An effective online instruction and assessment strategy depend on the learning environment, learning style, assessment tools, feedback channels, design application, and tool (Herrington, Oliver, & Reeves, 2012). Consequently, the instructor’s ability to transfer classroom techniques to online activities enhances student’s performance (Burrus, McGoldrick, & Schuhmann, 2007). The results from previous literatures revealed that assessment tool facilitates an individual’s learning curve. However, the design method and outcome must align with the objective of online learning programs. This paper provides an instructional guide to design and develop an effective online assessment for teachers in the UAE. Thus, the training guide will enhance the teacher’s ability to organize, develop, and implement an effective online assessment tool.
Audience
The training guide is appropriate for female teachers in the UAE.
The Training Objectives: Module
The training guide will improve teacher’s skill and collaborative effort to design and implement an effective online program. The trainer must categorize the training session into eight units, which include instructional design, screen design, interface design, capability of tool, user-friendliness, impact, communication skills, and team spirit (Herrington et al., 2012). However, the teacher must segment sessions into three modules, which include training content, assessment tool, presentation, and team spirit.
The training content model will address the instructional design, screen design, and interface design (Thaler, Kazemi, & Huscher, 2012). Consequently, the assessment tool module will address the capability of the tool, user-friendliness, and training impact. However, the presentation module will address communication skills and team spirit. The operation guide will assist teachers in preparing and designing an effective online assessment for student learning (Strom & Strom, 2013). Consequently, teachers can evaluate the learner’s needs based on the instructional design (Strom & Strom, 2013).
Module 1 (1 hour)
Module Objectives
- Compare different instructional design based on the learning needs
- Choose an effective instructional design
- Stimulate the learner’s needs with an appropriate screen and interface design
- Evaluate the training content
Training Content: Instructional Design
The choice of instructional design must align with the strategies of learning. The strategies of instructional design include organization, delivery, and management. However, the organization strategy describes the sequence and framework of the instructional design (Thaler et al., 2012). However, the sequence of instructional design includes job performance, simplicity, subject order, learning transition, dependent relationship, supportive relationship, and cause-to-effect. The delivery strategy describes the learning environment for the instructional design.
The channel of delivery include classroom, E-learning, M-learning, social learning, and lecture. However, the management strategy reveals the compatible variables of the learning process (Thaler et al., 2012). An effective management strategy influences the interactions between students and learning activities. It is important to categorize instructional design based on its attributes (Thaler et al., 2012). However, an effective online learning strategy must utilize one instructional design to boost productivity. Thus, teachers must understand the characteristics and benefits of instructional designs. Consequently, their ability to compare different design procedures will enhance the training content.
The list of instructional designs includes the ADDIE model, Merrill’s first principles of instruction, Dick & Carey model, Gagne’s nine events of instruction, Bloom’s learning taxonomy, and the ISD model. Thus, the teacher must analyze the instructional design models to enhance performance. The features of Merrill’s first principle of instruction include activation, demonstration, application, and integration. Consequently, the training team must enumerate the characteristics and attributes of Merrill’s first principle of Instruction.
The features of Dick & Carey Model include identifying, instructional goal, conduct analysis, analyze learners & contexts, performance objectives, assessment strategy, instructional strategy, design instructional guide, revise, and conduct program evaluation. However, the features of the Gagne’s 9 event of Instructions include gain attention, inform learner objectives, stimulate prior learning, present stimulus material, provide guidance, provokes performance, provide feedback, evaluate performance and enhance learning transfer.
The ADDIE Instructional Design
The ADDIE model is an instructional design used by educators to organize and present different career training to impact learning. The features of the ADDIE model include Analyze, Design, Develop, Implement, and Evaluate. As a result, teachers in the UAE can effectively develop and design an online assessment program using the ADDIE model. The first phase of the instructional design describes the goal, mission, and objectives of the learning program. Consequently, the design phase describes the learning process and framework. Educational instructors combine various assessment methods to create an effective delivery channel. The development phase combines the analysis and design recommendations to improve learning. As a result, the instructor formalizes the assessment procedures and training based on the instructional design. The implementation phase describes the learning process using an effective assessment channel.
