Abstract
The paper discusses the topic of energy-wasting and the patterns of energy consumption that can be outlined. It utilizes the SWOT matrix and the System (Stakeholder) Map to analyze the past, present, and future trends and habits contributing to the development of the problem. In addition, the study provides the findings of the literature review and suggests a possible solution to the issue.
Introduction
The presented assignment is focused on the problem of energy-wasting. The motivation for the choice of this topic is that currently, the world’s population contributes to the inefficient use of energy regularly, while many individuals are not aware of the impact of their actions (Murray et al. 2016). The problem of the research is that patterns of energy waste are ineffective and contribute to the problem of energy waste. The thesis of the study is that the global population should change its energy consumption habits. The previous research raises the question of the necessity of optimization of energy consumption.
Literature Review
The purpose of the research is to identify the factors that contribute to the development of the problem of energy-wasting. In addition, the study aims at analyzing the possible options for making a change in the field and eliminating the effects of the issue, using the evidence from recent studies. The majority of the authors investigating the issue agree that many people are not aware of the causes and consequences of energy-wasting (Jabłońska, Jursová & Billewicz 2015). In addition, the unsustainability of energy consumption and production has become an acute problem globally (Caetano et al. 2017). These arguments are feasible as they correspond to the population’s habits related to energy-wasting that can be observed today. This study argues that the measures to reduce inefficient energy consumption should be taken as soon as possible.
Methodology
The study was carried out in April-June 2019 in Sydney, Australia. The primary methods utilized for this research were:
- Literature review
- Exploring the design space (the SWOT analysis and the System Stakeholder Map)
The study involved a systematic literature review, during which the evaluation of peer-reviewed articles on the topics of energy-wasting and energy consumption was performed. The selection of works was made according to three criteria, including their 1) timeliness and applicability, 2) the presence of the analysis of factors contributing to energy-wasting, 3) the inclusion of statistical data or references to other studies in the field. After the systematic literature review had been performed, the design space was explored using the SWOT analysis of the past, present, and future trends in energy consumption and the population’s habits leading to energy-wasting (see Appendix I). The studies by Caetano et al. (2017), Hao et al. (2015), World Energy Council (2016), and Zarzo and Prats (2018) were utilized to analyze the existing tendencies. In addition, the System (Stakeholder) Map was developed to analyze the factors associated with the issue, including the lack of government regulations and personal habits (see Appendix II).
The project was developed based on the existing studies in the field as well. For example, the works by Marcinkowski and Zych (2017), Wa’el, Memon, and Savic (2017), Gul and Patidar (2015), and Mohamed et al. (2015) were utilized to analyze the problems associated with the use of electric kettles. The analysis showed that many global households contribute to energy-wasting due to overfilling kettles and boiling water inefficiently. To find the solution to this problem and develop the model of the Innovative Kettle, the recommendations by Khan and Halder (2016) and Fiorini and Aiello (2018) were considered. Thus, the justifications for the suggested modifications in existing models of kettles and the design of the new model are the existing studies that reveal that the current individuals’ habits contribute to energy-wasting and should be changed.
The study intends to include unstructured user observations to analyze the patterns of individuals’ behaviors related to energy consumption. The participants will be the local population willing to share their energy consumption habits. The individuals will be asked to record the patterns of the utilization of kitchen appliances, including the amount of water they use and the number of boiling times. The selected design concept is the Innovative Kettle that will help the users to avoid overfilling by using the Smart Boiling and the “Who is Boiling?” functions. In addition, the design involves the implementation of an insulated shell and a timer, which will allow individuals to boil water for a particular time and keep it warm. No changes or iterations in the design are expected.
Implementation
The Innovative Kettle is designed to reduce users’ energy costs, support the environment by eliminating the problem of energy-wasting, and help individuals to have timely access to water. The System (Stakeholder) Map (see Appendix II) of the issue of energy-wasting was used for the development of the Innovative Kettle; it describes the factors contributing to this problem. It was based on the findings of the current studies on energy consumption and waste patterns.
