Introduction
For the economic analysis, I have chosen to analyse the McDonald franchises. I have chosen this franchise because it is an industry where the profits are mostly affected by the quality of food and the customer service. It is also an industry which relies heavily on the labour and raw materials in the market.
Scarcity, Choice and Opportunity Cost
There are three fundamental questions in economics. This involves the issue of choice, scarcity and opportunity costs. In the first place, there is the concept of scarcity. There are resources which are scarce in the earth such as land and water. These are resources which the world wants desires more. In the business environment, there are also goods and services which are scarce which fetch a good price in the market. This motivates the sellers to get involved in the market in order to earn a profit. Due to scarcity, firms and individuals are expected to make choices that involve certain trade-offs.
The owner of the business has limited capital to start a business. He has to choose what business to invest in? What are the goods and services that the business will produce? Considering that the factors of production are scarce what is the combination of the factors of production to use? There is also the concept of opportunity costs. The resources that could have been used in the production of tea and coffee are now used to produce cakes and biscuits? The business owner should be aware of the opportunity costs. At an individual level there is also the issue of opportunity costs. The time taken by an individual to rest instead of working shows
the opportunity costs of the leisure time which is the wages foregone for that period. The government also has to decide which expenses they will devote higher funds than the other sectors. The government money spent in defence activities would have been spent in the education or health industry (Hoag & Hoag, 2006, 5).
Trade-Offs
There are various trade-offs that are involved in any business. Everything in business has an advantage and a disadvantage. There are various benefits of operating a franchise. The business owner gets to sell the products of a known brand in the market. McDonald has a strong brand in the market saving the owner high marketing and selling expenses. The owner is trained on the existing business model of the business. He finds that the business already has an established way of doing things. The models have been tested and been proven to be effective. He does not have to come up with the policies and procedures. The business has already been registered and all the legal procedures have been followed. The company reaches the customers in the mass market through websites. There are centralised call centres that take care of the customer’s queries, complaints or comments.
The business owner gets to have advice and professional support from the fellow business owners in the franchise business since they are facing the same business challenges. The company also holds regular annual and regional promotional campaigns that assist the franchise boost its sales. There are also conferences held where the franchise owners are educated on the business and how to handle the challenges that may come. The franchise owner also gains from the discounts in the purchase prices of the raw materials due to group purchasing. However there are certain trade-offs for the franchise owner. First of all, there could be nationwide campaigns that are mandatory which the owner has to participate in. He may be reluctant to participate since the promotion may not work in his market. The owner will have to incur these costs even though he has not bought into the idea. Secondly, the company may approve a plan to redesign the outlook of the franchise. The owner again incurs costs of redesigning his restaurants. The costs may be quite high. There are also the franchise fees, the insurance costs and the royalty fees that the business has to factor in when calculating its profit.
There is lack of independence. The business owner is not really the boss. He has to abide by the company rules and regulations. There will be mandatory rules on the suppliers and the equipment that the franchise should use. The management of the company may change yet the owner has signed a contract of fifteen years. The management may choose to take the company in a completely new direction that the business owner does not agree to but has to comply.
Factors Affecting the Quantity Demanded
There are several things that affect the demand of a product. In a franchise business, this would be the price of related goods and services. If the people are purchasing from the McDonald Franchise burgers and sodas, the price of soda would affect the consumption of burgers. If the price of soda goes up, the people will decrease their demand for burgers and vice versa. There is also the price of substitute goods. McDonald has several competitors in the market such as Starbucks, Pizza Hut and Dunkin. If the competitor prices should go down, the demand for McDonald products would reduce as people rush to buy cheaper items. Fast food is a luxury food and is not considered to be a necessity. It is for entertainment. A reduction in the income of the people would result in fewer goods demanded. Different franchises can face higher demand for the products depending on the demographic characteristics of the population. If the area is to open up and become a city with more population, demand will go up. If the influx of people into the area is especially young people, the company will benefit a lot since they love fast food more than elderly people. Being a fast food franchise and in the service industry, I expect the demand to be affected by the quality customer service levels. If the quality of service is poor and the food is not fresh customers will prefer other company’s franchises.
