Week 1: Definition and Meaning of Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is the act of starting or reviving new or existing business in order to capitalize on new and emerging opportunities in the business industry. An entrepreneur is a person who owns a business venture or a firm and is in-charge of its development (Nielsen & Lassen 2012, p.36).
Generally, entrepreneurs face a lot of uncertainty especially when coming up with a new product that did not exist before in the market. Even if there is a market, it does not translate into profitable entrepreneurial opportunity because entrepreneurs embrace available opportunities despite the available resources.
Depending on the level and business activity undertaken Entrepreneurs are different. To become an entrepreneur one must be resourceful and able to find solutions to challenging problems in order to achieve the planned objectives (Lemons 2012, p. 58).
It is evident from research that business owners who engage Entrepreneurial activities obtain great satisfaction.
In creating business ideas, several steps are involved that include: Getting creative ideas flow in order to accomplish the task, an entrepreneur must understand his or her limits that help in focusing the thinking process, seize upon inspiration, identify the problem, and study demographics to identify customers who appreciate your business idea most.
Good business ideas make an entrepreneur feel passionate about his or her business activity.
Week 2: Types of Entrepreneur
Idealist entrepreneur are mostly interested on working on what is meaningful to them and innovating new business ideas. Optimizer entrepreneur is mostly satisfied with being the owner of business venture which is his personal satisfaction.
The hard workers are a category of entrepreneur who welcomes the challenges that comes with entrepreneurship and harvest the most rewards if the business turns into multi billion dollar enterprise. They include persons who enjoy long working days to build large and more profitable businesses (Nielsen & Lassen 2012, p.39).
Sustainers are entrepreneurs who are interested with the growth of business venture and mostly multi task their personal life and business activities. They do not have big dreams and hopes of growing the business into multinational company.
Therefore, they only need enough cash to survive. People with a lot of energy who survive on the pressure of payroll, Meeting deadline, and payment of bills are juggler entrepreneurs.
An entrepreneur has several characteristics. First, he or she is creative by virtual of being able to organize business ideas before effectively managing the start of a business and later runs the business in order to monitor ideas (Lemons 2012, p.59).
An entrepreneur is committed to achievement no matter the challenge, has good leadership skills, is able to plan, and manage leadership skills.
Week 3: Types of Entrepreneurs
Builder or Creator: He is very excellent at making things work, whether it is making wedding cakes or painting. He or she is very optimistic at making things work according to set aspirations. The entrepreneur can start at a very slow pace due to lack of adequate knowledge and the necessary resources to marshal different ideas and implement them (Lemons 2012, p. 61).
Advisor is an entrepreneur with high knowledge, skills, and experience that other entrepreneurs are willing to pay for. It takes long period to be on the top and credit in type of entrepreneurship.
Caregiver entrepreneur is responsible for providing consistent and reliable care to others. Most of the time he does a lot of work but gets low pay, though the interest is in job satisfaction.
Communicator entrepreneur aims at communicating complex ideas to other people since he or she is good with words either written or spoken. There is a lot of competition based on innovation and new ideas.
An entertainer thrives at being in front of other people (Lin & Tao 2012, p.59). He or she loves making people happy, very outgoing, and enjoys spotlight because he can command the attention of the audience.
Week 4: Successful Entrepreneur
To achieve success in entrepreneurship, an entrepreneur should be able to understand him or herself, implement the systems and structures, identify the right people to hire, identify the right external team members, lead them, and scale the business enterprise.
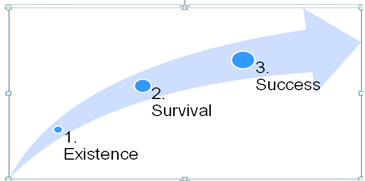
Five stages of Small Business Growth
Stage 1: Existence
The business is very simple and the owner does everything including supervising subordinates who should be of at least average competence (Lemons 2012, p. 59). The business strategy is simply to remain alive because the entrepreneur performs all important functions.
He or she is the major supplier of energy and directs the use of the capital and resources obtained from friends and relatives. The major challenge at this stage is customers’ attraction and delivering the products and services ordered by the customer.