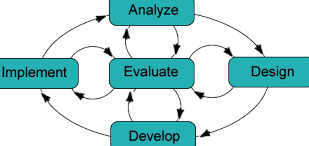
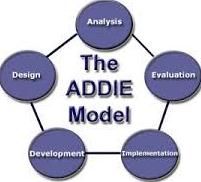
The facilitator engages the student with different training sessions to enhance learning. However, the evaluation phase assesses the purpose of training and its impact on the individual. Consequently, the summative or formative evaluation reveals the impact of the instructional design on the individual’s learning curve (Krathwohl, 2013). Thus, the ADDIE model improves the individual’s learning curve, evaluates the learning needs, combines different training materials, and evaluates the impact of the training design. However, other components of the training content include the screen and interface design (Krathwohl, 2013). Previous surveys revealed that students are either motivated or demoralized by the screen or interface design. As a result, the facilitator must establish an effective strategy that evokes the learner’s attention. Thus, educators must create a learning environment that provides a summative and collaborative approach to enhance cognitive experience (Krathwohl, 2013).
Drill for the Workshop Participants (1 hour)
The implementation process depends on the assessment questions. As a result, the trainee must develop assessment questions based on the instructional design. Thus, participants at the workshop will develop an assessment-guided question for ADDIE design.
The trainee must tailor the assessment questions to suit a specific audience.
Assessment questions for an effective design tool
- What is the problem statement for the online activity?
- What skill must I transfer to the student?
- What is the minimum requirement to understand the online activity?
- What is the duration of the course contents?
- How many changes are required during the program?
- Can I teach the problem statement online?
- Who identified the learner’s need?
- Why will the student proceed with the assessment?
- What is the period for the assessment?
- What is the limitation of the assessment?
As a guide for the workshop, the trainees will provide answers to these questions using the ADDIE model. Consequently, the trainer will evaluate the assessment questions based on the ADDIE model (analyze, design, develop, and implement). The drill will be the trainee’s assessment test for the workshop.
Simulation exercise: Design tool
The trainer will conduct a simple simulation exercise (using a participant assessment questions). Materials needed include laptop, PowerPoint program, Ms-Word, Internet service, and online apps.
Screen Design
The screen design facilitates the learner’s cognitive development. Previous surveys revealed that the screen design of an e-learning platform determines its performance. As a result, teachers must combine the elements of screen design to improve learning. For example, an online survey conducted in Ohio to test student’s response to career goals used a Penguin animation as the screen design. However, the Penguin displays a stimulating gesture when the e-learner fails a question. The survey revealed that students failed the test questions because they enjoyed watching the penguin’s display. However, the Penguin showed no emotions when the student answered correctly. Thus, the screen design and user interface must be developed to enhance student interactions with the module activities.
User Interface
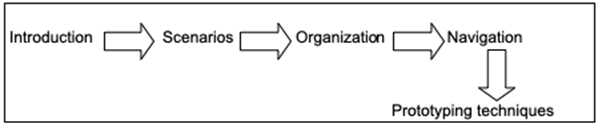
The user interface describes the visual component of the e-learning program. As a result, the facilitator must understand the importance of an engaging user interface. The user interface must be simple, organized, interactive, and engaging. However, the directions and navigation tools must be crisp and uniform. The user interface displays the soft-feel of the e-learning program (Kayler & Weller, 2007). As a result, a willing learner will revisit an engaging theme. The trainee must understand the basic elements of the user interface. Thus, the designer must apply supportive standards that provide a clear navigation, direction, and consistency. In summary, an interactive info-graphic empowers the online assessment program to enhance student’s learning experience. The trainer will conduct an interactive interface design test to enable the trainee develops user scenarios, a user object framework, navigation concept, and prototyping techniques.
Module Conclusion
The trainee must understand the concept and framework of an effective instructional design. Consequently, the structure of each module must have a rational, assessment strategy, and lessons learned section. The structural design will enhance the individual’s learning experience.
Module 2 (1 hour)
Module Objectives
- At the end of the training, the trainee will understand the importance of assessment tools for e learning.
- The trainee must adapt to different learning environment to satisfy the learner’s needs
- Ability to choose an appropriate assessment tool for the target audience
- Ability to evaluate the capability of tools used for online assessment
- The tool must promote and facilitate learning experience
Assessment Tool: Capability of Tool
The ability to design an effective assessment tool facilitates the student’s performance. As a result, an appropriate assessment tool improves the feedback channels of communication (Sewell, Frith, & Colvin, 2010). However, the instructor’s ability to categorize an assessment tool depends on the learning experience. Thus, an effective assessment tool correlates the student’s learning experience with formative assessment. The facilitator must organize the assessment program and feedback based on the learning outcome. The assessment will evaluate the learner’s experience and cognitive reasoning.
