- Abstract
- Introduction
- Entrepreneurship in Small business and Leadership in Freelance and Real Estate
- Overview of Small Businesses and Freelancing
- Importance of Small Businesses and Freelancing
- Leadership in Small Businesses and Freelancing
- Applications of the Study
- Implications of Research
- Conclusion
- References
Abstract
The goal of the paper is to examine the concept of freelance work and its potential growth in the context of contemporary financial forces. The dialectic learning method, founded on a network of public and corporate scientific techniques, system evaluation, and other approaches, serves as the report’s theoretical foundation. The analysis facilitates the ability to separate the favorable and unfavorable elements of the growth of freelancers in the worldwide market based on examining economic data and demographic surveys.
Introduction
Small businesses and freelance work are emerging segments within the current markets. As flexibility is more commonly employed both by companies and individuals aiming to establish start-ups, industries are becoming more reliant on creative business ideas as well as a more digitalized workforce. The global economy is highly reliant on emerging organizations as well as freelance positions, a phenomenon that can be attributed to the changes generated after the COVID-19 lockdown. The benefits include opportunities for autonomy and independence as well as the growing popularity of both sectors. However, ineffective leadership in freelance work, as well as the instability of the external environments, affect online job positions as well as small businesses and work in real estate. Nonetheless, the growing interest in the segments mentioned above generates opportunities for development and operations within these particular sectors.
Entrepreneurship in Small business and Leadership in Freelance and Real Estate
Are small business entrepreneurship, freelancing, and leadership areas of concern? The current study paper illustrates research in the following subtopics: a brief overview of entrepreneurship and freelancing, the importance of small businesses, leadership in freelancing, and small business functionalities. It is important to note that the job market as a whole is changing as companies switch from older business models to newer, more cost-effective workforce management techniques. As a result, freelance work is becoming more prominent, and entrepreneurship is more accessible due to the emerging demand for innovation and the lack of barriers limiting individuals from generating start-ups. This paper highlights the growing demand for new businesses and freelance positions, the need for self-management regarding leadership, and the instability as well as positive elements correlating with the segments.
Freelance work is a potential avenue for jobs and small businesses. It is common practice in many Western nations and is expanding rapidly worldwide. For people all across the world, freelancing is a new career path. It is essential to establish the significance of this line of jobs in illuminating the market’s shift to modern business architecture. Modern business predicates understanding and proficiency using recent desktop and data innovations. Thus, innovation employed in entrepreneurial establishments, as well as the digitalization and flexibility of freelance positions, highlight the current dynamic of the global economy and job market.
Overview of Small Businesses and Freelancing
Freelance employment was once considered unreliable and unsustainable both from an economic and social standpoint. However, as the market shifted, the sector became more widespread. The majority of contemporary multinational firms outsource certain positions to lower the cost of manufacturing and workforce management. As a result, freelancers are in demand in multiple various areas. A freelancer is a self-employed individual who operates on the job market through flexibility and professional autonomy. Doctors, surgeons, journalists, interpreters, attorneys, and business advisors are included. Likewise, small businesses established through entrepreneurial efforts facilitate similar traits such as independence and creativity. According to researchers, small businesses generate more than 84% of the global GDP and facilitate the establishment of half of the job positions. Moreover, because more than 100 million small organizations are created yearly, the sector will continue to grow (Alsaaty & Makhlouf, 2020). However, the challenge is surviving long term as only 20% of such organizations are on the market within the first decade of their establishment. Entrepreneurs of small businesses encounter difficulties navigating the market, especially under the condition of limited resources.
It is vital to highlight that while freelance jobs do not constitute the majority of the positions on the job market, the industry is changing. One of the reasons why various online jobs are available is COVID-19 and the restrictions that companies have faced, which generated the need for remote workers. By employing freelancers, organizations can obtain high-quality personnel without additional costs such as renting office spaces, purchasing equipment or paying salaries despite the lack of need in case the position is only employed for a short-term project. However, the freelancers themselves are faced with barriers, as established by researchers. Namely, it is reported that a lack of economic stability, clear work boundaries, and the inaccessibility of bonuses hinder efficiency (Nawaz et al., 2020). Thus, both benefits and negative aspects correlate with the current job market shift.
