Introduction
The Emirati is a very interesting group of people of Arab ethnicity. They actually constitute the families that rule in the dynasties in the United Arab Emirates. These groups of people can be traced to have originated from the Bani Yas clan. Nonetheless, there are some other groups from outside that have been integrated into the Emirati community. The first institute of higher learning in the United Arab Emirates was the establishment of the UAE University in 1977. This university has been very significant in this fast-growing nation. The university was set to allow the young Emirati to be able to attain better and higher education needs as well as enhance the culture of the Emirati Community and the entire Arab society at large. While making an effort to prepare future leaders and workers, higher education in the country still faces problems of cultural, ethical, professional, and societal origin that seem to be very complex. These have actually slowed the pursuit of education by many of the young Emirati men. This paper shall address the factors that have affected career choices among young Emirati men. Specific focus will be on the educational and environmental aspects. The focus group is young men in the university; the second year to fourth who fall below the age of 25 years.
Educational and Environmental Factors That Influence Emirati Young Men Career Choices
The unemployment rate in the United Arab Emirates is about 12 percent and this is suspected to be even higher among the Emirati Young people (Holland, 1997). This is a very big deal since it may affect the future policymakers when addressing the community’s social problems. A research conducted by the international security revealed that council many young people are not actively involved in employment while the few that are in some form of employment prefer doing business (Fox, 2007). By assessing the social links between the unemployment rates, it very important for the study to highlight ion the educational factors that could be behind the trend while also addressing the impact that environment has had on the same ( Archer, et al 2003). Problems of unemployment due to societal ills often cause public and international security anxieties (Findlow, 2005).
Research on career choices is supposed to address a number of questions that are of interest with regard to the young Emirati men. Education and environment is very critical in that kind of study (Forstenlechner, 2010). Basically there is also need to address the issues of governance as well. Labor market and the role of culture, role of government and what individual felt about education and getting employment (Holland, 1997). On the social and expressive factors, many young men, about 58% are actually frustrated; feel insecure or depressed by the unemployment situation. Similar results have been the same for university student who say they would feel resentful if they ended up unemployed. Young men are increasingly facing pressure from the society to try sand find employment while at the same time the feel that there are very limited choices in the labor market (Holland, 1997).
Educational Factors
The education system in UAE which these young men go through has been accused of not preparing them well enough to face the challenges in the fast developing world. Many people feel that more Arab and English should be taught in universities and high school levels (Findlow, 2005). Communication can be a problems considering that Emirati young men hold their culture in high regard as it is the norm of the society of which they are part, to focus on religion, learn and master Arab culture. This means that they do not pay enough attention to English or consider it less important. However a greater percentage of young men have noted that their insufficient prowess in English language would greatly influence they employability (Findlow, 2005). It’s evident that in the current world, English has become a de facto language for official use whether it’s in office employment, business, or scientific research; most of the operations are conducted in English (Rees, et al 2007). There is often a problem for f foreigners to master English and even the native English speakers to struggle and achieve fluent English.
With greater advancement in technology and research investments, There is a concern that the non-English speaking people in Asia and Gulf could be discriminated from scientific knowledge and cannot therefore competitively participate and enjoy the shared knowledge made available by science. English more convenient for use in science support its use with basis of its practicality and efficiency (Holland, 1997).
Another important educational factor is the job market. Over the past 10 to 5 years, there has been a very strong campaign by employment advisors and employers for graduate jobs. This was stimulated by the fact that the choices for university were totally mismatched with the labor market available (Archer, et al 2003). For instance, it’s been observed that from the year 2000 to the year 2003, there was a big increase in the number of student who studied education, arts and religion (Holland, 1997). This in fact was a bout two thirds of the entire student population in the higher education. The remaining fraction chose to study other career lines like medicine, engineering and other technical sciences. Over the past decade or so, the students have not been making good choices since they considered higher education as a factor of social class rather than to earn economic worth, regardless of the fact that the income thereafter was a very crucial motivator for switching jobs. Some few Emirati young men even regard it as a way of escaping boredom at home (Archer, et al 2003).
