Introduction
Soda Company is a leading premium drinks company operating within the Eurozone. The company is re-known for its outstanding distribution of alcoholic beverages across Europe. The brands of the company include Rikish Cola, Amidos, Vitz, Speedoff, Refresher, Bane drink, and a wide range of spirits. The company’s brands have existed in the market for many years since 1930, when the company was established. While most of the company brands have been developed recently, the company continues to develop new brands to meet the changing customer tastes and preferences. Over the years, the company has strategically penetrated the European market through geographical expansion.
This has enabled the company to tap into the emerging markets within the region. By the year 2005, the company was ranked third in terms of market expansion and corporate portfolio within the European’s alcohol beverages industry. The company managed to maintain growth stability in the region until the year 2008. This is the time when the company started facing the adverse effects of the financial and economic crisis that affected the Eurozone. The instability of the euro, as a common exchange medium and the financial crisis in the Eurozone, has caused severe problems to the company and harshly affected the profitability. The company has had to put up with the impacts of the turmoil by slashing operational costs, but all has not been fruitful. Despite the efforts put in place by European Union member states, it seems that the situation is not to stabilize in the near future. Therefore, the company has embarked on various strategies to ensure future growth (Jernigan, 2009).
European alcohol beverage industry
The alcohol beverage industry consists of alcohol producers and marketers. Europe has the world leading producers and exporters, contributing to a quarter of world’s alcohol (Jernigan, 2009). Most of the world trade in alcohol is centered in Europe which accounts for about nine billion euros of trade value to Europe. Some of the major companies involved in alcohol production are Soda, Scottish Courage, Baltic Beverages Holdings, Heineken, Carlsberg Breweries, Inbev, Diageo, and Gruppo Campari (Jernigan, 2009).
Eurozone crisis
Many countries in the Eurozone are grappling with severe burdens of debt (Tran, 2012). This situation has caused panic due to the economic instability that would eventually cause unprecedented economic turmoil in the Eurozone. It is even feared that this can cause the disintegration of the union and the collapse of many companies in Europe. These events have triggered various measures to be instituted by the Eurozone member states to curb any further damage that the crisis can cause. European Union member states have employed various strategies including financial bail-out of Spain and Greece and other struggling economies to contain the crisis (Tran, 2012). The member states have continuously worked to strengthen and protect the euro, to financially and economically integrate the region.
The main problems facing the company are financial and operational problems. The company is struggling to keep up with the high operational costs; that have been the cause of the problems, by worsening banking and financial systems (Lloyds, 2012). This situation makes it difficult for the company to raise capital from the private capital markets for business expansion purposes. The company cannot afford to redeem its financial instrument in capital markets because of the volatility of the capital market interest rates. Furthermore, the situation is worsened by financial institutions, which have carefully reduced lending due to insufficient capital to cover capital requirements. The company is also experiencing difficulties raising capital through the issuing of stocks and shares in the capital markets. This is negatively impacting on the investor willingness to invest in the securities that the company offers. The Eurozone crisis has also contributed to slow growth in company business due to the effect of the sluggish economic development in the Eurozone. This has negatively impacted on the company profitability in the last four years.
The European financial crisis has also caused cyclic weaknesses to the company; hence forcing the company to cut its capital expenditure. However, this has resulted to slow recovery. This is in terms of growth capital cuts, thus investors have considered it wise for the company to invest abroad. Therefore, the company has decided to pursue a growth strategy through merger with another company in Brazil. The company has also acknowledged that structural changes need to be addressed. The company appointed a cross-functional team that consisted of various professional experts. This team developed a contingency plan to address the financial problems facing the company. The team recommended merger with an established Brazilian company.
Merger
In a merger, two businesses join forces to form one single business entity. The existing shareholders retain their stocks in the merging companies (Gurusamy, 2009). The merger of Soda Company and Puerto Diva Brewer come at a time when Soda Company operations have been crippled by the financial crisis in European countries. Therefore, it is due to this reason that the company is pursuing merger as a growth strategy for the benefit of its stockholders. By merging with one of the most profitable companies in Brazil, the project is important in the reduction of losses as tax write-off and the expansion of the company as a whole.