Freelancers are relatively affordable, have particular expertise, and are skilled at digital work. Companies are switching to new hybrid approaches to meet their workforce requirements, which is why establishing freelance positions is an effective technique (Stephany et al., 2021). Numerous entrepreneurs with the talents that businesses require are joining the trend of outsourcing to smaller businesses that may be flexible and cost-effective. For businesses that avoided contingent labor but now recognize its usefulness, COVID-19 has established an important message.
Importance of Small Businesses and Freelancing
The emotional value of local businesses to community organizations is rooted in the buying and trading among peers and coworkers. The monetary benefits of making local purchases further highlight individual companies’ importance in rural areas and big towns. As a result, economics highlight that the trend of company displacements affects the economy of the areas from which the organizations migrate (Einiö & Overman, 2020). Furthermore, small businesses generate job openings and serve as the foundation for the largest US companies. Customers are excellently contributing funds to their neighborhood by supporting small local companies. High amounts of cash produced by a flourishing neighborhood corporation translate into larger tax outflows, particularly local property taxes. A profitable small company may raise property prices across a neighborhood, enhancing household incomes and increasing local governments’ revenue from property levies.
Small companies are also prone to development if effective strategies are employed. Many of the current giants in the software business started as “hobbyists,” building hand-assembled devices in small workshops and officers. Instances of how a small company’s innovative ideas can revolutionize the world can be highlighted through Google and Amazon. Large enterprises that start as small frequently remain in the area where they were initially founded (Hawkes, 2018). The presence of a major organization in a town might further aid in job-making and monetary incentives, fostering an environment favorable to the growth of new small enterprises.
Similarly, freelance work correlates with multiple benefits both for the individuals operating in the segment and companies requiring assistance. Online work has emerged as a driver of economic expansion. Self-employed people are job generators through their work and skills. Such employment is generated every time a contractor leaves a more extensive organization to work autonomously full-time (Paek, 2021). Regular employment correlates with monthly salaries, taxes, and insurance. When a corporation hires a freelancer under a contract, the only expense is the work that the individual does with no additional costs. This entails no employment-related overhead expenses. This provides firms with ample funds to invest in an expansion that may eventually result in additional earnings to support local economic development.
Independent contractors can reside and work everywhere because of the nature of their profession. Digital migrants have become more prevalent due to the growing demand for freelance jobs (Merritt, 2021). This enables contractors to reside and spend profit on other important corporate areas, such as development and research. The phenomenon can lead to a boost in economic growth in both large cities and rural towns. The expansion of the freelancing economy will result in one thing, which is the overall development of the industries operating with freelance positions. The global economy will experience benefits from an increase in online job opportunities, which positively affects both companies and individuals who decide to aim for autonomous jobs.
Leadership in Small Businesses and Freelancing
Corporate success depends on effective management, especially during a crisis. It is practically challenging for firms to develop and flourish without competent administration, which is essential in a dynamic market. Small organizations frequently require strong direction and resilience. Such firms, whose workforces may only include several people, risk disintegrating if their organizational hierarchy is threatened and unstable. A company requires guidance, a strong vision, and solid objectives. As a result, everyone associated with the business works toward a common objective to increase productivity (Kotlar et al., 2018). Regular guidance and supervision are also crucial despite the demand for independence. Although many individuals are autonomous and can complete tasks with less direction, leaders can implement strategies to offer assistance and support. Certain businesses may have rigorous timelines and guidelines, while others focus on transformational styles in which the leader leads by example. Contract workers often believe that having strong management qualities is less critical for individual contractors who operate alone or remotely, yet certain norms are still to be established.
It may be evident that independent contractors only manage themselves, which is why leadership is redundant. In addition, the majority of freelance workers express the desire to have no boundaries regarding leadership and organization duties through independence. However, freelancers are often hired by companies that require work on specific projects or have positions that do not correlate with long-term collaborations with employees. In this case, leaders indirectly affect freelance work. However, researchers highlight that the leadership style effective under these conditions allows for autonomous management and work flexibility (Flood, 2019). Thus, the managers are to supervise project flow while allowing freelancers to remain independent and autonomous in how they approach their tasks.
Effective leaders motivate their followers to perform at a high level. With the appropriate instruction, such experts also have the propensity to develop and manage successful business plans (Paek, 2021). Training, leadership skills, and business stock values are strongly correlated. Managers with the appropriate training guide their teams to higher levels of effectiveness and production. These, in turn, result in more sales and better income margins. Since superior expenditures in people, and capital provide higher dividends than those made by firms with less emphasis on their talent management, effective leadership aids in the improvement of economic success.