It’s very important to increase the scope of studies in the universities so that the student can have the relevant skills for the job market. This has however been defended on grounds that the new job demands were not in existence ten years ago so educators could not invest in such skills at higher levels (Toledo, 2006). Since the inception of the first university in 1977, many universities have proliferated across UAE. There has been an increase in the number of people with post-high school education. A Variety of fields to study have also been introduced in the recent past (Archer, et al 2003). This means that the choice or career will depend on the skills acquired and the market availability. The choices are so diverse since many fields are available. However, many young Emirati men when asked why they attended university colleges, an overwhelming 43 percent responded that they just wanted to learn something new while a 26 percent went to college in anticipation of better employment. 0ne percent said they just needed something do so as to be busy (Godwin, 2006).
Attaining practical skills is as very important factor in education. This is also related to career advice from employers. Many young men feel that after college they need to be employed in the public sector. They also express a lot of criticism for many factors concerned in the private industry (Rees, et al 2007). The private sector is perceived to be offering lower wages and that there was very low job security with extended working hours (Archer, et al 2003). This means that many young men studied coursed they closely associated with public ventures and this in turn would affect their career choices in future (Godwin, 2006). Few of the people would opt to go to the private sector only when the working conditions are improved – salaries were high, flexible or shorter hour of work and provision of training programs. It’s also important to note that greater motivation would come from government when in emphasizes on education, training programs and creation of more job opportunities (Pines, 2003).
Environmental Factors
There are several factors that influence career choices fro Emirati young men. Basically the Emirati society was not very enthusiastic in advancement of education (Forstenlechner, 2010). This is attributed to the type of lifestyles that they have been leading. Some grow up and attend school with family responsibilities on their shoulders and hence focus on the careers that would be less demanding of their time. However there are several ways in which people have been observed to transform from college education into employment (Findlow, 2005). The Emirati young men are considered to be very conventional people. As a result, they make their career choices based on four basic characteristics: self efficiency – this is questioning whether they will be able to handle the tasks; outcome expectation – this is assessment of what would be the consequences of entering such a job; goals – these are questions like “what do I want to achieve in life” and contextual support and Drawbacks – these are actually the societal effects that one would have to deal with (Archer, et al 2003).
Self efficacy aspect can be linked to self-concept which can further be narrowed to career choice. Some people believe that they cannot do certain careers since they are very demanding. The contextual drawbacks and supports can be described as factors of cognitive career choice – preconditioning. Many young men are unable to venture into careers that they have not information about. This also relates to the consequences expected (Pines, 2003). This means that few people would want to venture into new field otherwise the majority will prefer studying the courses that have existed for so long and proceed directly to careers very familiar.
Career counseling is a strong factor that influences young people in their choices. Currently UAE lacks a sound system that is market – oriented to assist young people from universities. This has made the transition from universities to job market very complicated for the young men to cope up with. The lack of proper guidance can aggravate the problem more if not corrected in time (Crabtree, 2007). Essentially many young men make their choices for degree programs because of the influence from peers and family. Students are hence limited in their capacity to follow dreams and make independent decisions. Basically advices from non qualified individuals tend to incline towards what they hear in regular (Pines, 2003). Currently everybody is talking about Information technology and hence the number young people enrolling for IT are overwhelmingly high. Many young men have impracticable expectations of the career market.
The jobs market as its be identified is a great factor in career choice since its also common sense that one cannot choice venturing into a career that is non-existent and expect to be employed. The commerce sector in the United Arab Emirates attracts many young men; this is because many of the young people have ambition of entering entrepreneurship or getting employed on family business (Crabtree, 2007). Many of the young as cited prefer government jobs rather that from private firms. This could be a problem of unrealistic expectations that the young men have acquired to enter the job market (Godwin, 2006).
Misinformation leading to preconditioning is also a major environmental problem. Many people are currently investing degrees that would lead them to IT and e-commerce sectors because they think that these industries have very strong demands. They fail to realize that in a short while, these fields will be totally saturated. This means that many young people are not considering what they do as career selection but rather as work just for convenience (Pines, 2003).
Culturally, UAE is still young, modern and a fast developing nation. The country has embraced the latest technology and its advancement is evident in almost every aspect. However being an Islamic country, incorporating the western influence has often been a setback since Islam and the west do not mix. Furthermore the Emirati society is deeply rooted in their culture and the heritage from their founding fathers (Crabtree, 2007). They also hold strong stance on religion regarding Islam as a strong faith. These beliefs are very critical to the daily lives of the Emirati young men. This is because Islam is somehow patriarchal and the men will hold strong stands in religion. This can affect their choices in life like work. However, many the go through university education think more critically. Currently the cultural factors have very little impact on the decision individuals make regarding work (Vanheule & Verhaeghe, 2005).