The quantity demanded changes by the demand curve moving either outwards or inwards (Mankiw, 1998, 68). This should not be convinced with the changes in the demand when the price of a product changes. Whenever the price of a commodity increases or decreases there is movement along the demand curve. It does not shift. What shifts the demand curves to the right or to the left are changes brought about by other factors apart from the price.
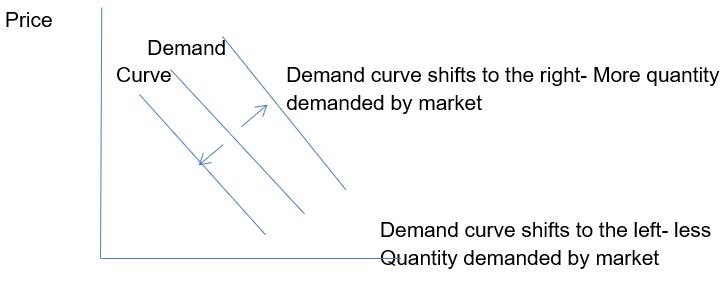
Factors Affecting the Supply
There are several things that affect the supply of a product. When the prices of the factors of production increase, this affects the cost of production and the quantities that the sellers will be willing to produce in the market. Higher prices of the factors of production will reduce the quantity. McDonald franchises sell various products. If the returns of producing burgers are higher than the returns of producing pizza products, then the business will prefer producing a high supply of burgers and reducing the supply of pizzas. Improvement in the technologies used in food production will benefit the company as it will have lower costs of production. If the farming technology improves, the franchises will get raw materials for preparing the food at lower prices. This will cause the company to produce more.
The food industry is susceptible to natural events and calamities such as floods, earthquakes and droughts. This can adversely affect the supply of raw materials which in turn will reduce the supply of the products in the market. The number of franchises in the market also affects the supply of fast food from McDonald in the industry. Where there are many sellers, there is more supply of the product.
Government Intervention in Markets
Advantages and Disadvantages of government intervention eg price controls and minimum wages
The impact of minimum wage laws in the market? The minimum wage would increase the cost of production. Labour is one of the factors of production. The franchise will seek to recover the high costs by raising the prices of the products so as to transfer the prices to the consumers of the good (Mankiw, 2010, 121).
The proponents of minimum wage argue that it helps alleviate poverty. There are those households where they have one person who is generating the income and he or she needs to be able to earn sufficient money to take care of the basic needs. It also prevents employee exploitation by employers who are not willing to pay them well. The disadvantages of minimum wage are that it causes unemployment and high prices of goods. The consumers end up paying the extra costs.
The employers will reduce the number of employees when the minimum wage laws are implemented. This is because they want to reduce the production costs. Secondly, the unemployed lose a chance to learn on the job and gain experience which would have assisted them to get better paying jobs. The minimum wage laws usually affect the semi-skilled and unskilled workers. The government also intervenes in the market by putting price controls. The government may decide to put rent controls in the rent industry. The controls are designed to help the poor find affordable housing. It will enable them to live in a good house. However, these rent controls end up adversely affecting the same people it should be helping. The landlords refuse to build, maintain or repair the buildings due to the low profit that they are making (Schotter, 2008, 338). The poor end up living in uncomfortable or unhealthy conditions.
Factors Affecting the Demand for Labour
In a franchise there are several factors that would increase the demand for labour. A change in the use of the other costs or factors of production will influence the demand of labour in two ways.
There are those factors of production such as machines which have a substitute relationship with labour. If the franchise automates most of its billing services, the company will require fewer workers. This will reduce the demand for labour in the firm. There are those factors of production which are complimentary. An increase in the factor of production will cause an increase in the demand for labour. If the business owner gets more capital to expand the business, he will be required to hire more workers in the company. The demand for labour has gone up (Rittenberg, Tregarthen, 2009).
Where there is a change in the quantity demanded in the market, there will be an increase in the demanded labour. Suppose there is an increase in the demand of McDonald’s burgers and refreshments in the market? Due to the high demand in the market the price of the product will go up. The business owners will therefore be encouraged to engage the factors of production to provide higher amounts of the product in the market. The reverse relationship is true. If the quantity of the food product reduces, the labour demand will go down (Arnold, 2010, 291).