Stage 2: Survival
At this stage, systems development is very minimal since the entrepreneur is still synonymous with the business venture. So, the main objective is just survival. The business may grow in profitability and size and then move to the third stage.
Due to the limited number of employees, the business operations are very simple because the employees are supervised by the sales manager or foreman.
Stage 3: Success
The business owners are faced with a decision of whether to keep the business stable and profitable or exploit its accomplishments and expand (Lin & Tao 2012, p.60). The entrepreneur consolidates and marshals resources for growth.
Among the important tasks at this stage is making sure that the business stays profitable so that it does not outrun its cash resources and it develops managers to meet the needs of a growing organization.
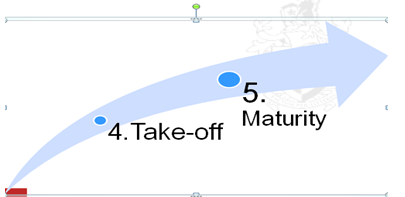
Stage 4: Take-off
The top management must be very competent to handle complex and growing business environment. The major challenge at this stage focuses on how to finance and grow rapidly (Nielsen & Lassen 2012, p.40).
This is very critical part in the business life and if the business overcomes the challenge of a growing company both managerially and financially it can grow into a large enterprise.
Stage 5: Maturity
The business venture has got the staff and the managerial resources to engage in detailed strategic and operational planning (Lemons 2012, p. 60).
The management is decentralized, experienced, and adequately staffed. The entrepreneur separates himself from business operations and finance.
(Gumpet, 1983)
Week 5: Creating business Ideas
An effective leader creates good business ideas that are easy to follow and implement. He is a person with passion to achieve objectives that are beyond his personal interest. He has vision and dream that will benefit the society and persons in the surrounding area (Lemons 2012, p. 57).
A passionate entrepreneur makes difficult and courageous decisions and finally translates them into action. He holds values that are life giving to the society, he should be able to respect others, and deal with diversity (Lin & Tao 2012, p.58).
A successful entrepreneur must have both confidence and humility combined which enables him to identify what is required.

(Gumpet, 1983)
Week 6: Competitor Analysis
This is assessment of both strengths and weaknesses of current and potential competitors in marketing and strategic management. It provides strategic plans both in terms of defensive and offensive which help in identifying threats and opportunities (Lemons 2012, p. 61).
In formulating business strategy, entrepreneurs must consider the strategies of its competitors though in highly fragmented commodity industry the move by any competitor may be less important.
Porters’ Five Force
In a pure competition the degree of risk adjusted must be uniform across all firms and industries .Michael porter developed the most influential analytical model that can be used in assessing the nature of competition in industry (Lin & Tao 2012, p.60).
Porter states that there are five forces in an industry that determine profitability and long-run attractiveness in an industry. They include the threat of substitute products, the threat of new market entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, and the existing competitors rivalry.
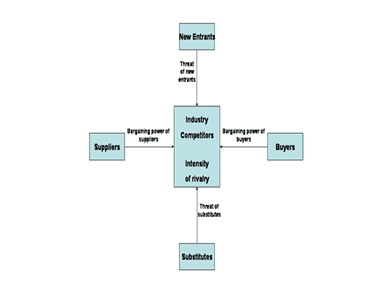
(Porter, 1971)
Business Exit Strategy
Many business organizations have opted to sell the business to someone else or to some other company as a way of exiting from the market. It involves: The transaction conducted between two private parties without government consent.
Two businesses may join together through a merger to establish value on each business and then combine the two to form one bigger company (Lemons 2012, p. 53).
Business partners can also sell the company in a stock market through an initial public offering which has higher benefit because a business venture stands a chance to get the biggest amount payable of any exit strategy.
Week 7: Challenges faced by An Entrepreneur
Most entrepreneurs are challenged to grow and sustain their business venture in a slow growing economy with limited financial resources.
Many owners of small business do not have proper knowledge on cash management which is a major cause of curtailed business loan and restricted credit (Slavec & Prodan 2012, p.112). Both internal and external challenges are major threats which hinder entrepreneurial development.