In conclusion, small and independent businesses are important for the development of local economies. Innovative individuals apply creative methods to connect resources and generate growth across ethnic, societal, economic, and ecological contexts. Entrepreneurs are to create strategies that, in the long run, will deal with macroeconomic and climatic barriers and, in doing so, improve the quality of life in the region where they are located. The unique difficulty considerably broadens small businesses’ understanding of their role in economic and cultural advancement. Additionally, freelancers facilitate a less costly workforce management strategy and provide needed assistance for organizations requiring short-term collaboration for specific projects.
Applications of the Study
The current study illustrates the emerging opportunities correlating with small businesses and freelance work as well as the challenges that correlate with the phenomenon. Thus, on the one hand, entrepreneurs can implement the aforementioned statistical and qualitative data when establishing an organization. Based on the employment of the measured variables, entrepreneurs can expect opportunities for growth and success due to the current state of the market. Nevertheless, they are to consider that emerging organizations are susceptible to failure due to disturbances in the external environment. On the other hand, freelancers can apply the study to determine the benefits and negative aspects of the selected career path. On the one hand, a dynamic and creative outlet is available, while on the other hand, freelance work does not effectively align with career progression and strict professional boundaries (Norbäck, 2022). Nonetheless, the study can be applied to determine the potential of the aforementioned selection or segments.
Implications of Research
Statistical variables that have been generated through evidence-based research highlight the potential and challenges correlating with small businesses and freelance work. Namely, one of the limitations is the instability of emerging enterprises. Specifically, small businesses are more prone to disturbances due to external factors. For example, a study examining 5800 emerging firms has established that more than 40% were temporarily closed, and almost 2% were indefinitely closed due to COVID-19 restrictions (Bartik et al., 2020). This suggests that such organizations are yet to become relatively stable regarding income and profitability during crises. Additional research highlights the potential for freelancers, specifically individuals operating online projects and initiatives.
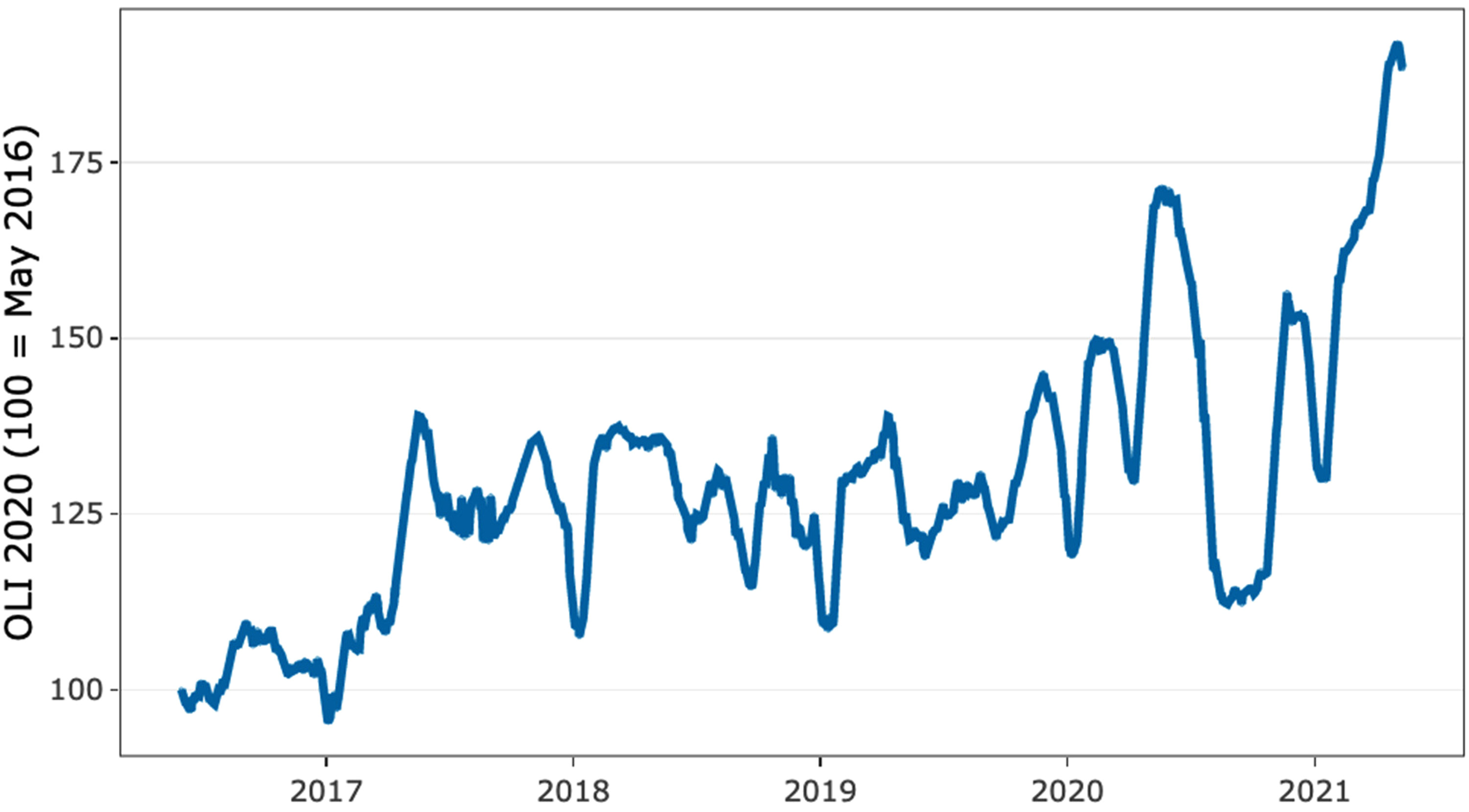
Figure 1 highlights the growth in online projects (90%), which implies that the demand for freelancers is growing and opportunities are arising in this particular sector (Stephany et al., 2021). The same research has determined the most demanded positions on the market, with software development, multimedia, and writing and translation as the most popular positions. Based on the current trends, which align with the further development of the field, small businesses, and freelance opportunities will continue to expand and have a higher impact on national and international GDPs.
