Introduction
Ethnobiology refers to a scientific approach of studying the relationship between human beings and their interactions with the environment (Bornstein 2010).
It is evident that the human population is going to pose serious health risks if corrective measures are not adopted. This paper is an assessment on drinking and bathing water in Sabah.
Background
Sabah is a Malaysian state located in the eastern side of the country and which borders Sarawak and Indonesia. This is Malaysia’s second largest state with a population of about 3,117,405 people occupying its expansive 73,631 km2 (Yusuf 2009).
Sabah is a poverty stricken area and residents hardly afford a comfortable life. It is evident that their lives are daily struggles dictated by nature despite having fertile agricultural lands, scenic mountains and its strategic location near the sea.
This means most people do not have access to clean drinking and bathing water (Ellington 2008).
Poverty
Poverty refers to a state of being in dire need of help in terms of food, clothes and shelter. This region has a high number of poor people and this means water is a precious commodity here.
Illiteracy is a significant factor that contributes to high poverty level in this region and this has forced these people to remain poor even though they are endowed with natural resources (Bowie 2011).
Although, this state exports palm oil and petroleum it has a high poverty index since this trade is controlled by minority groups. Poverty makes people unable to access drinking water except from the hydro plant located near the town as shown in the diagram below (Bowie 2011).
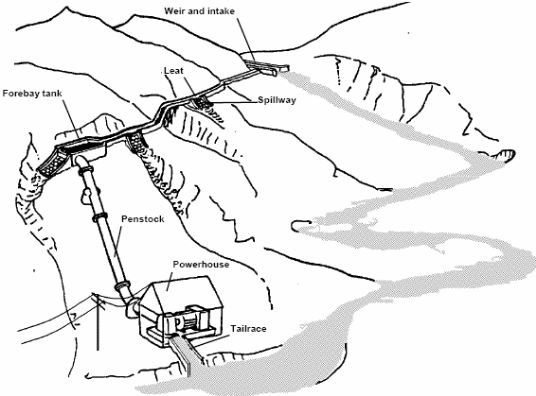
In addition, the hydro power stations serve many people and this means its supply capacity is overstretched. Water rationing cannot be ruled out since every block must get water according the number of buildings and inhabitants (Bowie 2011).
Unemployment stands at 60 % despite this state having many resources and opportunities to exploit them (Hill 2012). This state was colonized by the Japanese before the Second World War. Slave trade was a thriving business since this place had a ready supply of human labor to European countries.
The British colonized this state, occupied most of the fertile lands and controlled port activities. However, the Second World War remains a sore memory in this region due to the economic and human suffering experienced during that time (Bowie 2011).
They did not settle in rural areas but instead lived and constructed water supply networks in urban centers.
The local government is in charge of running its affairs and should develop its water supply to maximize on the state’s potential to ensure all citizens get clean water.
There is the need to establish industries in remote regions to ensure water is tapped from the sea for their use and also for the local communities (Flag Fen 2009). Local communities enjoy some services like security, transport and water supply when industries are located close to them (Hill 2012).
However, the available hydro plants are not enough to supply clean water to the entire population. The diagram below shows the number of blocks served by the water plant (Bowie 2011).
The urban population enjoys a developed transport and communication system with developed road and rail networks, airport, sea port and a variety of local transport system (Bornstein 2010).
The local urban authorities have offered an efficient transport that eases movement of traffic and people from one place to another. However, majority of the rural areas experience water shortages due to various factors.
First, the rural region is mostly mountainous and constructing water plants and supply network are a serious challenges.
In addition, constructing a water network to supply water to the higher mountainous region is next to impossibility (SAWO 2011).
Thirdly, most locals are peasant farmers engaged in subsistence production; therefore, constructing an efficient water system in this region will be a waste of resources. Instead, the local authorities should drill bore holes for them.
Objectives Analysis
Problem-Based Objectives
The urban population has already proved that there is a possibility of constructing a hydro plant to pump water from the sea to the nearby buildings (Yunus 2009).
Even though, supplying water to rural areas may be expensive this will be a long term investment that will ensure people get sufficient clean water for drinking and bathing. The availability of clean water guarantees residence a healthy environment (Hill 2012).
