Market for laptop computers
As mentioned in the case study, the research found a strong evidence of a positive relationship between computer usage and fatigue among school children. This implies that the more they use the computers the more fatigued they become.
Therefore, there is possibility that the usage of computers among school children will be reduced so as to keep them active for long in school. The result of the research is likely to lead to a reduction in the number of hours that school children spend computer usage.
Therefore, there will be a decline in the demand for laptop computers among school going children both in the short run and in the long run. The impact of the research can be demonstrated graphically as shown below (Perloff 2012).
Short run
Assume that the market for laptop computers is perfectly competitive and that the firms in the industry are earning supernormal profit, the initial equilibrium position is illustrated below.
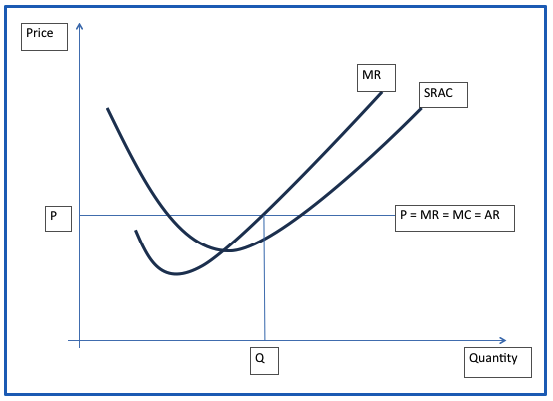
In the diagram above, the short run equilibrium price is P while the equilibrium quantity is Q. The equilibrium is attained at the point where the marginal cost equals price and marginal revenue (P = MR = MC).
At this point, the firm operating in the laptop computer industry will earn supernormal profit as illustrated above. The diagram illustrated above shows how the new research will impact on the laptop computer market equilibrium in the short run (Perloff 2012).
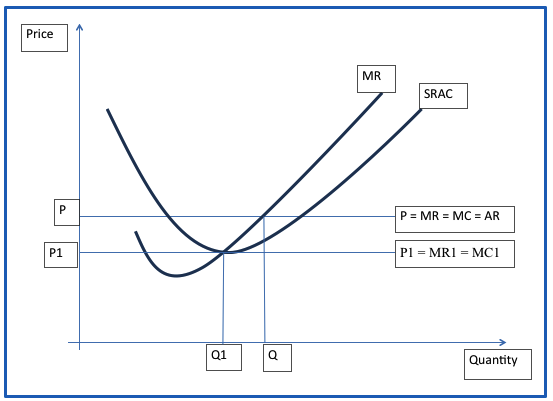
The results of the new research will result in the reduction of quantity demanded from Q to Q1. With the reduction of the quantity demanded by the consumers, the supplier will reduce the quantity they produce.
Since it is a competitive market, a reduction in quantity demanded will result in a reduction of the price. The new equilibrium price will be P1.
The firm will have a new equilibrium position that is the point where P1 = MR1 = MC1. At this point, the profits of the firms will be reduced from supernormal to normal profit (Parkin 2007).
Long run
The initial equilibrium position of the firm in the long run is illustrated in the graph below.
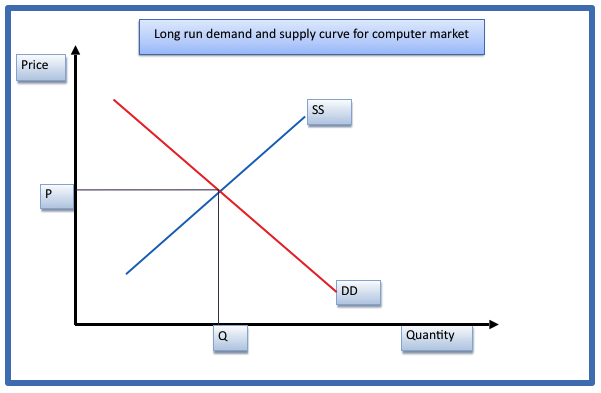
In the long run, the equilibrium is attained at the point where demand and supply curve intersects. The equilibrium quantity is given by Q while the price is P.
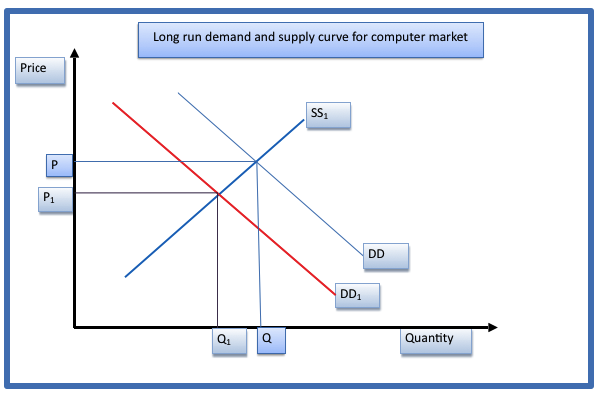
A reduction in the quantity demand will result in the quantity demanded from Q to Q1 will result in the reduction of the price of the laptop computers from P to P1.
