Introduction
Hewlett-Packard (HP) is a global technology corporation that serves consumers, small and medium-sized companies (SMBs), big enterprises, and public, private, and nonprofit organizations (P3s) in the areas of government, healthcare, and education. The company operates in the personal computer and printer markets, offering related services and products in information technology (IT) infrastructure, storage, and security. The company was founded in 1939 by William Hewlett and David Packard, with a global workforce of over 50,000 employees (HP annual report, 2022).
HP operates in a highly competitive technology industry characterized by rapid technological changes, intense competition, and a strong focus on innovation and new product development. Several issues, including political and commercial tensions between the countries in which HP operates, have had a significant impact on the company’s bottom line, as indicated by an assessment of HP’s PESTEL analysis (Miller, 2022). However, it is anticipated that the firm will be able to maintain its position as the market leader due to its strong brand and reputation for quality and innovation.
Short-Term Liquidity
The current ratio, also known as the working capital ratio, measures a company’s current assets against its current liabilities, i.e., the Current ratio equals current assets divided by current liabilities. A current ratio of 1 or higher is generally considered healthy, indicating that the company has enough existing assets to cover its short-term liabilities (Fernando et al., 2022).
For HP Inc. in 2022, the current ratio was 0.76, meaning that for every $1 of current liabilities, the company had $0.76 of current assets (Nirino et al., 2021). This is considered unhealthy, indicating that the company lacks enough current assets to cover its short-term liabilities. A current ratio of less than one can lead to financial difficulties, including defaulting on loans, difficulty obtaining new credit, or struggling to pay bills on time. This can negatively impact the company’s reputation and make it challenging to secure new business or maintain relationships with suppliers and vendors.
Moreover, a low current ratio can also be a warning sign for investors, suggesting that the company may be at a higher risk of defaulting on its debt obligations, which can lead to a decline in a company’s stock price and make it difficult to raise new capital (Yu et al., 2019). In addition, if the company cannot meet its short-term financial obligations, it could default on its debt, which can negatively impact its credit rating and make it more expensive for the company to borrow in the future.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Another way to analyze a company’s short-term liquidity is to look at its cash and cash equivalents. From April 2022 to July 2022, HP’s quarterly cash and cash equivalents increased from $ 4,477.00 million to $5,386.00 million. However, from July 2022 to October 2022, they remained constant at $5,386.00 million. From October 2020 to October 2021, HP’s annual cash and cash equivalents decreased from $4,864.00 million to $4,299.00 million. From October 2021 to October 2022, the amount further decreased to $3,145.00 million (HP Annual Report, 2022). That reduction can indicate various implications based on HP’s performance.
The corporation can have cash flow issues due to a decline in cash and cash equivalents. The firm may be using its money to pay off debt or make other investments if its cash and cash equivalents are declining, rather than earning enough to meet its costs. This could make it challenging to fulfill immediate financial responsibilities, such as making wages or paying bills.
Additionally, a drop in cash and cash equivalents can indicate that the business is investing in future development. For instance, a company may reduce its cash and cash equivalents if it uses its capital to fund new endeavors, purchase rival businesses, or enter untapped areas (Hutahayan, 2020). This may indicate that the company is investing in expanding its business.
Quick Ratio
The quick ratio, calculated by dividing a company’s cash and equivalents by its current liabilities, signals whether a business has enough liquid assets to cover its short-term debts (Gokul, 2020). A healthy ratio is 1.0 or higher. However, HP’s quick ratio is 0.47 (HP reports, 2021), meaning the company cannot fully cover its immediate obligations. This low ratio suggests potential financial distress and raises concerns about HP’s ability to meet its short-term debt (Yu et al., 2019). It can also indicate poor working capital management, which may lead to inefficiencies and cash flow issues, especially if the company has excess inventory or poorly managed receivables and payables.
Operating Efficiency
The term “operational efficiency” refers to a business’s ability to produce products or services while minimizing expenses and maximizing output. In relation to HP, “operational efficiency” refers to the firm’s ability to manufacture its goods and provide customer service successfully and efficiently. Gross margin, operating margin, and asset turnover are only a few of the financial measures that may be used to evaluate a business’s operational efficiency.