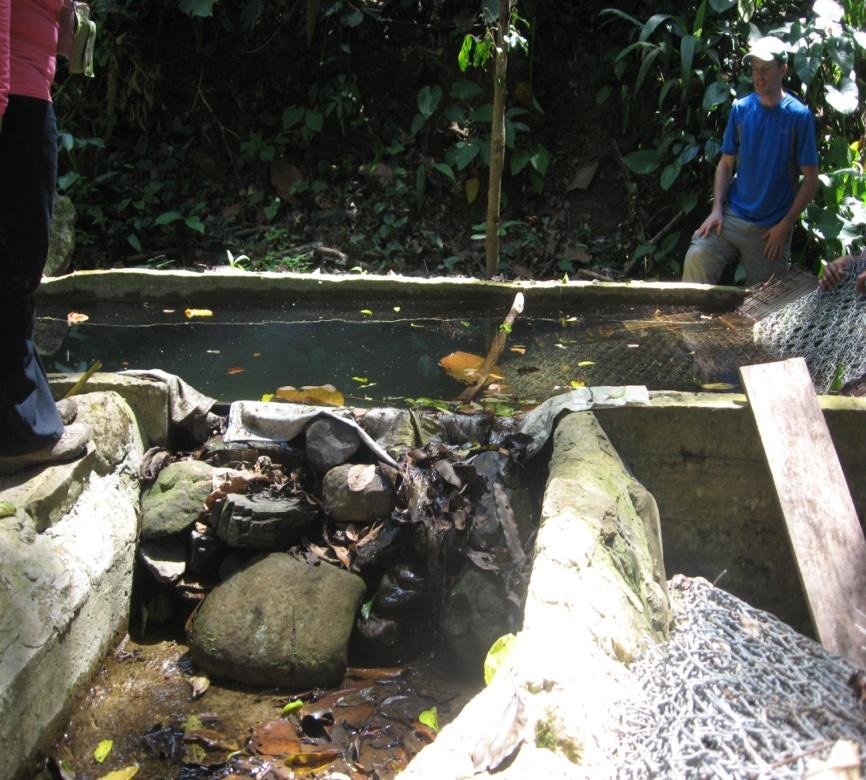
Currently, there are many water treatment plants that ensure all residents get clean water for domestic use. In 1989, the Flag Fen Wastewater Treatment Works was completed and serves a population of about 190, 000 people (Flag Fen 2009).
This is a private company that offers water and sewerage management services to the local population. The diagram below shows a typical settling tank that ensures visible dirt is collected and sieved off (Bowie 2011).

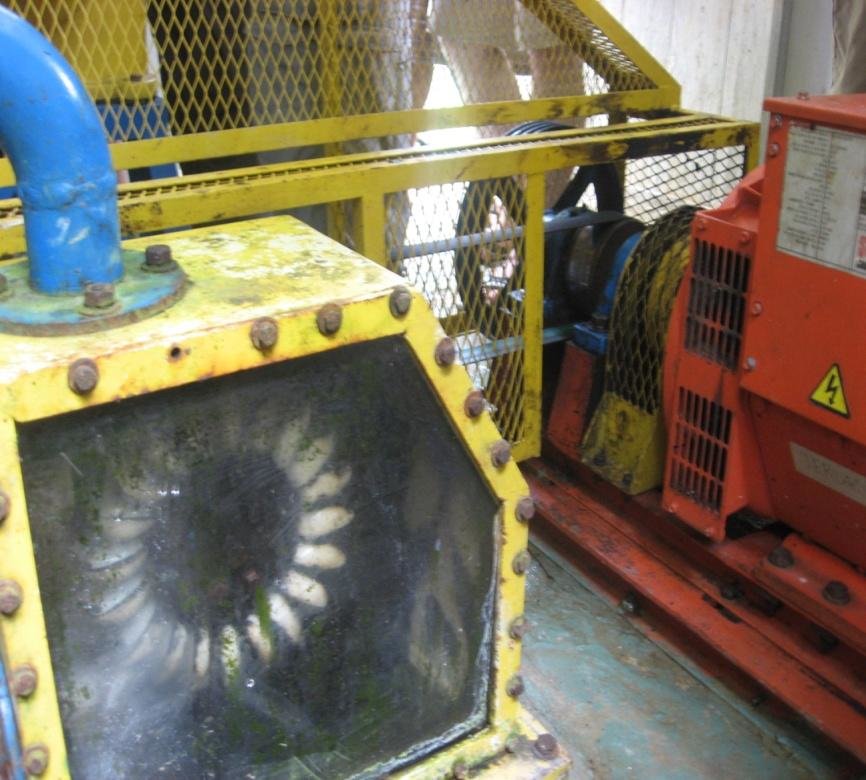
Secondly, this place is endowed with natural resources that are not available in many other states. Most locals are employed in saw mills and other companies interested in oil and petroleum explorations.