External challenges lie within the restrictive government policies that take too long or fail to approve loans and business operation licences.In addition, internal challenges are within the business either how the entrepreneur handles the business or relates with the customers (Lemons 2012, p. 58).
Marketing Strategy
Marketing mix is very important when a business is determining brand or product selling point. The four Ps of marketing are very useful in analysing the marketing mix of any business venture. They include: Price, product, promotion, and place (Lin & Tao 2012, p.58).
All methods of advertisement used by a marketer to provide product information to the consumer entail promotion. Marketers must research on the life-cycle of different products to configure the product mix so that ach product complements the other.

Week 8: Entrepreneurial Finance
Potential entrepreneurs must focus their attention on key aspects of financial management. Before starting business operation entrepreneurs must consider cash flow and cash which are the basis of entrepreneurial finance (Lin & Tao 2012, p.55).
In entrepreneurial ventures, critical adjustments are volatile to financial adjustment, short, and compressed time period.
Capital markets are frequently in accessible by the private entrepreneurial ventures because they are very invisible and often disorganized. Sufficient cash is very important for a small business to survive because it must pay employees and suppliers.
Break-Even Analysis
This is a technique based on categorizing production costs between variable and fixed production cost. Variable costs are costs that vary when production output changes but fixed cost remains constant through out the production process.
Fixed cost does not have any relation with changes in production volume (Slavec & Prodan 2012, p.108). To determine the level of sales, production, and sales value, total variable and fixed costs are compared with sales revenue.
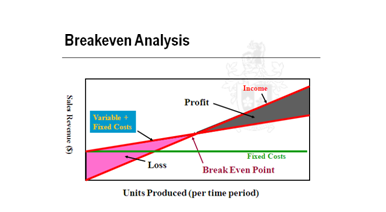
Represented by the graph above, fixed cost remains constant and is represented by the horizontal line. Total cost (fixed+variable) is a sloping line that increases with increase in sales volume. When income exceeds total costs break even is reached (Slavec & Prodan 2012, p.110).
Week 9: Intrapreneurship
Intrapreneurship refers to initiative undertaken by employees in large organizations to do a certain duty without being ordered to do (Lemons 2012, p. 53).
Therefore, an intrapreneur focuses on creativity and innovation, and transforms an idea into a more profitable opportunity while working in the same business environment. Therefore, Intrapreneurs are within entrepreneur because they aim at achieving the goals of the business organization.
Week 10: Importance of Financial Information to Entrepreneurs
Financial statement helps an entrepreneur in managing a business enterprise proactively. Financial statements should be generated on a monthly basis. They include: An income statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet (Lin & Tao 2012, p.52).
The income statement measures all the business revenue sources against the expense of the business for a specified time period. The balance sheet provides an overview of the business assets, owners equity, and liabilities for a given time period. It includes the current assets, fixed assets, and other assets such as long term business investment, cash value of life insurance, and compensation due from employees.
Liabilities include the current liabilities which are obligations of the business due within a year, long-term liabilities, and owner’s equity. The cash flow statement is designed to consolidate the accrued basis of accounting which is used to prepare income statement and balance sheet back to cash basis (Slavec & Prodan 2012, p.106).
List of References
Lemons, D 2012, ‘When to Start Collecting Social Security Benefits: A Break-Even Analysis’, Journal of Financial Planning, vol.25, no.1, pp. 52-60.
Lin, X & Tao, S 2012, ‘Transnational Entrepreneurs: Characteristics, drivers, and success factors,’ Journal of International Entrepreneurship, vol.10, no. 1, pp. 50-69.
Nielsen, S & Lassen, A 2012, ‘Images of Entrepreneurship: Towards a New Categorization of Entrepreneurship’, International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, vol.8, no.1, pp. 35-53.
Slavec, A & Prodan, I 2012, ‘The Influence of Entrepreneur’s Characteristics On Small Manufacturing Firm Debt Financing’, Journal For East European Management Studies, vol.17, no.1, pp. 104-130.