Their General Life and Their Way of Defining Priorities
There have been reports that Emirati people in the Arab peninsula are very contradictory people. There are moments when the nation experience great events and incidences and times when they are hard hit (Rees, et al 2007). UAE is a not much of a victim of squandered government finances and poor policies like many developing nations. Yet, the country is making an effort to better the living standards of its residents. The effort the nation has made is great having grown from seven small impecunious regions in the desert to a modern state (Pines, 2000). With improving governance, the UAE was able to develop a diverse economy that is getting to the top of the world as one of the highest living standards. The nation depends on oil and the money generated has been used to construct very good infrastructure and to widen the scope of the nations’ economy. About half a century ago, there was not electrical grid, telephone systems, modern education centers, Indoor plumbing and public health facilities, the literacy level was only 20 percent. Very few women attended school (Pines, 2000). Currently the city of Dubai is characterized by skyscrapers. Abu Dhabi is becoming a very strong tourism and business center with great airport construction going on.
Emirati seem to have mastered the concept of self-reliant very fast and are working tirelessly towards it. Investing and venturing into new areas is becoming their way of life. The vision of the UAE leaders is to make Dubai a leader in world business. Looking at the trend at which the nation is growing, and then achieving that vision can be made possible (Pines, 2000). The society which used to be patriarchal with total oppression of women is completely transforming. Men are encouraged to spend more time with their families and engage in social and community activities (Pines, 2003). Many of the men have taken the initiative to help in house hold duties and encourage women to attend school, college and enter the job market (Toledo, 2006). The domestic duties can be shared since the conventional way of life in which only the man was a sole bread winner is fading away. Many women are getting degrees and increasing competitiveness of the country.
Women are no longer appreciated just as wives and mothers but also as prospective leaders. As the country moves forwards, so should the women. Emirati leaders believe that in the modern economy, men and women should be equal partners. However there is a very big challenge considering the fact that even in the western nations where women empowerment begun long ago has not been able to attain the perfect compromise (El-Sanabary, 2002).
The Emirati young men have in the past lacked motivation to study or work harder get employment. Many young men still do not see the need for college education. Some individuals in fact simple aspire to be silent partners to the foreign business that are being set up in UAE (Knight, 2006). It’s very difficult to inspire the need for education and improvement of ones credentials in a nation that is increasingly being seduced by subsidies. Currently, young Emirati men are presented with better study and working conditions; free education, better pay, short and flexible working hours and healthcare. Regardless of the government effort – Emiratization – to infuse the young Emirati into the market, very few people are seen to rise up to the challenge. In terms of technology, as much as the government is encouraging its use, many people still do not have the skills for competitive venture. Family has been a priority for the Emirati men though recently that has changed to a more balanced lifestyle (Pines & Yanai, 2001).
Men set their priorities differently. Some put their business first while others have been observed to extend more to family. This at times affects their work or studies. Family businesses are very common and are always passed on the next generation as they grow to form very large business empires. The major facto the influence priorities is friends and family (Crabtree, 2007). It’s been noted that families that believe strongly in business usually tend to get their children study business oriented degrees so that they can be back in business more productive. This limits choices for the said children. The families that still oppress women will see men not participate in the bringing up of the family. Family structure of Emirati is mostly extended though nuclear ones are often complete (Pines & Yanai, 2001). Children are only expected to leave their household when marrying. Housing is within a compound surrounded by walls. Their staple food is rice.
The Reason of Choosing Their Major
A critical moment in university education is when it comes to choosing a major. There are several researchers that have been carried out in UAE to investigate how the university students selected their major (Burt, 2007). As it has already been highlighted in the preceding text that the nation does not have proper system of career advisory body, student face tough moment in finding relevant majors for what they hope to do I future career wise. In one such research carried out by Gallacher and other asked students to create a list of four majors they would like to pursue: They were also asked to list some of the factors that lead to their choices of the majors. Surprisingly enough, about half of the students who participated in the research gave only one choicer of a major. They explained that they would have known the major they wanted before joining the university (Gallacher, et al 2010).