Thus, the ability to convey the teacher’s experience will determine the capability of the assessment tool. To evaluate the capability of the assessment tool, the trainer must compare the learning outcome with the design objectives. However, the teacher must avoid the bell curve assessment, inappropriate design framework, invalid assessment, and a poorly structured question. The evaluation scale must be uniform; however, some results must be graded higher. Thus, the assessment design depends on the learning objectives (Thede & Sewell, 2009).
Assessment Tool: User-friendliness
An appropriate assessment tool can engage students for an extended period. As a result, an effective assessment tool motivates the student’s cognitive reasoning. The design must align with the module objective to improve performance (Thede & Sewell, 2009). The list of teacher applications for online assessment includes the Learningpod, Moodle, Revision Quiz maker, Socrative, That Quiz, Poll everywhere, Testmoz, Coursmos, Gnowledge, Classmaker, Edmodo, and Joomla Quiz Deluxe. However, the facilitator must consider the target audience to enhance task comprehension.
Consequently, the facilitator must explain the online assessment techniques to avoid human error. The explanation will contribute to the overall performance of the learning program. The assessment techniques include pedagogical considerations, assessing interaction, and self-assessment (Thede & Sewell, 2009). However, the online components of an effective assessment technique include drop box, supplemental reading, instructional notes, external link, threaded discussion, synchronous chat environment, e-mail, and self-test. Please note that an effective assessment tool must serve as a student mentor and not an evaluation platform.
Module 3 (1 hour)
Assessment Tool: Impact
The proof of knowledge depends on the assessment technique; however, the assessment tool depends on the desired outcome. Thus, the teacher must determine the training content, and the proof of knowledge (Williams, 2012). The impact of the online assessment will form a cumulative process, a profile constructed strategy, or a student profile assessment.
Presentation and Team Spirit: Communication Skills
An effective online assessment tool must have the 4Ps of presentation. The teacher must explain the components of presentation, which include Plan, Prepare, Practice, and Present. The plan framework describes the relevance of the online program for the audience (Scardamalia & Bereiter, 2009). Consequently, the prepare strategy organizes the introduction, ideas, and the conclusion of the desired objectives. The practice strategy evaluates the trainee feedback, training content, and assessment tools to enhance performance (Scardamalia & Bereiter, 2009). Finally, the present strategy engages the student to improve the learning experience. Please note that the three Cs of communication supports the presentation strategy. Thus, the communication channel must be consistent, clear, and nice. To enhance team spirit, the trainer must be transparent, understanding, engaging, and compelling.
Consequently, the assessment tool must be meaningful, organized, specific, challenging, and innovative. The presentation strategy must include the desired outcome, the introductory module, and activities for each training session. Thus, the trainer must integrate new assessment strategy, administer a pre-assessment activity, provide instructional activities, punctuate the course outline with the assessment task, and develop a summative assessment.
References
Burrus, R. T., McGoldrick, K., & Schuhmann, P. W. (2007). Self-reports of student cheating: Does a definition of cheating matter? Journal of Economic Education, 38(1), 3-16.
Herrington, J., Oliver, R. & Reeves, T. (2012). Patterns of engagement in authentic online learning environments. Australian Journal of Educational Technology, 29(4), 59-71.
Kayler, M., & Weller, K. (2007). Pedagogy, self-assessment, and online discussion. Educational Technology and Society, 10(1), 136-147.
Krathwohl, R. (2013). A revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy: An overview. Theory into Practice, 54(7), 212-218.
Scardamalia, M., & Bereiter, C. (2009). Computer support for knowledge-building communities. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 7(3), 265-283.
Sewell, J. P., Frith, K. H., & Colvin, M. M. (2010). Online assessment strategies: A primer. MERLOT Journal of Online Learning and Teaching, 6(1), 297–305.
Strom, P. S., & Strom, R. D. (2013). Curbing cheating, raising integrity. Essential Readings Condensed for Quick Review, 72(8), 42-50.
Thaler, N., Kazemi, E., & Huscher, C. (2012). Developing a rubric to assess student learning outcome using a class assignment. Teaching of Psychology, 41(2), 113-116.
Thede, L. Q., & Sewell, J. (2009). Informatics and nursing: Competencies and applications: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Williams, J. (2012). Technology education for teachers. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media.