Unemployment
Equilibrium in the labour market is attained at the point where labour supply equals labour demand. Any distortion of the equilibrium position either from the demand or supply side lead to disequilibrium (Parkin 2007).
- A construction worker laid off laid off because of a decrease in the number of new building projects is an indication of a reduction in the demand for labour. A decline in demand leads to a long term unemployment and a decline in the wages because it might take a long period of time before the decrease in the number of building project changes.
- A mining engineer who loses her job at a mine in an isolated area is likely to result in long term unemployment. The engineer may not be in a position to get a another job quite easily since the mine is isolated.
- Floods are seasonal and are bound to end after a period of time. The floods can cause havoc to the fruits and it may take a period of time before the fruits are ready again for picking. Therefore, a fruit picker laid off because of floods experiences a short term unemployment because they may be engaged again once the fruits are ready for picking.
- Competition can lead to a decline in sales hence loss of jobs. Therefore, a cook in a fast – food outlet who loses his job when a new restaurant opens across the street experiences short term unemployment. It is because the cook is likely easily getting a job from the competitors.
- A seamstress with little formal education who loses her job when the company she works for shuts down due to competition from overseas is likely to experience long term unemployment. With little formal education, the seamstress may find it difficult to get another job because the job market is growing to be increasingly competitive. Therefore, the number of workers having a large number of formal employment is increasing.
Reserve Bank of Australia’s monetary decision
Reasons for changes in the Australian economy
The recent changes in the economy of Australia were majorly caused by the global financial crisis. The global financial crisis was instigated by the overflowing of the housing bubble in the United States. This caused an increase in the default mortgage rates in the United States.
This triggered an increase in the amount loans issued by the commercial banks. The condition persisted for a period of time and resulted in a decline in the GDP hence the global financial crisis.
Apart from the global financial crisis, the conservative consumer behaviour also led to the reduction of consumption expenditure hence a decline in GDP.
Further, the value of currency of the company deteriorated significantly during this period. These factors resulted in the deterioration of the economic condition in the country (Parkin 2007).
How an interest rate cut by RBA may help address the current economic conditions
There are policies that can be put in place to mitigate the improve the economic condition of the country. A number of both the expansionary fiscal and the monetary policies can be used to correct the current economic condition.
An example of an expansionary monetary policy is reduction of interest rate. A decline in interest rates results in a decrease in the cost of borrowing. This will encourage borrowing hence an increase in the cost of borrowing.
In the AD – AS model, the aggregate demand curve will shift outwards as a result of the interest rate cuts. This causes the price level to increase. The aggregate supply curve will not be affected. The impact of the policy on the AD – AS model is illustrated below.
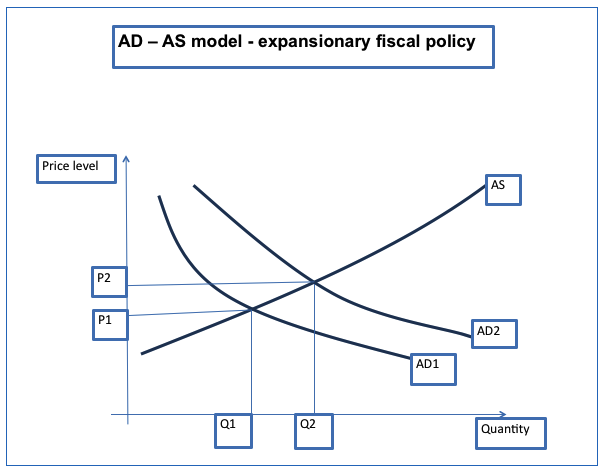
Expansionary fiscal policies shift the AD curve from AD1 to AD2. This results in an increase in the price level from P1 to P2. The amount of output also increases from Q1 to Q2.
Thus, it can be observed that the reduction of interest rates results in an increase in the price level in the economy (inflation) and an increase in the amount of output. An increase in output intern leads to a decline in the amount of GDP.
Thus, it can be observed that a decline in interest rates stimulates the economy (Parkin 2007).
References
Parkin, M 2007, Economics, University of Michigan, USA.
Perloff, J 2012, Microeconomics, Pearson Education, England.