Wage Determination in free markets
Wages are determined by the interaction of the labour supply and demand curves in the market (Baumol & Blinder, 2008, 421). In a perfectly competitive market, there are many firms offering similar jobs. There are many workers who have the required skills and experience that is required. The workers also have all the information on the wages and employment opportunities in the market. In a perfectly competitive market, the firm takes the wage price to be the equilibrium point where the labour supply and labour demand interact as follows:
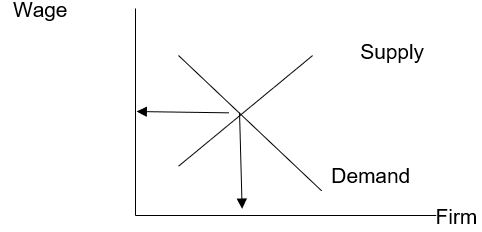
The labour demand curves however vary in different markets. Comparing the wages structures in the law and restaurant industries shows the wage differentials in the two markets. In the law industry, particular skills and education is required of the lawyer. Secondly, the marginal revenue of a lawyer is high. He has the capability to make a lot of money for his company. On the other hand, in the McDonald business, there are many workers who can perform the work in the franchise with a bit of on the job training. The marginal revenue per worker is lower compared to the marginal revenue of a lawyer. The supply curve for the lawyers is therefore inelastic while for the McDonald industry it is elastic. The wage determination structures for lawyers and the fast food industry will therefore be as follows:
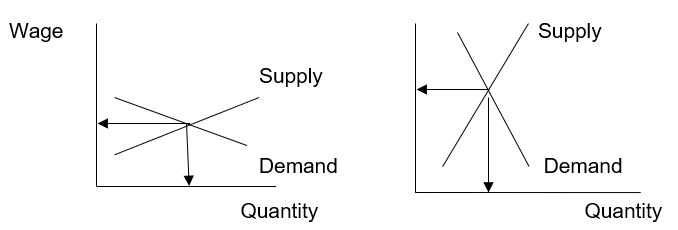
The law of diminishing returns
In economics customers are viewed as rational beings who are focused on maximising their satisfaction or utility as known in economics. The law states that as one increases the quantity consumed of a product it comes a point where additional units of the product do not give the same level of satisfaction to the consumer (Baumol & Blinder, 2004, 87). The extra units have lower marginal utility. If one had bought icecream, the twentieth scoop of the icecream does not give the customer the same satisfaction as the first scoop of the ice cream. This law does not apply for the addictive consumption scenarios. An addict will go to any lengths to get an extra unit of drug or alcohol. These cases are considered as anomalies.
The law of diminishing returns is applied to other areas such as labour. If a firm employs more workers it will result in higher output or productivity, however it comes a pint where additional units of labour do not give the same level of output as the initial units had. At this point the firm should not hire any more labour. The law of diminishing returns states that as one consumes a good, the total utility increases however the marginal utility reduces. The law of diminishing utility therefore plays a big role in the combination of goods that the individual will purchase from the market. He has limited money or a budget he is working with. He will therefore purchase the combination of goods that gives him the highest levels of marginal utility. It becomes a choice of allocation of his scarce financial resources.
Short-Run and Long-Run Costs
Production costs in the firm are analysed either in the long run or in the short run. In the short-run analysis, the only fixed factor of production is capital. It may not be possible to adjust the level of capital in the short run. However, all the other factors of production in the short-run are variable costs such as labour and raw materials. What about in the long run? In the long run, all the costs of production can be varied even the capital (Carbaugh, 2010, 77). The businesses however have to analyse their costs both in the short-run and in the long-run to ensure that the business is making a profit. The short-run and long-run costs are analysed in comparison to the business revenue both in the short-run and long-run.
References
Arnold, A. (2010). Microeconomics. Web.
Baumol, W. & Blinder, A. (2008). Microeconomics: Principles and Policies. Web.
Baumol, W. & Blinder, A. (2004). Microeconomics: Principles and Policies. Web.
Carbaugh, R.(2010) Contemporary Economics: An Applications Approach. Web.
Hoag, J. & Hoag, A.(2006). Introductory Economics. Web.
Mankiw, G.(2010). Principles of Microeconomics. Web.
Mankiw, G.(1998). Microeconomics. Web.
Rittenberg, L. & Tregarthen, T.(2009). The Demand for Labour in Principles of Microeconomics. Web.
Schotter, A.(2008). Microeconomics: A Modern Approach. Web.