Though these two companies manufacture slightly different product, the merger is important in complimenting the Soda Company business. At the same time, the merger’s purpose is eliminating the warehousing costs that the company will have, otherwise incurred if direct investment is made in Brazil. The company dynamic cutting edge manufacturing technology is seen as strength to allow the development and streamlining the Brazilian alcohol beverages industry.
Merger is given priority because the company realizes that it will be operating in a new country and thus needs to acquaint itself to the new business environment. Merger is seen as an ideal growth strategy because the company will have proper platform and management to support its business. Merger is selected basing on performance, market and agency or management factors (Gurusamy, 2009). The selected team of experts identified mergers because of the rapid growth it guarantees to the company once the company begins its operation in Brazil.
Merger strategy
Puerto Diva Company in Brazil has been selected and approached for this merger project. The company is one of the major alcohol distillers in Brazil with a wide distribution network in Brazil and neighboring countries. The company has had decent growth patterns in the past decade, with its brands continuously penetrating the market. The extensive distribution network established by Puerto Diva Company offers the opportunity to market the brands of the company in the ever growing beverage industry in Brazil. Major alcohol brands distilled and distributed by Puerto Diva are Tusker, Alvaro, Novida, Ganso, Indica, and Whitecap. Puerto Diva brewer specializes in beer brewing only.
Strategic merger with the identified company is aimed at creating business synergies. In the long run, this will lead to increased market share, stable client base, and strong corporate business (Gurusamy, 2009). The merger is in line with the company’s overall growth strategy since it enables earnings and sales growth of the company. Furthermore, it facilitates changes in the model of the company, which is to enable the company grow and accumulate cash on its balance sheet.
Mergers will also help the company to increase its international competition. This will also allow the company to invest in research and development. It is expected that the new venture will be considerably profitable due to greater efficiency that will be acquired through economies of scale. This is taken as a stepping stone towards achievement of efficiency in the operations of the business.
The merger fits the company’s overall strategy of creating a long term value of company stockholders through geographical expansion and worldwide coverage. The merger has the capacity to enable the company increase global supply of company brands. Furthermore, the merger aims at enabling the company stretch targets to increase productivity and profitability so that the long term shareholders interests are guaranteed. This merger is taken as a key opportunity for the company to market its valuable brands to the world market through regular cycles of innovation and development.
Strategic planning is crucial in protecting the proposed merger from failure. The company has undertaken such a project previously and thus it will not be the first time it engages in such a venture. Over the years, the company has merged and acquired regional firms in a bid to expand its businesses. However, each project is unique and is bound to be affected differently. For this merger to be successful, the company, through the strategic committee, has identified several rules that are treated as strategies to make the whole process a success.
The company has comprehensively analyzed Puerto Diva Brewer market performance and market position. The analysis also considers the future market opportunities, market trends and customer perception of the company product brands. These marketing and performance dimensions have been crucial in the framing company merger strategies.
Risk analysis
The company has realized that this new venture is risky and thus appropriate risk management methods have been instituted. There are uncertainties surrounding the business itself and risk that the business is likely to face in Brazil. Through risk analysis, the company identified three potential risks that can uncertainly affect the new venture. Market, operational, and financial risk are the major risks the business is likely to encounter. The company plans to analyze the risk information and convert them into valuable decision-making information. The critical risks will be worked on by the management and appropriates plans actions to address the risks put in place. The risks are to be prioritized through an action plan drawn to integrate all the risks. The action plan stipulates how each risk is to be addressed. The status of the risks will be tracked to ameliorate them. Tracking of the risk will be done through risk matrices to enable evaluation of the status of mitigation. Adequate control system will be useful to check whether the planned way of risk mitigation is followed to make amendments to the plan where necessary. Feedbacks communication risk management system will be vital in the overall interaction of risk mitigation measures.
The risks identified also include post merger risks. Studies carried out shows that post merger risks are unavoidable, and every company is likely to be affected (Gerds, Strottmann & Pakshalika, 2012). According to Gerds, Strottmann and Pakshalika (2012), many managers overlook post merger risks when crafting merger agreements. These risks can create problems to the merging companies if not addressed promptly.
