Introduction
Financial Reporting Council (FRC) is an independent regulatory body that seeks to promote high-quality corporate governance on proper reporting and investment. The FRC is structured to have board members, senior personnel, and a reviewing panel. The FRC has several benefits that are useful for accounting entities in the aspect of keeping uniformity and fair reporting. The council is mandated to formulate, issue and revise accounting policies that govern the reporting of financial statements. They also ensure all stipulated policies are fully adhered to. All this is done to safeguard the public financial governance and also to keep the same reporting framework across the globe. The council has to observe objectivity, integrity, and independence while undertaking its mandate. This is of key importance since it should not be compromised in various objectives.
Structure of Financial Reporting Council
FRC is a limited guarantee corporation that is partially funded by the government, industry, and the board. The board is appointed by the secretary of state business, innovation, and skills. They play a critical role in overseeing and developing the standards of the accounting industry (Fleming 37). The codes and standards committee offers advice to the FRC board on issues of systems, setting standards, and policy issues. On the other hand, the conduct committee offers advice on matters about behavior involved in the daily activities of the reporting. All these are in essence to foster high-quality reporting. Such high-quality factors include monitoring, overseeing, investigation, and discipline matters (Yaffey 27).
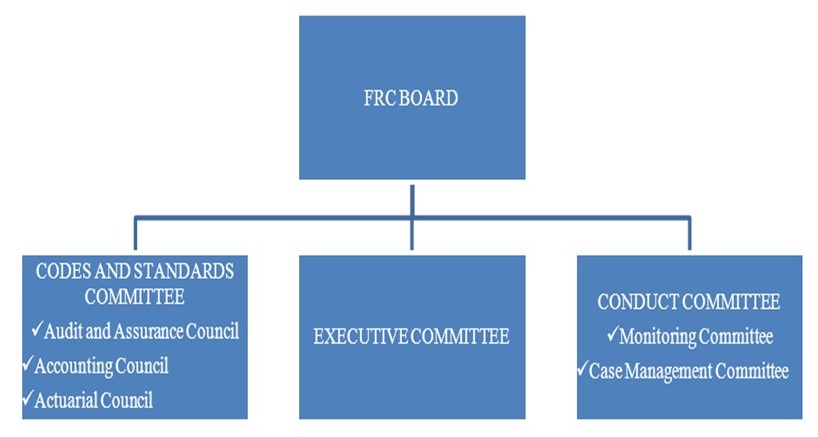
The monitoring committee, which is under the conduct committee, is composed of the financial reporting review panel while the case management committee consists of a tribunal. Additionally, according to the former structure, the FRC incorporated six bodies that were the Accounting Standards Board, Financial Reporting Review Panel, Accountancy, and Actuarial Discipline Board, the Professional Oversight Board, and Auditing Practices Board. The Accounting Standards Board issues accounting standards throughout the region since it is recognized for that particular purpose in the Company’s Act. However, it was overtaken by FRC in 2002 (Kondor and Dimitri 48).
The Financial Reporting Review Panel ensures the provision of financial information for the compliance of public and private corporations. These relevant accounting requirements are to be complied with, including the Company’s Act. Both boards for Accountancy and Actuarial Discipline are the basis for establishing the frameworks and setting legal formalities for participation with other accounting bodies. The major work is the investigation of the conduct of professional firms (Hughes 13).
An oversight panel guarantees that the reporting agencies formulate appropriate policies and administer effective conduct to its members. The members should be punished in line with the Company’s Act and statutory requirements. The body may inspect support of the FRC. However, in case of any disadvantages, professional organizations sanction the companies. Also, the board runs an Audit Inspection Unit, tasked with overseeing the auditing corporations, and advocates for any activities on controlling governmental and professional agencies.
The board may monitor the activities of the actuarial firms regarding educational, disciplinary, ethics, and career development issues for the members. Members of the board are from a widely spread category of qualifications and experiences (Yaffey 39). The Auditing Practices Board has the responsibility for setting up auditing standards. The main objectives involve the enhancement of public confidence in the process of auditing. In essence, public trust will be attained because of the quality and relevance of audit services for public interests. However, the board has been transferred to FRC, while the objective remains the same.
