Introduction
Business organizations strive to excel in their respective areas of operations through ensuring proper customer satisfaction. To achieve this, the organization needs to be unique through identifying the competitors in the same industry, examining what they offer to the customers, and noting down the key weaknesses in their products in relation to the current needs of the customers.
A competitive advantage is developed from the distinctive capabilities of these organizations (Kotelnikov, N.d). The kind of loyalty that customers develop of a particular product/service and the associated brand should be of great consideration to the management of such organizations since this ensures its sustainable development.
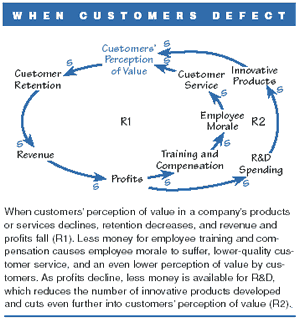
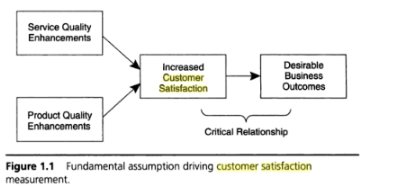
The outcome (success or failure) of an organization is greatly affected by the quality of product/services that it offers (Abdullah & Rozario, 2009, p.185; Allen, 2004). A product/service will be evaluated after a customer has experienced it and used the experience to make a judgment.
This will determine whether the client will use the service next time or not as well as the likelihood that he/she will propose this organization to others who are in need of the services. Customer experience then becomes an important source of value creation (Petermans et al, N.d).
This phenomenon describing customer behavior is particularly pronounced in the service industry. The level of satisfaction that customers derive from the quality of services of a given organization will enable them to be strongly attracted to and retained as the company’s key clients.
It has to be noted that customer satisfaction in a given service organization is affected by various factors both within and outside the organization (Abdullah & Rozario, 2009, p.185).
Factors like the location of a given organization and its accessibility, the variety of services offered, the internal environment, and the organizational culture reflected on the behavior and conduct of the employees are all essential in adding value to the product and services of an organization. Customers are likely to be attracted to institutions where the staff members are friendly, clean, and issue quick services.
Fairmont Mayakoba Riviera Maya resort is one of the facilities of the larger Fairmont Hotels and Resorts, an international player in the hospitality industry. It has been noted that ‘Fairmont is a leader in the global hospitality industry with a distinctive collection and worldwide reputation for excellence’ (Fairmont Hotels and Resorts, 2012).
The resort was opened in 2006 being located near Playa del Carmen in the community with various facilities for luxury (Fairmont MAYAKOBA, 2012b). Fairmont Mayakoba covers a 45-acre piece of land with networks of waterways that form a beautiful canopy in Riviera Maya along the coast of Caribbean Sea (Fairmont MAYAKOBA, 2012a).
The natural settings of the facility as well as the management strategies that have been applied by the organization leadership are keys to the milestone that the institution has recorded in service delivery in this region. Many other luxurious resorts have shown commitment to strong establishment along this coast (Alisau, 2004).
This is likely to pose challenges to Fairmont Mayakoba. The organization takes pride in providing all-inclusive resort services to its customers. This paper focuses on this organization and the strategies it employees to add value to its services to increase customer satisfaction.
Aims and objectives of the Report
This report aims at providing a critical analysis of the operational and management strategies that are employed by the Fairmont Mayakoba Riviera Maya resort in creating external value to its services. The report examines the values that the organization has added to its services in order to have a competitive advantage over the other players in the industry.
It focuses on the benefits that the company has derived from applying these operational strategies. Based on these findings and the available literature, the report also aims at providing recommendations to the management of the organizations on the other strategies that can be employed in order to add value to their services to increase customer satisfaction.
The findings and analysis
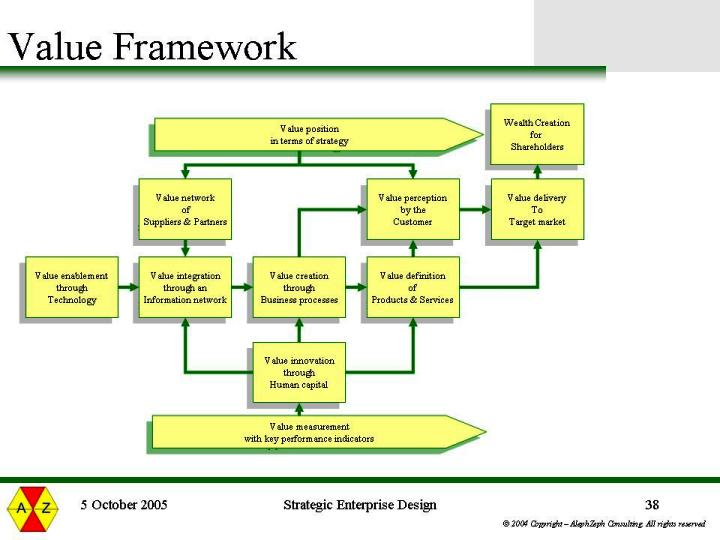
The value-creation theory
Value creation in any organization provides a mechanism through which it can be judged (The Economist, 2009). Maximum customer satisfaction may be difficult to realize especially in the service industry with intangible products (Vermilion, 2007). Customer perception becomes an important factor that contributes to customer satisfaction and yet it cannot be controlled fully by the service provider (Cochran, 2003).