The strategic committee identified four post merger integration risks and classified them in four categories of risks. The four categories identified include synergy, structure, people and project risks. Synergy risks identified are potential factors that could stem from lack or minimal achievement of the planned actions (Gerds, Strottmann & Pakshalika, 2012). Synergy risks are likely to be caused by poor quality of the financial figures that Soda Company and Puerto Diva Brewer present during the merging process. Furthermore, synergy integration may be downplayed by hazards that are likely to make the implementation of the goals extremely complex (Gerds, Strottmann & Pakshalika, 2012). If the implementation of the plan is going to sidestep any integration step, then it may further aggravate synergy risk (Gerds, Strottmann & Pakshalika, 2012). The merging companies’ management has been involved in the integration and planning processes to ensure that the merger synergy work properly.
Employee resistance risks are also unavoidable during the integration of the merger. It is expected that, at one point during the integration of the two companies, the project might face employee resistance at various levels (Gerds, Strottmann & Pakshalika, 2012). This scenario is highly probably since the two companies cannot have two portfolio managers simultaneously. The merger is expected to cause job layoffs, and it is likely to generate resistance from employees from both companies. Furthermore, some of the affected employees in the reshuffle have to relocate from Brazil to Europe and vice versa. Employees who feel sacrificed in the deal are likely to resist change (Gerds, Strottmann & Pakshalika, 2012). Since this is investable, the company, through the budgetary committee, allocated cash to be used as compensation packages. This was to be used to compensate workers who might be affected by the integration of the companies.
Brazil economic overview
The company’s investment division has noted that the structural problems in the Eurozone might lead to slower economic growth. This was the major reason as to why the company should go global and invest in Brazil. Brazil has been chosen because of its sound economic structures and attractive interest rates. Brazilian capital markets also look attractive and less volatile in the recent years.
Brazil economy is the largest in South America and the world’s sixth by the nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The economy is expected to accelerate further and be ranked as the world’s fifth by the end of 2012 (Helmke, 2011). The Brazilian economy has had a steady growth from the year 2002 with its GDP growing at an annual average of five percent. By the year 2009, Brazilian GDP was estimated at R$ 3.143 trillion. Brazilian economy growth has been a result of the county’s competitive and freer market that has led to fiscal sustainability and liberalization of the economy. These measures have encouraged economic sectors competitiveness and private sector development (Helmke, 2011).
Brazil has made this economic stride despite past economic experiences. The country was on the verge of economic collapse when extreme recession caused its export to dwindle in 1990s. However, due to the sound economic policies and programs, the economy was revamped and resulted to what is being witnessed today (Helmke, 2011).
The major economic sector components that have witnessed growth and contributed to Brazilian GDP are the industrial sector, services sector, and agricultural sector (Helmke, 2011). The services sector is the biggest contributor accounting for sixty-seven per cent of the total Brazilian GDP, and it is the largest sector in Brazil economy. The industrial sector contributes twenty-eight per cent of Brazil GDP. On the other hand, agricultural sector, which is predominate sector in Brazil, contributes to approximately six per cent of the total Gross domestic product (Helmke, 2011).
Brazil is among the fastest emerging market in the world today, and this has resulted to increased foreign investment. Brazil is regarded as one of the most attractive investment destinations for foreign investors due to its sound economic structure. The high market interest rates and lucrative resource endowment act as an impetus for more foreign investment.
The Brazilian government has over the years given production subsidies in a bid to increase the sectorial productivity (OECD, 2009). Majority of subsidies goes to agricultural production. The Brazilian government is subsidizing the agricultural sector as a way of protecting producer from the high cost of farm inputs (OECD, 2009). Without the support of the government through subsidies, the Brazilian agricultural sectors could be in complete jeopardy. There are also government subsidies in the industrial sector that are aimed to increasing production of local commodities for the export market. The most recent example is $38 billion government’s subsidized credit to the ethanol sector that is aimed at increasing “sugar production and milling industries while ultimately doubling the annual turnover of the ethanol industry” (Lane, 2012, para 1).