Conclusion
It is certain that freelance work, including in the field of real estate as well as small businesses, is becoming more prominent in today’s market and global economy. Statistical evidence highlights that emerging organizations constitute a large portion of the worldwide GDP, while freelancers, especially in the IT field, are more in demand within the job market. However, evidence also highlights that small businesses are more prone to instability in the external environment. At the same time, online work correlates with a lack of set boundaries, payments, and overall effective management. Regarding leadership, focusing on individuality and autonomous management appears to have an effective result on the workforce, including temporary freelancers. Despite the aforementioned barriers, the importance of the research aligns with the changing nature of today’s economy and the dynamic in which the sectors that imply flexibility and independence, such as freelance work and entrepreneurship, generate opportunities for growth and development.
References
Alsaaty, F. M., & Makhlouf, H. H. (2020). The rise and fall of small business enterprises. Open Journal of Business and Management, 08(04), 1908–1916. Web.
Bartik, A. W., Bertrand, M., Cullen, Z., Glaeser, E. L., Luca, M., & Stanton, C. (2020). The impact of COVID-19 on small business outcomes and expectations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(30), 17656–17666. Web.
Einiö, E., & Overman, H. G. (2020). The effects of supporting local business: Evidence from the UK. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 83, 103500. Web.
Flood, F. (2019). Leadership in the remote, freelance, and virtual workforce era. Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance, 1–5. Web.
Hawkes, N. (2018). Google tech company must spell out how it will make money from the NHS. BMJ. Web.
Kotlar, J., De Massis, A., Wright, M., & Frattini, F. (2018). Organizational goals: Antecedents, formation processes and implications for firm behavior and performance. International Journal of Management Reviews, 20. Web.
Merritt, G. (2021). More migrant jobs, or fewer, in post-COVID-19 labor markets?People Power. Web.
Nawaz, Z., Zhang, J., Mansoor, R., Hafeez, S., & Ilmudeen, A. (2020). Freelancers as part-time employees: Dimensions of FVP and FJS in e-lancing platforms. South Asian Journal of Human Resources Management, 7(1), 34–60. Web.
Norbäck, M. (2022). Maintaining a freelance career: How journalists generate and evaluate freelance work. Journalism Studies, 23(10), 1141–1159. Web.
Paek, E. (2021). Does overwork attenuate the motherhood earnings penalty among full-time workers?Work, Employment, and Society. Web.
Stephany, F., Kässi, O., Rani, U., & Lehdonvirta, V. (2021). Online labor index 2020: New ways to measure the world’s remote freelancing market. Big Data & Society, 8(2), 205395172110432. Web.