Gross Margin
Gross margin represents the percentage of revenue remaining after subtracting the cost of goods sold. Between October 2018 and October 2022, HP’s operating margin averaged 19%, peaking at 21.1% in 2021 (HP report, 2021). This margin is considered low, suggesting HP struggles to manufacture its products or services affordably. A low gross margin can signal several issues: intense competition driving prices down, reliance on expensive materials or labor, or ineffective supply chain management leading to elevated costs (Sciarelli et al., 2019). It also indicates weak pricing power, suggesting that HP may be unable to pass on increased costs to customers.
Operating Margin
Operating margin measures a company’s profitability, calculated as operating income divided by revenue. As of October 31, 2022, HP’s operating profit margin was 6.81% (HP Annual Report, 2022). This margin is considered low, indicating that HP is not generating a high income level from its operations relative to its revenue. A low operational profit margin may indicate excessive operating expenses, non-operating costs, or a lack of overall efficiency.
Since the ratio measures profitability, a low value for the derived statistic indicates that profitability is significantly low (Sciarelli et al., 2019). A lower operational margin, similar to a lower gross margin, may indicate that the firm is facing intense competition, which puts pressure on pricing. Lastly, a low operating margin may be a sign that HP is less able to invest in growth prospects, which would undermine its flexibility.
Asset Turnover
The quantity of sales or revenues produced per dollar of assets is known as asset turnover. The asset turnover ratio measures how effectively a business uses its assets. For the three months ended October 31, 2022, HP’s asset turnover was 0.38 (HP Annual Report, 2022). A higher turnover ratio is favored, as it implies that the company is more effective in generating sales or income than a lower ratio, which indicates that the firm is not efficiently utilizing its assets (Howard et al., 2022). A low asset turnover ratio may indicate that HP is not maximizing the use of its assets to generate income. This can imply that the business has a lot of idle assets that are not being utilized effectively or that it is not investing in resources to increase its income. Ineffective management of the company’s inventory levels, accounts receivable, or accounts payable might be the cause, resulting in inefficiencies and higher expenses.
Capital Structure
Table 1 highlights vital ratios that can be used to analyze HP’s capital structure. The following description will focus on three key ratios: debt-to-capital ratio, debt-to-assets ratio, and interest coverage ratio.
Table 1. HP Inc.’s Solvency Ratios/Capital Structure
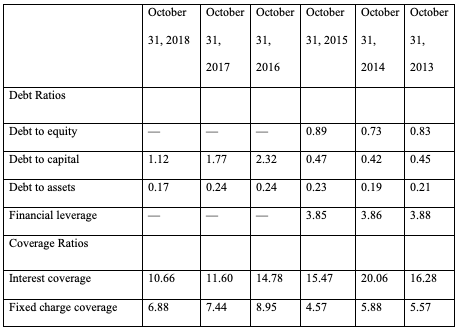
Debt-to-Capital Ratio
The debt-to-capital ratio is calculated by dividing the company’s interest-bearing debt by its total capital, which includes both long-term and short-term obligations. From 2016 to 2017 and from 2017 to 2018, HP Inc.’s debt-to-capital ratio increased (HP Reports, 2021). An improved debt-to-capital balance means that the proportion of debt to capital has decreased, which is generally considered a positive indicator of a company’s financial health. It suggests that the company has been paying off its debt or raising more equity, which can make it more financially stable and less vulnerable to economic downturns.
Debt-to-Assets Ratio
The debt-to-total-assets ratio reveals how much of a company’s assets are controlled by shareholders vs how much is owned by creditors. The debt-to-assets ratio for HP Inc. declined from 2016 to 2017 but then improved and leveled off to match its 2016 level in 2017, before dropping to 0.17 in 2018 (HP annual report, 2022). A decrease in a company’s debt-to-assets ratio implies that the company has a lower level of debt relative to its assets.
This financial shift, indicating the company has either reduced its debt, grown its assets, or done both, is usually seen as a positive sign of its overall financial health. It suggests the company is becoming less leveraged and relying less on borrowed money (Olibe et al., 2019). Therefore, a lower debt-to-assets ratio indicates that a corporation is less susceptible to economic downturns and, thus, less likely to default on its obligations.
Interest Coverage
Interest coverage is a ratio that measures a company’s ability to pay the interest on its debt obligations. It is calculated by dividing a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by its interest expenses (Trong & Nguyen, 2020). HP Inc.’s interest coverage ratio deteriorated from 2016 to 2017 and from 2017 to 2018 (HP Annual Report, 2022). A reduced interest coverage ratio for HP would indicate that the company’s EBIT is insufficient to cover its interest expenses (Indriyanti, 2019). This would suggest that the company may be experiencing financial difficulties and is at a higher risk of defaulting on its debt obligations.