The Brazilian wages national minimum wage is annually adjusted to conform to the economic situations prevalent in the country (Geiger, 1976). By the year 2009, the minimum wage rate per month stood at R$ 465. This increased further to R$ 545 per month in the following year. Brazilian states are mandated to set higher wages. Additionally, wage rates are different depending on the sector and the state. However, states are not allowed to set wage rates lower than the national wage rate level (Geiger, 1976).
Financing
The company capital budget is a very important tool in that it describes how the company financial resources will be allocated in the anticipated project. The company has prepared a comprehensive outlay of capital that is required to finance the whole merger. Since the merger promises great future returns to the company, the company treated the budgeting process with great care and consideration.
The company has a strategic capital outlay to finance the merger. In its budgetary allocation to finance the merger, the company explored different methods of raising capital. Two ways have been selected to finance the merger. These are bank loan and issuance of securities in the capital market. The company strategic affairs committee has anticipated a merger cost of € 1,750,000 (including € 200,000 for structural changes and legal fees). The merger costs are to be incurred once, and all the stockholders have been informed through general meeting. When the costs should be underwritten once the merger starts operating.
The firm realized that the merger can be costly. Therefore, prompt budgeting of the costs involved was made. The identified costs include legal transaction costs, technological costs, relocation or migration costs, administrative and public relation costs, and operational costs. The budget making process was well informed about the magnitude of the entire project and its implications to the company.
The total amount of money required for the merger is spread to cover three elements in the merger budget. The budget covers three capital budget elements. These elements include revenue enhancement, operating process changes and capacity maintenance. The three elements are to be actualized through acquisition of equity in Puerto Diva Brewer.
Majority of expenditure will be on the operational activities of the merger. The total cash to be spent on the operational activities is estimated to be € 500,000. The legal work and technical training, for staff changes and skills development, will cost approximately € 150,000. Audit and tax return expenses are estimated at € 100,000, and this will be part of the legal transactions fees in the year budget. Accounting and fundraising, which combine financial and development systems, as well as controls and loan applications, will cost approximately € 100,000.
It is expected that the merger is going to cause some forms of retirements and job cuts of the existing staff. Similarly, it is also expected that the merger will also require structural transitions and recognition events. A total amount of € 150,000 has been allocated to cover the related costs. During the operationalization of the merger, merging companies’ stockholders need to be informed about the progress. Additionally, the community partners of the companies are to be communicated to regarding the merger performance and operational goal. Therefore, a total amount of € 100,000 has been allocated to cater for public relations and marketing expenses.
The merger will be advertised through various media. This will enable the company to reach out to the different stakeholders and the general public in a comprehensive manner. From the estimations, this is going to cost € 100,000. Since this merger will result to a new business entity, software development costs are inevitable. The new business entity has to acquire a new system, website and other software development tools. It is estimated that the cost of software development is going to cost € 30,000. The companies’ merger is a manufacturing venture that requires technological changes in the manufacturing processes of the existing plants. Puerto Diva brewer has specialization in beer manufacturing whereas Soda Company majorly deals with wines and spirits.
Capital expenses are important in the maintenance and renovating of business property to improve its usefulness. Considerable manufacturing plants adjustments are necessary to facilitate the production of wines and spirits. A total figure of € 250,000 has been allocated to cater for the technological changes in the manufacturing technologies. The € 250,000 also includes the short terms cost related to information transmission and information technology. Other miscellaneous operational expenses including signage of properties and stationery expenses are estimated to cost € 10,000. A total amount of € 150,000 has been allocated to cater for the purchase of additional vehicle for the new venture.
The budgeted capital is to be financed by a bank loan in Brazil. The company settled on borrowing from Brazil. This was regarded as the best option owing to the financial problems that have affected the local banks in Europe due to the effects of Eurozone crisis. The banks in the Eurozone have greatly reduced their lending because of the uncertainties brought about by the European financial turmoil. Furthermore, lending rates in Brazil are considerably affordable compared to European rates. Brazil has also unveiled new stimulus measures that are aimed lowering lending rates for companies in a bid to protect the country economy from slowing global economy and European debt crisis (Pariz & Otoni, 2012).