Personal interest was a major factor that was listed to influence the choices compared to family which is believed to be very influential (El-Sanabary, 2002). Previous researchers had indicated that job availability, wage level, social status of the job and family were more influential that personal interest. On the assessment of who had the greatest control over their choices about 75 percent of the participants indicated that a member of their family, though many of the student had attended career presentations before. Parent had greater influence especially the fathers (Gallacher, et al 2010). Friends were least on the ranking. The dependence on family on critical decision is seen to be even across a number of culture but more consistent among the Emirati community.
Having the awareness of the various majors is very important in decision making since with limited knowledge the decision is definitely limited. It’s interesting that the best known major that one can pursue is business. Over 70 percent of students can confidently mention it. Many students only know of few majors while some knew only one (Gallacher, et al 2010). The majors that indicate lower awareness among the student in UAE include international studies and Medical fields (Health sciences). It’s also worth noting that those students who knew about such uncommon majors were likely to specialize in these categories like pursuing political science of nutrition. Some specializations like education, law and engineering were hardly considered. Information technology is currently increasing in awareness (Crabtree, 2007). This means that the choice of majors could be limited by awareness problem since many students only know of business and art.
Perception of the majors is also an important influence. Basically the choice would be based on the perceived ease of finding a job, salary expectations and the social position such a career holds in the society (Burt, 2007). Business is usually preferred by the young Emirati men due to t he ease of finding a job after college and the salary expectation (Vanheule & Verhaeghe, 2005). Second to it, is the international studies, this however receive most selection due to its social ranking. Despite the students following their interests, it’s evident that this is swayed by discernment that business offered a broader category for the preferred job (Gallacher, et al 2010).
- Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivational Factors That Affect Choices
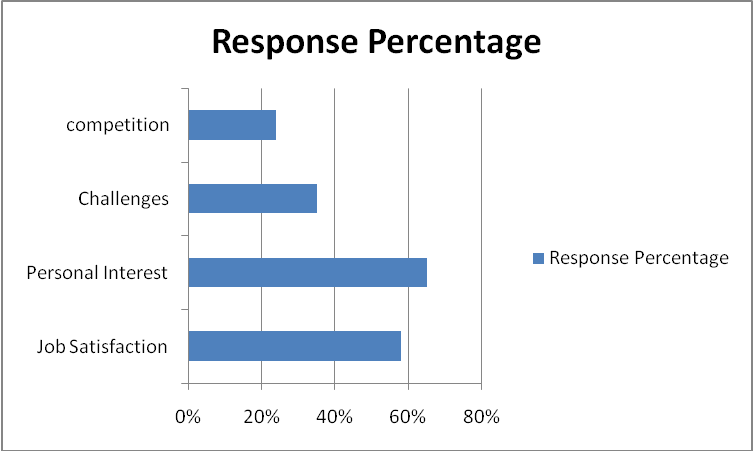
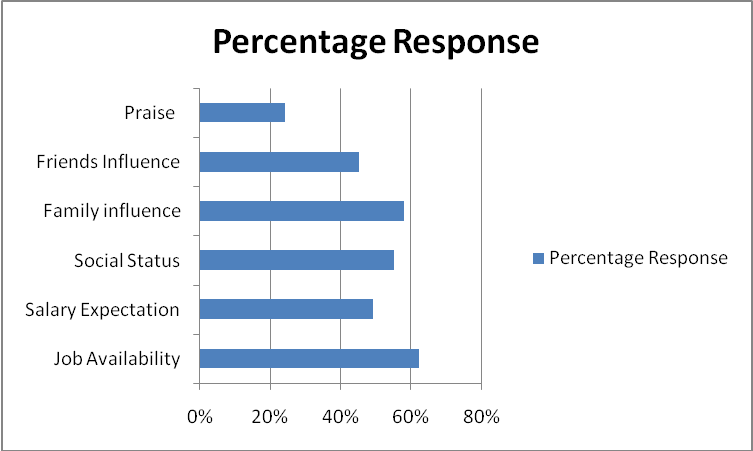
- The motivation towards choices of careers among the young Emirati men is also categorized under the major disciplines of motivation that have been developed by motivation theorists (Crabtree, 2007). The internal and external factors of motivation are the categories. Intrinsic motivation comes from within and it’s inspired by enjoyment to face challenge, interest in certain field, job satisfaction and competition. Extrinsic factors include the social status consideration by society, the pay, family and influence from friends, availability of jobs and appreciation from other people (Ali, 2008).