Results & Evaluation
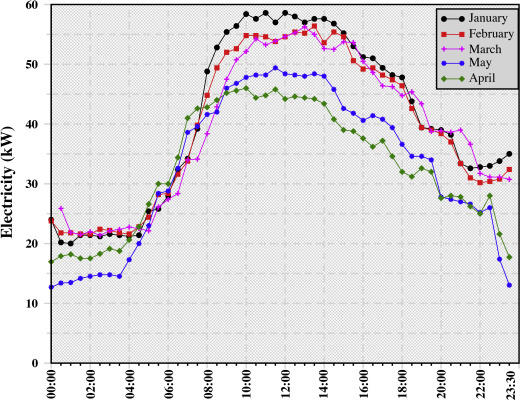
The key findings of the literature review show that individuals in many countries tend to overfill kettles or boil water several times instead of using it efficiently. In addition, it was found that the patterns of energy consumption vary at different times of the day and months of the year (see Figure 1). If the real data were analyzed, the unstructured observations and individuals’ records would be utilized to outline possible patterns of energy-wasting.
The SWOT analysis (see Appendix I) showed that the past trends and present habits associated with energy consumption differ from the environmental, socio-cultural, economic, and legal perspectives. For instance, access to renewable energy has allowed for reducing energy waste compared to the previous decades; in addition, necessary legislation has been implemented in many countries. However, high financial investments may be needed to eliminate the problem. Moreover, many individuals continue to use energy ineffectively and contribute to the development of the problem. The results of the literature review correspond to the findings of the presented study. Thus, according to the study’s purpose, the factors that cause the problem were identified.
Discussion
Currently, the patterns of energy-wasting among the global population reveal that energy consumption remains an acute topic that should be resolved. The implementation of environment-friendly designs, such as the Innovative Kettle, can address this problem without forcing individuals to change their habits entirely. The possible limitation to using such technologies on a global scale is the lack of public awareness of energy-wasting and its consequences. In addition, there are ethical constraints as the organizations cannot accuse individuals of behaving inappropriately and causing significant damage to the environment. The possible solution is to enhance the understanding of the problem among the population gradually while continuing to design environment-oriented products.
Conclusion
The study shows that the global population should change its energy consumption habits to eliminate the problem of energy-wasting. The possible limitation of this research is that it is focused on one aspect of the issue, rather than other causes of the problem. The future work should discuss other habits and trends that lead to energy-wasting and suggest products that the population can use daily to minimize the impact of the cause.
Appendices
System (Stakeholder) Map
Sustainability SWOT Matrix
Reference List
Caetano, NS, Mata, TM, Martins, AA & Felgueiras, MC 2017, ‘New trends in energy production and utilization’, Energy Procedia, vol. 107, pp. 7-14.
Fiorini, L & Aiello, M 2018, ‘Household CO 2-efficient energy management’, Energy Informatics, vol. 1, no. 1, Web.
Gul, MS & Patidar, S 2015, ‘Understanding the energy consumption and occupancy of a multi-purpose academic building’, Energy and Buildings, vol. 87, pp.155-165.
Hao, H, Liu, Z, Zhao, F, Li, W & Hang, W 2015, ‘Scenario analysis of energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions from China’s passenger vehicles’, Energy, vol. 91, pp.151-159.
Jabłońska, M, Jursová, S & Billewicz, K 2015, ‘A split personality?–differences in people’s behavior in the field of energy conservation at home and in the workplace’, Rynek Energii, vol. 5, no. 120, pp. 119-123.
Khan, I & Halder, PK 2016, ‘Electrical energy conservation through human behavior change: perspective in Bangladesh’, International Journal of Renewable Energy Research, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 43-52.
Marcinkowski, A & Zych, K 2017, ‘Environmental performance of kettle production: product life cycle assessment’, Management Systems in Production Engineering, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 255-261.
Mohamed, AM, Al-Habaibeh, A, Abdo, H & Elabar, S 2015, ‘Towards exporting renewable energy from MENA region to Europe: an investigation into domestic energy use and householders’ energy behaviour in Libya’, Applied Energy, vol. 146, pp. 247-262.
Murray, DM, Liao, J, Stankovic, L & Stankovic, V 2016, ‘Understanding usage patterns of electric kettle and energy saving potential’, Applied Energy, vol. 171, pp. 231-242.
Wa’el, AH, Memon, FA & Savic, DA 2017, ‘An integrated model to evaluate water-energy-food nexus at a household scale’, Environmental Modelling & Software, vol. 93, pp. 366-380.
World Energy Council 2016, World energy resources, Web.
Zarzo, D & Prats, D 2018, ‘Desalination and energy consumption. What can we expect in the near future?’, Desalination, vol. 427, pp.1-9.