Swap
Currency swap is an agreement where two companies or parties exchange one currency for another (Clark, 2002). According to Clark (2002), currency swap is an essential instrument in transferring assets and liabilities from one currency to another (Clark, 2002). The whole transaction will involve domestic Brazilian currency swap from United States Dollar since it is the standard international exchange. It involves exchanging the total amount of loan and fixed interest rate payments into another currency between both parties. The principle amount is exchanged at maturity (Clark, 2002). Each company will repay the loan at maturity. The diagram below represents the currency swap that will be involved in the loan acquisition.
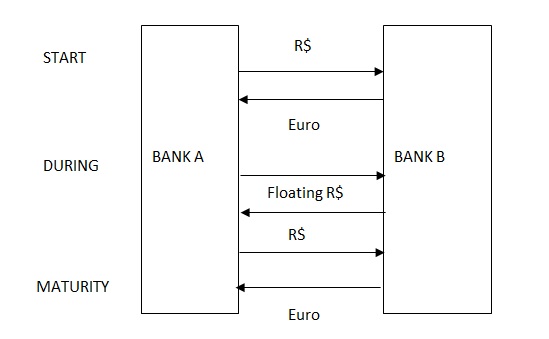
This swap is done on a fixed loan to a fixed rate on the loan. The company chose to borrow from Brazilian market because of the low interest rates that tend to fixed. Therefore, foreign exchange provides the company with a comparative advantage as compared to other companies in the industry (Clark, 2002). From this scenario, interest rate swap is helpful in achieving the desired financial obligation of both companies. The interest rate swap is to be carried out through an investment bank as an intermediary in the transaction (Clark, 2002).
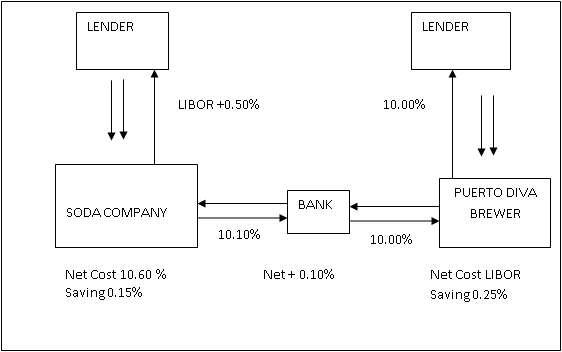
Soda Company has borrowed a twelve month floating rate of Libor + 0.50 per cent. A five year fixed rate at 10.75 per cent. Puerto Diva Brewer borrows a twelve month floating rate of Libor + 0.5. The fixed five year rate for Puerto Diva Brewer is 10.00 per cent. This reduces Puerto Diva floating rate borrowing costs. This implies that the Puerto Diva Brewer has a higher credit rating than Soda Company. However, Puerto Diva can only borrow at 0.5 per cent better in terms of floating rate terms, whereas Soda Company fixed rate of 0.50 per cent is an advantage. The diagram below shows a 10.00 per cent net payment. Puerto Diva is left with its desired floating rate of borrowing – at a rate of LIBOR saving 0.25 per cent per annum.
LIBOR rate of Soda Company +0.5 per cent making a fixed payment of 10.10 percent in exchange for a float rate of Receipt of LIBOR. This leaves Soda Company with 10.60 per cent thereby saving 0.15 per cent. The bank in return earns 0.1 per cent per annum for taking the credit risks of the merger.
Risk hedging
Risk hedging is an investment position taken by a company that is intending to invest. This is meant to offset any potential losses can be brought about by a companion investment. Risk hedging is important when constructing various financial instruments during investment in domestic or foreign economy (Organisation de coopération et de development économiques, Global Forum on International Investment, & Global Forum on International Investment, 2003). Foreign Exchange risk hedging is important in the ascertaining likely risks of investing abroad. It also helps in the identification of nonfinancial actors within a foreign economy, which might be affected by currency issues.
International investments are always susceptible to various risks that result from foreign exchange rates and currency value variations. The companies investing have conventionally used hedging instruments such as currency futures, forwards, and options in trying to avoid and avert the risks. However, not all risks can be hedged, and managers have to consider how complex the risk is in trying to deal with it. Examples of risks that can be hedged include currency risk, interest rate risk, equity risk, volatility risk, credit risk, and commodity risk (Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, Global Forum on International Investment, & Global Forum on International Investment, 2003).
