable outcomes.
The three common inequalities in a country are wealth, pay, and income. Inequality in pay income entails discrimination in payments from employments. Wealthy inequality is realized in many areas including private pension rights, property, stocks, and bolds. It explains the unequal distribution of assets hindering some groups from improving their economic status (Alfani & Ammannati, 2017). Income inequality entails the unfair distribution of money obtained from employment including bonuses, salaries, and wages. Unequal economic opportunities and income affect some groups in society making it difficult for them to advance their position.
The problem is a major issue of concern in many countries since its traps some people in poverty by limiting their chances of advancement. Gender wage inequality is one of the examples of wage inequality affecting many people in the United States today (Alfani & Ammannati, 2017). Discriminations against women have existed for many years and it is still being experienced today including in the developed countries. Many employers are paying women low payments including when they serve similar roles with men. Moreover, many women are facing difficulties acquiring jobs despite having all the necessary qualifications.
There has been significant growth in women’s labor force participation starting from the second half of the twentieth century. Many are attempting to pursue higher education and work for extended hours to improve their economic position. However, this has not stopped the existing discriminations against them especially the women of color (Alfani & Ammannati, 2017). The gender wage gap continues to place women at a disadvantage when negotiating salary increments.
This explains the output level reflecting all the benefits and costs linked with a transaction. It entails the equilibrium attained when the market outcome considers the effect of externalities. It is achieved at the intersection of marginal social cost (MSC) and marginal social benefit (MSB). The level is sometimes referred to as the allocative efficient level of output. A market failure usually occurs in case the output is realized at a different level. According to the microeconomic theory, people make decisions and chooses goods and services presented for sale. Personal gain is usually influenced by the desire to enhance the public interest.
The market outcome may sometimes differ from what is generally considered optimal. The market failure is realized in the case of an externality where the cost or external benefit is extended to a third party instead of the seller or buyer (Alfani & Ammannati, 2017). For instance, zero pollution cannot be considered the optimal level but it can be realized by considering the economic decision rule and equating the marginal cost to the marginal benefits. The presence of a negative externality implies that a cost was extended to a third party who was not involved in the consumption or production of the good. These may include air pollution from power plants or factories or noise from industries that are affecting residents in the neighborhood.
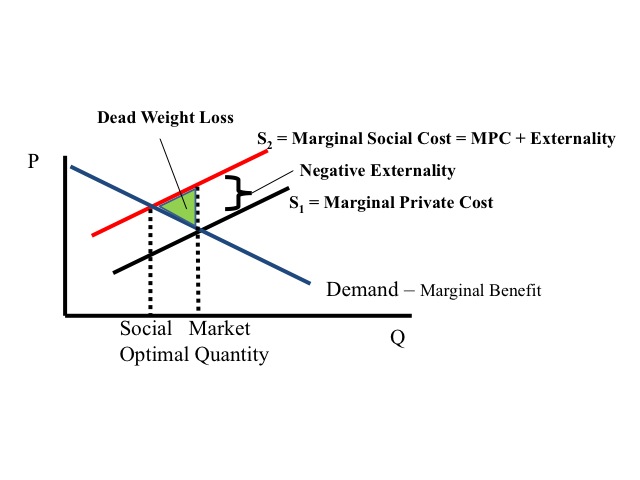
The graph above explains the market and socially optimal outcome as well as prices and quantities during a market failure. It helps explain that a factory that fails to pay for the created negative impact of pollution, is likely to realize outcomes that are greater than the socially optimal level (Payne et al., 2017). Externalities usually exist in the consumption or production of goods and services.
Negative production externalities arise when pollutants are generated during the creation of goods or services. Negative consumption externalities arise when undesirable actions during the consumption process occur. For instance, consumption of alcohol can influence a driver to cause an accident and kill pedestrians. Positive Externalities occur when less than the socially optimal quantity is produced because of the presence of additional benefits to society (Brigham Young University, 2021). Education is one of the examples because it benefits the involved individual as well as a society since the involved person is likely to initiate desirable projects.
Government can intervene to promote market fairness and eliminate inefficiencies towards the achievement of a socially preferable outcome. It can address market inequalities by introducing subsidies, taxation, and regulations. It can promote social welfare by regulating negative externalities and eliminating existing monopolies. Many approaches should be considered depending on the situation to hinder unintended negative implications while promoting beneficial goals including advancement and national unity. Government should promote efficiency by ensuring appropriate allocation of resources and fair distribution of wealth. Regulations can help break unregulated inefficient cartels and markets that affect development and raises entry costs.
References
Alfani, G., & Ammannati, F. (2017). Long‐term trends in economic inequality: the case of the Florentine state, c. 1300–1800. The Economic History Review, 70(4), 1072-1102. Web.
Brigham Young University (2021). ECON 150: Microeconomics.Brigham Young University. Web.
Kraus, M. W., Park, J. W., & Tan, J. J. (2017). Signs of social class: The experience of economic inequality in everyday life.Perspectives on Psychological Science, 12(3), 422-435. Web.
Payne, B. K., Brown-Iannuzzi, J. L., & Hannay, J. W. (2017). Economic inequality increases risk-taking.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(18), 4643-4648. Web.
Schaeffer, K. (2020). 6 facts about economic inequality in the U.S. Pew Research Center. Web.