One of the factors affecting the customer perception of service quality is the physical environment in which the services are offered. A number of physical signs can determine the quality of service in the service industry. These include the ambient conditions within and around the premises like the temperature, lighting, sound (music, loud noise), odor, or the coloration at a given place.
Some guests may prefer warm/temperate places for recreation whereas others may prefer cool areas. Guests have varied perception on loud music as well as intensity of lighting in the hotel rooms. Bad smell and dull coloration will definitely lead to poor perception.
The physical environment will also include the layout and interior design of various premises within a service providing facility (Sarkissian, N.d). The whole premise is then structured so that related services are situated in close proximity for convenience. The other component of the physical environment is signs, symbols, and artifacts.
There is a need to have proper signage to provide guidance to the new visitors on the location of various services. Signs and labels give direction while the symbols and artifacts help in portraying some image about the organization. Service menus are often located at strategic locations at the entrance of these premises with a customer help desk for more inquiries.
Another important aspect of the physical environment is the employees’ appearance, attitudes and behaviors as well as the behavior of other guests. The service industry requires employees in decent attire. The employees have to be orderly in their conduct and there needs to be a uniform dressing code that is to be used by all the employees. Rowdy guests dressed in some unpleasant manner may be a nuisance to the others who will develop negative perception about the institution.
All the above components of the physical environment will affect the guest’s perception of the quality of services that are offered in a given hotels. The Mehrabian-Russell Theory holds that service environment generates emotions that eventually lead to some behavioral response by customers (Lutz & Kakkar, 1975; Billings, 1990, p.5; Kearney et al, 2007, p.2).
Other than the physical environment, the servicescape also affects customer perception and ultimate satisfaction. Organizations in the service industry empower themselves by making promises that are appealing to the clients as concerns the value and benefits of their services (Shenouda, N.d, p.2).
The organizations rely on employees to improve the quality of their services (Hayes, 2008). It is then the responsibility of all the employees of the organizations to ensure that the promises are fulfilled through their strong commitment to the organization’s objectives (Abdullah & Rozario, 2009, p.185).
The core values that have been established by the organization will enable the employees to achieve these objectives. The values include ‘creativity, customer focus, agility, teamwork, integrity, diversity, and responsibility’ (Gronfeldt & Strother, 2006, p.2; Shenouda, N.d, p.2). By knowing and living by these company values, the employees are able to keep the promises to customers.
The employees also need to be courteous and knowledgeable in their respective areas of assignment in order to enhance quality and dependability. They should make the customers to have a feeling that their needs are of important considerations to the management of the organization (Sarkissian, N.d).
In order to achieve this, management of these organizations should perform intensive recruitment and selection of employees. They should also provide thorough training on how to enable the employees develop positive encounters with the customers. There is a need to be responsive to the diverse needs of clients.
Customers will be attracted to quick, reliable, cheap, and responsive services that conform to their expectations (Cochran, 2003, p.1). The employees should be able to provide fast services if, and when, they are required by the clients (Sarkissian, N.d).
Several organizations providing food services have a wrong perception that customers are only interested in food and that they will be satisfied as long as they can find something to eat (Abdullah & Rozario, 2009, p.186). Nonetheless, this is not always the case since some customers may be happy when they enjoy services in the company of their families thereby calling for expanded services. Various luxurious facilities can add on to the value of services in such organizations.
The value creation strategy at the resort
Investment involves putting resources at risk with an intention of obtaining a greater value in return. Value is created if this return is finally obtained (Fuller, 2001, p.1). In order to achieve this, the investment opportunities are examined. The net present value of future benefits from such investments is also calculated and an investment is that is likely to create some economic value is pursued (Fuller, 2001, p.1).
Value should be defined and created for the customers, employees, and investors/shareholders, as they are all important in sustainable growth of the company (O’Malley, 1998; Pieterse, 2005). For instance, if customers lose interest in a given service due to low value, the return will be low and this will extend to affect the employees as well as the stockholders. There will be no funds for more research and development (O’Malley, 1998).