The company identified interest rates, and currency risks as the potential financial risks that might have encountered during the implementation of the project. Foreign exchange risk is likely to have profound financial effects on the project investment is not properly managed. The risk has a potential of affecting the project cash flows as a result of fluctuation in exchange rates between Brazilian dollar and the euro. If the foreign exchange rate increases, the cash in-flow will be significantly reduce whereas the cash out-flow will be bloated. The unanticipated changes in exchange rates might cause shifts in demand of company brands hence affecting company profitability.
The company has a likelihood of interest rate risk when it borrows money in Brazil. Megaprojects like mergers are vulnerable to this risk and can be damaging if left unchecked. If the interest rates are going to increase, then the value of the prices of securities that the company will have offered in the capital market will ultimately fall. The company projects that the interest rates might be considerably low in the short term. However, the long term rates can shift dramatically, and this might negatively impact on the project revenues and expenses. Since this project is financed by the bank and bond loans, cost might overrun project revenues due to increase in interest rates.
Interest rate risks and foreign exchange risks if left unchecked can cause massive financial problems during the implementation of the project. The company is willing to trade these risks as they emerge during the operation of the new enterprise in Brazil. Hedging will be essential in eliminating the risks that may accumulate in the balance sheet of the business over time. The company has identified two instruments from the available instruments to be used to deal with these risks.
Currency swap instrument will be use to minimize foreign exchange risk. Currency swap has been selected because it offers the most appropriate rationale in minimizing foreign exchanges risk. The companies will exchange starting principles at the spot rates that will be prevailing at the time of exchange. The companies will swap the currencies at predetermined rates hence enabling the company to trade more careful with the risk. In case the euro will be depreciating, the company will be protected, but we are bound to lose if the euro appreciates.
Forward instrument will also be utilized in the minimization of foreign exchange risk. An agreement between the companies will be vital in the realization of this strategy. This is aimed at reducing the risk associated with the fall in the euro that Soda Company will be using in the transactions. Swap instrument will also be used to hedge the interest rate risk. The company will enter into a swap contract by buying an option to enable it enter into IRS analogue in case of an increase in the interest rate. The company will then make upfront payments to floor the loss.
The above instruments only address risks that can be hedged. On the other hand, the company is aware of risks that are likely to confront the company and which cannot be hedged. The company has identified model risk as the potential risks that will be difficult to hedge since they are extremely hard to quantify. The company was of the opinion that since the risk assumptions might not be correctly identified, the accuracy of parameters to address it might be tantamount.
Raw material hedging
The major raw materials that will be used in the manufacture of products are grapes, fruits, ethanol, maize, and barley. The raw material risk will be solved through contract farming with medium and small scale farmer who will primarily supply the raw material for the project. The farmers will be offered predetermined contract prices of their agricultural commodities on the annual basis.
Pros and cons of the project
Many countries have over the years opened up their economies for international investment. Concurrently, the level of international mergers has also increased due to the available opportunities that these economies are providing. The Brazilian economy has been at the top in allowing more direct foreign investment within its diverse agricultural, service, and industrial sectors (Helmke, 2011).
There are numerous benefits that accrue from pursuing international mergers to both the country offering the investing opportunities and the investor. The project will be of great benefit to the company and the shareholders as a whole. The project is expected to reduce costs through trimming of marketing costs and low cost raw materials in the long run (Schamotta & Media, n.d.). This attributed to relatively low prices of barley in Brazil due to government agricultural subsidies. Furthermore, the company is going to utilize Puerto Diva manufacturing plant thereby considerably reducing the costs.
The project is going to increase market penetration at a global level by enhancing accessibility to customers (Schamotta & Media, n.d.). The project will contribute to extensive coverage of the Brazilian market and use it as a further step of accessing the Latin America market. According to Schamotta and Media (n.d.), merger projects are important in allowing the company to diversify its business line and start offering a greater range of products and services. Mergers expose the company to more consumers through identification of available product development opportunities. The merger project is going to allow the company to tap into production of beer as new products.