- The intrinsic motivation Emirati young men experience personal interest which includes the enjoyment they will experience in a certain area of specialization, zeal to face challenges in the modern world, the job satisfaction and being valuable in competitive world (Crabtree, 2007). The intrinsic motivation has been the perceived job market (ease to get employment), family influence, salary, social rank and praises from other people.
Conclusion
Career choice for young individual is a very important decision in life since of the choices made end up being a lifetime investment. This therefore means that before a choice is made, the young individual should be well informed about it and should be able to integrate other related factors. The decision should basically meet the personal needs and interest because career is something that one has to live with the rest of his life. However id based on other people opinion, it could end up being very frustrating. Its proper to listen to advice from family and friends even consider what the whole society says but the ultimate decision should be based on individual assessment of all the factors that are related to the career choice. Interest, ability to do the job and satisfaction should guide such decisions.
Reference
Al Ali, J. (2008). “Emiratisation: Drawing UAE Nationals into Their Surging Economy”, International Journal of Sociology and Social Policy, Vol. 28 No.9/10, Pp.365-79.
Archer, L., Hutchings, M., & Ross, A. (2003). Higher Education and Social Class. Issues of Exclusion and Inclusion. London: Routledgefalmer
Burt, J. (2007). Impact of Active Learning on Performance and Motivation in Female Student. Learning and Teaching in Higher Education: Gulf Perspectives. Vol 1. Zayed University.
Crabtree, S. A. (2007). Culture, Gender and the Influence of Social Change amongst Emirati Families in the United Arab Emirates. Journal of Comparative Family Studies, 38(4)
El-Sanabary, N. (2002). Education in the Arab Gulf States and the Arab World: An Annotated Bibliographic Guide. Taylor & Francis.
Findlow S., (2005). International Networking In the United Arab Emirates Higher Education System: Global-Local Tensions. Compare: A Journal of Comparative and International Education, Vol. 35, Issue 3, Pp 285 – 302
Forstenlechner, I. (2010). Workforce Localization In Emerging Gulf Economies: The Need To Fine-Tune HRM. Personnel Review. Vol. 39: Issue: 1: Pp 135 – 152
Fox, W.H (2007). The United Arab Emirates: Policy Choices Shaping the Future of Public Higher Education. CSHE Research and Occasional Paper Series. University Of California
Gallacher, D., Skuba, A. & Al-Bahri, R. (2010). Awareness and Perceptions of Available Major Programs by First Year Zayed University Students. Learning and Teaching in Higher Education: Gulf Perspectives, 7 (1).
Godwin, S. (2006). “Education And Emiratization: A Case Study of the United Arab Emirates”, the Electronic Journal of Information Systems in Developing Countries, Vol. 27 No.1, Pp.1-14
Holland, J. (1997). Making Vocational Choices: A Theory Of Vocational Personalities And Work Environments (3 Ed.). Lutz, Florida: Psychological Assessment Resources Journal of Career Assessment, Vol. 10, No. 2, 233-257
Knight, J. (2006). Internationalization of Higher Education: New Directions, New Challenges, the International Association of Universities, October, 2006
Pines, A. M. (2000). Treating Career Burnout: A Psychodynamic Existential Perspective. Journal of Clinical Psychology. In Session: Psychotherapy In Practice, 56, 1-10.
Pines, A.M. & Yanai, Y.O. (2001). “Unconscious Determinants Of Career Choice And Burnout: Theoretical Model and Counseling Strategy”, Journal of Employment Counseling, Vol. 38 Pp.170-848
Pines, A.M. (2003). Occupational Burnout: A Cross-Cultural Israeli Jewish-Arab Perspective and Its Implications for Career Counseling. Career Development International. Vol. 8, Issue 2, Pp 97 – 106
Rees, C., Mammon, A., Bin Braik, A. (2007). “Emiratization As A Strategic HRM Change Initiative: Case Study Evidence from A UAE Petroleum Company”, the International Journal of Human Resource Management, Vol. 18 No.1, Pp.33-53.
Toledo, H. (2006). The Problems and Prospects of Emiratization: Immigration in an Imperfect Labor Market, Dubai Economic Research Awards, Dubai.
Vanheule, S. & Verhaeghe, P. (2005). Professional Burnout in the Mirror: A Qualitative Study in Lancanian Perspective. Psychoanalytic Psychology, 22: 285-305