Profitability
Net Profit Margin
The ratio measures the percentage of revenue that remains after accounting for all expenses, including taxes and interest. As of October 31, 2022, HP’s net profit margin was 5.09%, down from 6.21% in 2021 (HP Annual Report, 2022). Various factors, such as an increase in costs, a decrease in revenue, or a combination of both, can lead to a reduction in the net profit margin (Hutahayan, 2020). A decrease in the net profit margin can also indicate that the company faces increased competition, thereby reducing its pricing power. It could also show increased overhead costs and/or decreased sales.
Trend Analysis and Recommendations
Based on HP’s previous financial performance (in terms of liquidity, performance efficiency, and capital structure), it is reasonable to expect the firm to remain financially secure in the future, despite recording a lower net profit margin. For the future, HP must align with emerging trends that will help unwind old rules of financial management, which may lead to uncertainty during the company’s operations. First, HP’s chief financial officer should radically simplify the structure to allow for a continuous, streamlined matrix, enabling HP to be leaner and more efficient in unlocking the value of the products it offers in the market.
Moreover, the person in charge of financial controls in the internal realm should treat talent as scarce because that is where modernism has reached. That calls for anchoring efforts to source the talent and skills required, as well as how to attract key talents and manage them effectively to deliver a valued agenda in terms of finances. Lastly, HP, through its management, should adopt a new ecosystem that views other companies as collaborators in transforming the world. HP is a company that has performed dramatically financially, despite operating in a competitive environment. Its high turnover ratio and low debt-to-asset ratio indicate a financially healthy company.
Conclusion
Since HP’s operating profit margin is low, its income rates are also typical. HP recently recorded an asset turnover that marginally indicated a decline in the turnover ratio. Table 1 displays its capital structure ratios, allowing financial experts to identify the key elements that must be considered for financial success. Due to differences in shareholder ownership and influence, the debt-to-asset percentage has decreased.
According to HP’s interest coverage ratio, the corporation might be unable to service the interest on its debt commitments. The profit margin has shrunk when comparing the financial figures for 2021 and 2022. The business must adopt new economic structures to accommodate market offerings. HP can also accomplish its goals by managing the company’s talent. The advice is based on recent financial initiatives that may lead to improved financial security in the future.
References
Gokul, R. (2020). Comparative Balance Sheet in Grindwell Norton Ltd. Web.
HP Inc. (2021). HP Inc. reports fiscal 2021 full-year and fourth-quarter results. Web.
HP Inc. (2022). 2021 HP annual report. Web.
Hutahayan. B. (2020). The mediating role of Human Capital and Management Accounting Information Systems in the relationship between innovation strategy and internal process performance and the impact on corporate financial performance. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 27(4), 1289 Web.
Indriyanti, M. (2019). The Accuracy of Financial Distress Prediction Models: Empirical Study on the World’s 25 Biggest Tech Companies in 2015–2016 Forbes’s Version. KnE Social Sciences, 442-450. Web.
Miller. K. (2022). A rational and pragmatic PESTLE analysis of Hewlett-Packard. Crow jack. Web.
Nirino, N., Santoro, G., Miglietta, N., & Quaglia, R. (2021). Corporate controversies and company’s financial performance: Exploring the moderating role of ESG practices. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 162(2), 120–341. Web.
Olive, K. O., Rezaee, Z., Flagg, J., & Ott, R. (2019). Corporate diversification, debt maturity structures, and firm value: The role of geographic segment data. The Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance, 74, 206-219. Web.
Sciarelli, M., Landi, G., Turriziani, L., & Tani, M. (2019). Corporate social commitment from investors’ perspective: Evidence from Italian and UK asset management companies. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 10(3), 12–23. Web.
Trong, N. N., & Nguyen, C. T. (2020). Firm performance: the moderation impact of debt and dividend policies on overinvestment. Journal of Asian Business and Economic Studies. Web.
Yu, W., Jacobs, M. A., Chavez, R., & Yang, J. (2019). Dynamism, disruption orientation, and resilience in the supply chain and the impacts on financial performance: A dynamic capabilities perspective. International Journal of Production Economics, 218(4), 352. Web.