The project integrates two companies that have different technological and human resources endowment. The company is going to maximally benefit from the best minds following the integration of the companies. This presents a chance for the company to improve its human resource skills. Additionally, through research and development, the company is likely to generate innovative products that will be important to the company (Schamotta & Media, n.d.). A technological advantage acquired through the merger is vital in achieving efficiency by eliminating redundancies on the operation of the business.
The project is expected to contribute to the achievement of economies of scale in the operation of the business. In the long run, the project is expected to expand the size of the company thereby leading to efficient use of machinery and equipment. At the same time, the productivity of the company is expected to increase due to the complementary nature of the merger.
Though the project is attractive, there are some disadvantages that the project may present to the company. International mergers are usually complex than local forms of merger due to variances in operational and marketing dimension from region to another. Though the project is going to substantive increase in company market share, there are some project cons.
The project might result to structurally different entity established in a different market (Kiriazidis & Tzanidakis, 1995). This may lead to long communication resulting to difficulties in implementation of managerial decisions. According to Kiriazidis and Tzanidakis (1995), the management of such project might turn out to be a complex exercise thereby resulting in diseconomies of scale.
A number of factors may also influence the success of the projects. Factors such as cultural differences, communication difficulties, and regulatory rules may adversely affect the company in the new market. Differences in corporate culture might cause disorientations of employees and manager. If these factors are not properly integrated in the project, it might lead to profound project difficulties.
In the long run, the project could result to a giant entity that might reduce industry competition. This might make the company suffer from noncompetitive stimulus and low stock prices. The shareholder will be disadvantaged in case such a scenario happens. Additionally, it could result to increased consumer cost leading to low volumes of purchases.
Conclusion
The Eurozone crisis has had profound effects on many companies operating in the region. The most affected companies are those that operate in more than one member state within Europe. Soda Company, which operates in four different countries in Europe, has been hit hard by the crisis. The crisis has affected company profitability and operations in the four countries that the company operates. There are no prospects that this crisis is going to end any soon. Thus, the company identified global expansion as the only strategy that is going to facilitate the growth of the company. A strategic merger with a Brazilian brewer company has been sought. The rationale of picking Brazil as an investment destination is based on the consideration that Brazil is an economic hub in southern America. The country is also one of the world’s emerging economies. The proposed strategy is viable and offers many advantages to the company. The shareholders have approved the project, and it is to be implemented in a due course. The decision to pursue this project has been reached after going through a sequential analysis of the financial and nonfinancial risks involved. The strategic committee appointed by the company board has drawn a structured plan of how the project shortcomings and risks are going to be addressed.
References
Clark, E 2002, International finance, Thomson Business, London.
Geiger, T 1976, The General Electric Company in Brazil, Arno Pr: New York.
Gerds, J, Strottmann, F, & Pakshalika, J 2012, Post merger integration: Hard data, hard truth, Deloitte, Web.
Gurusamy, S 2009, Financial services, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi.
Helmke, J 2011, Remittance-led development: rebuilding old dependencies or a powerful source of human development? A view on Latin America, Kassel Univ. Press, Kassel.
Jernigan, DH 2009, “The global alcohol industry: an overview”, Addiction, vol. 104, no. 1, pp. 6-12.
Kiriazidis, T, Tzanidakis, G 1995, “New developments and prospects of the European financial services industry”, European Business Review, Vol. 95, no. 1, pp.24 – 31.
Lane, I 2012, Brazil sets up $38 billion ethanol subsidy program to stimulate expansion, Biofuels Digest. Web.
Lloyds, TSB, 2012, Decoding the Eurozone crisis, How does the Eurozone crisis affect UK Markets, Web.
OECD 2009, Agricultural policies in emerging economies, Monitoring and evaluation 2009, Web.
Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, Global Forum on International Investment, & Global Forum on International Investment. (2003). Attracting international investment for development, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris.
Pariz, P & Otoni, L 2012, Brazil unveils stimulus, cuts BNDES lending rate, Web.
Schamotta, J, Media, D ND, The advantages of company mergers, Web.
Tran, M 2012,Eurozone debt crisis poses serious threat to emerging markets, Web.