Besides, a strong link occurs between customer satisfaction, customer retention, and profitability (Hill & Alexander, 2006, p.1). The management at the Fairmont Mayakoba Riviera Maya resort has been sensitive to the factors that add value to their services and has employed a number of strategies.
The organization has employed the principles on servicescape theory in the design of the premises and in execution of activities. A servicescape generates stimuli to the customers and enables them make some cognitive judgment about the service provider (Lin, 2004, p.165; Michaelia, 2008, p.3).
A client whose needs are met or exceeded will develop good attitude towards the service provider (Hill et al, 2007, p.1). Hotel is an important component of any resort. The Riviera Maya resort has a hotel as one of the key facilities. The Fairmont Mayakoba Riviera Maya hotel provides ‘an unequalled travel experience in five different ecosystems- mangrove, tropical forest, lagoons, water canals, and coastal dunes’ (Fairmont MAYAKOBA, 2012a).
There are a number of hotel amenities under the hotel management. These include AAA-Four Diamond, Las Brisas, Café Maya, and La Laguna all providing an array of food services. The food services can also be provided to the visitors in their rooms. There is a 24-hour in room dining service to ensure flexibility so that the clients are served when there is need (Fairmont MAYAKOBA, 2012a).
The resort has a reservation of the ancient culture and the seascape creates a concerto of pleasing sounds and smell (Cincinnati Magazine, 2009). Fairmont Mayakoba also provides excellent accommodation services.
It has 401 rooms designed according to the beautiful contemporary standards and spreading throughout the main premise (Fairmont MAYAKOBA, 2012a; Prism Business Media, 2006). There are also a number of hotel villas distributed throughout the resort’s land coverage.
The natural setting of the property enables easy transport to different locations within the facility. A number of lagoons make transport to different premise easier through simple water vessels some of which can be operated even by the juniors.
Visitors with their private vehicles park the vehicles at the main entrance and the ‘remaining transport throughout the Fairmont Mayakoba is accomplished via covered boats called lanchas, electric golf carts, bicycles or on foot’ (Fairmont MAYAKOBA, 2012b).
A number of sports facilities and other social centers are available within the resort. It is also close to some major sports facilities like the Jim McLean Golf School. The management of the resort is also concerned with cultivating and improving skills in the visitors of all ages.
The Discovery Club & Adventure Camp gives the visitors an opportunity to improve their creativity and innovative abilities (Fairmont MAYAKOBA, 2012b). The juniors are guided through various adventures that explain the natural or cultural phenomena. They are also engaged in various artistic works that can improve their skills.
Another important aspect of the organization is good leadership and organizational culture reflected on the conduct of employees. The warm reception by the concierge at the entrance adds value to the services. These individuals give proper direction to the clients on the services that are available at the different sections of the establishment as well as helping the clients to plan their stay at the resort (Fairmont MAYAKOBA, 2012b).
The market strategy in marketing mix – 2Ps
Products
The management of the resort has employed an effective marketing mix to ensure maximum customer satisfaction. The author focuses on the product (services offered) as well as place (location and distribution of the services). The resort offers a variety of services as has been stated earlier. This includes food and accommodation services as well as entertainment services.
There are guest facilities like conference halls as well as social and cultural centers. Besides these, there is a full service health club and beauty salon both available at the Willow Stream Spa- a section of Fairmont Mayakoba hotel. The 20,000 square-foot facility with 20 treatment rooms provide various treatment services (Fairmont MAYAKOBA, 2012b).
The treatment here is instigated by the resort’s environment that gives unique experience to the customers (Bassett, 2006, p.79). A full service club is also available for the kids who have accompanied their seniors to the resort (Fairmont MAYAKOBA, 2012a).
Places
The various services are available at various locations. Food services are available at different locations. These include La Laguna Grill & Bar that provides breakfast, lunch and dinner, Las Brisas (offering seafood), El Puerto (located within the main building); Café Maya, and Lobby Lounge that provides tropical cocktails, sushi, as well as music (Fairmont MAYAKOBA, 2012b).
The efficient means of transport within the facilities enable movements here to be easy. The management of resort has improved access to their services through establishing offices in countries like Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Chile, and UK (Fairmont MAYAKOBA, 2012a) from where clients can seek information and book for services. Reservations to the resort can also be made online. This practice of e-business creates value through ‘transforming the rules of competition through unprecedented ways’ (Amit & Zott, 2001, p.494)
Conclusions and recommendations
Resorts are places of luxury that individuals visit for leisure and luxury purposes. They are important destinations for tourists to a given country. As such, various social amenities should be available in the resorts. The visitors to these places may often take long during like during some holiday/vacation.