The funds generated from these activities can be used to finance other hydro projects by purchasing more powerful generators and turbines that will pump more water than this one shown below (Bowie 2011).

Industrialization is an important aspect of social and economic development in all regions. This state has adopted the use of modern port facilities and transport system.
However, there seems to be a slow pace in adopting modern technology in rural areas (Yusuf 2009). This state should use modern water pumps that will facilitate the distribution and supply of clean water to all regions.
The village population is engaged in subsistence farming due to lack of water and limited farming technology. There is no way these people can use their drinking water for irrigation since it is a precious commodity yet the government has focused on other economic aspects and forgotten this sector (Ellington 2008).
Therefore, there is the need to revamp water supply by using channels, pipes and generators to supply water for domestic use.
In addition, the proximity of this region to the sea has exposed it to water pollution due to the high number of oil spillage and other trash (SAWO 2011). Moreover, the sea is located in the lower end of the town and this means all rain water washes the dirt downstream (Yunus 2009).
People must establish dump sites to deposit all garbage that is usually washed to the sea. In addition, they must have clean containers to keep water to avoid contamination.
Community health is a pillar to healthy living and no country can develop without equipping its health facilities. This state has neglected and failed to provide clean drinking and bathing water to the locals.
Health is a basic human need that surpasses all other needs; therefore, states must ensure their citizens get clean water for domestic use.
Non Governmental Interventions
There are various non governmental organizations that provide sanitation services to the local population. For instance, the Flag Fen Wastewater Treatment Works is a private company that offers water treatment and supply services (Flag Fen 2009).
There is a connection between the local population, government and non governmental; organizations.
The government gives tenders to private companies to conduct research on water management and present their proposals for consideration to undertake various projects. In addition, the local population offers labor for these organizations and market for their products.
The government ensures these organizations perform their duties according to the terms and contracts stipulated by their contracts. Therefore, the government’s role is mainly supervisory. Some organizations work with local authorities to ensure water catchment areas like Yayasan forest.
In addition, women groups like the Saba Women’s Action-Resource Group (SAWO) are now calling for the government to intervene and regulate commercial logging to protect local forests (SAWO 2011). Their efforts will play significant roles in ensuring water catchment areas are protected.
Conclusion
Development of clean water supply systems is a conscious activity that involves proper planning and executing the proposed recommendations. Having natural resources is not a guarantee that a nation is set to develop if the resources are not exploited.
References
Bornstein, D. (2010). Social Entrepreneurship: What Everyone Needs to Know. New York; Oxford University Press.
Bowie, A. (2011). The Politics of Open Economies: Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Thailand. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Ellington, J. (2008). The Power of Unreasonable People: How Social Entrepreneurs Create Markets that Change the World. New York: Harvard Business Review Press.
Flag Fen. (2009). The Flag Fen Wastewater Treatment Works. Flag Fen. Retrieved from www.tcirenewables.com/downloads/brochure_flagfen.pdf
Hill, H. (2012). Malaysia’s Development Challenges: Graduating from the Middle. London: Routledge.
SAWO. (2011). Sabah Women’s Action-Resource Group. SAWO. Retrieved from www.en.sawo.org.my
Yunus, M. (2009). Banker to the Poor: Micro-Lending and the Battle against World Poverty. New York: Public Affairs Press.
Yusuf, S. (2009). Tiger Economies under Threat: A Comparative Analysis of Malaysia’s Industrial Prospects and Policy Options. Washington: World Bank Publications.