The resorts should provide services like food, drinks, and lodges for accommodation. There should be sports facilities and sources of entertainment like music and cultural/historic icons within these premises. The resort has understood quite a number of these necessities and efforts have been made to put them in place.
It has various hotel amenities with several dining options. There are also a number of sports and recreational facilities within the property. The staffs at the various premises are knowledgeable in the hospitality industry and ensure that the customers are provided with proper guidance and timely services.
The resort has facilities to accommodate even the junior individuals so that a whole family can have a nice visit to the facility. Dining options accommodate all cultures thereby enabling individuals to follow their tastes and preferences.
Nonetheless, more adjustment needs to be made on the services at the resort to improve the overall quality. An important requirement of these tourist destination centers is a shopping mall from where the tourists can go shopping conveniently.
The resort has a small business center that provides computer solution services, communication services, printing and copying. The center operates for 12 hours from 7 a.m. to 7 p.m. There is need for an establishment and expansion of shopping center in the resort that includes all the essential commodities. The shopping mall also needs to operate for 24 hours a day.
Reference List
Abdullah, D., & Rozario, F., 2009. Influence of Service and Product Quality towards Customer Satisfaction: A Case Study at the Staff Cafeteria in the Hotel Industry. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 53. Web.
Allen, D., 2004. Customer satisfaction research management: a comprehensive guide to integrating customer loyalty and satisfaction metrics in the management of complex organizations. Milwaukee: ASQ Quality Press.
Alisau, P., 2004. Upscale Steps Up. Successful Meetings, 53(9). Web.
Amit, R., & Zott, C., 2001. Value creation in e-business. Strategic Management Journal, 22; 493-520. Web.
Bassett, M., 2006. Mexico’s Riviera Maya: The Fairmont Mayakoba. Corporate Meetings & Incentives, 25(9); 70-71, 2p. Web.
Billings, W. L., 1990. “Effects of Store Atmosphere on Shopping Behavior” (1990). Honors Projects. Paper 16. Web.
Cincinnati Magazine. 2009. ’09 Best Restaurants: Fairmont Mayakoba. Emmis Communications, 42(6). Web.
Cochran, C., 2003. Customer satisfaction: Tools, Techniques and Formulas for Success. Chico: Paton Press LLC.
Fairmont Hotels and Resorts, 2012. Welcome to Fairmont Hotels & Resorts. Web.
Fairmont MAYAKOBA. 2012a. Welcome to Fairmont Mayakoba, Riviera Maya resort. Web.
Fairmont MAYAKOBA. 2012b. Guest services. Web.
Fuller, D., 2001. Value Creation: Theory and Practice. Web.
Gronfeldt, S., & Strother, J., 2006. Service Leadership: The Quest for Competitive Advantage. London: Sage Publications.
Hayes, B., 2008. Measuring customer satisfaction and loyalty: survey design, use, and statistical analysis methods. Milwaukee: ASQ Quality Press.
Hill, N. et al. 2007. Customer Satisfaction: The Customer Experience Through the Customer’s Eyes. London: Cogent Publishing Ltd.
Hill, N., & Alexander, J., 2006. The handbook of customer satisfaction and loyalty measurement. Burlington: Ashgate Publishing Company.
Kearney, T. et al. 2007. Servicescape: A Review of Contemporary Empirical Research. Sixteenth Annual Frontiers in Service Conference, San Francisco, CA, pp58. Web.
Kotelnikov, V., Sustainable Competitive Advantage: How to survive against your competition over along period of time. Web.
Lin, I., 2004. Evaluating servicescape: The effect of cognition and emotion. Hospitality Management, 23; 163–178. Web.
Lutz, R., & Kakkar, P., 1975. The psychological situation as a determinant of consumer behavior. Advances in Consumer research, 2; 439-454. Web.
Michaelia, C., 2008. The Role of Servicescape in Convention and Exhibition Centres: -Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre and AsiaWorld-Expo. Web.
O’Malley, P., 1998. Value Creation and Business Success. The Systems Thinker 9(2). Web.
Petermans, A. et al. Measuring emotions in customer experiences in retail store environment. PHL University College and Hasselt University, Department of Arts and Architecture. Web.
Pieterse, J., 2005. Value creation generates wealth. Web.
Prism Business Media. 2006. Fairmont Mayakoba, Association Meetings 18(4); 42. Web.
Sarkissian, A. Customer Satisfaction Tips for the Service Industry. Web.
Shenouda, J., Service Leadership (Goodwill speech). Web.
The Economist. 2009. Value Creation: The ultimate measure through which a company is judged. Web.
Vermilion, D., 2002. Improving customer satisfaction in the Service industry using Failure Mode and Effects Analysis. Web.
Vermilion, D., 2007. Improving customer satisfaction in the Service industry using Failure Mode and Effects Analysis. Web.