Work of the Financial Reporting Council
Upholding high principles of audit, actuarial and accountancy practice is one of the primary tasks of the council. It does this by being accountable to the national assembly and its significant range of stakeholders (Biondi and Soverchia 26). The FRC body obtains funds from the non-statutory analysis and abides by the principles of improved recognition through extended public consultation.
This council is tasked with the responsibility of promoting high-quality corporate governance and reporting. The framework sets the code and standards for accountancy, auditing, actuarial, and investing communities (Biondi and Soverchia 29). It does this by overseeing the conduct of the professional members involved. The FRC’s foremost task is ensuring every employee’s equality and uniformity of opportunity through acknowledging diversity with the values. From the commitment it has signed up to undertake, the council seeks to Think, Act and Report the public’s initiative that will enhance greater transparency on gender job issues (Oppermann 11).
The other function, according to the FRC’s culture of openness and collaboration, is to ensure that the capital market gains from up-to-date and useful information on company performance and the behavior of the board. The disciplinary process entails the decision to investigate, Investigation process, the decision about disciplinary actions, referral to the Tribunal, hearing by the tribunal, and allows imposition and cost orders.
The disciplinary investigation can be done through referral of cases by professional bodies to the FRC and the decision of FRC to investigate a matter. The committee charged with considering the case is called the conduct committee. This court determines whether the investigation criteria have been met. The investigations are done by the executive and the discipline team (Oppermann 12).
Role of Financial Reporting Council
The role of FRC is contained in the core objectives of auditing and accounting. These goals include:
Accounting standards
These rules should allow the users of financial statements to come up with and do an evaluation of allocating the limited resources. The accounting standards help directors in the discharge of obligations that relate to financial reporting. Accounting standards help in assessing performance, state of assets and liabilities, financing items, and investments. These standards promote the relevance, reliability, understandability, and comparison of financial statements.
Auditing standards
Relevant and comprehensive guidance information is provided by the auditing standards. It is important for opinion formulation and reporting. Accounts are enabled to check for compliance of the reports to the Company Act. Additionally, these reports are a requirement for the preparation of the audit report that is reliable and understandable to users of the financial reports (Biondi and Soverchia 31). Facilitation of the state’s economy is done by the auditing standards. Capital cost reduction along with corporations’ possibility to compete on the global market makes this possible.
These rules maintain investor confidence, even in the capital markets. Getting involved in technical deliberations of the accounting standard bodies for the FRC is minimized by the Company Act. FRC does not have power over the Australian Accounting and Standards Board (AASB) regarding developments, approving, or vetting standards recommended by the board (Biondi and Soverchia 35). The standard-setter maintains its independence because of the prevailing provision.
Benefits of Financial Reporting Council
The benefits of FRC include bigger chances for employment amongst the citizens. It also attracts more Foreign Direct Investments because of the protection of a uniform regulatory body. The FRC Act also helps in reshaping the state risk management system that aligns the public and private sector responsibilities. It also sanctions the misbehavior of the managing of public interest firms by raising the board members’ competence and responsibilities.
FRC helps to recognize the standard accounting limits since the financial statements were not sufficiently prepared to cover the response to a wide margin of stakeholders concerning relation to the operations. For instance, most financial statements do not capture the intrinsic value of intellectual assets that belong to an entity. Additionally, the financial risk may not be sufficiently adjusted in the statement of financial position. The FRC promotes a correlation in the financial statements’ standards using various approaches. Such approaches seek to offer insight on disclosures, footnotes, qualitative indicators for assessment and performance, and the overall governing system put into use. The FRC helps in putting an end to the details necessary for using the International Financial Reporting Standards. This will ensure a general revision of the accounting system to enhance the exposure to practically apply the standards (Penno 34).
The adoption of both FRC and IFRS helps to attain a framework that matches the dimensions of the performance of firms’ transactions and events. It also enhances direct reporting to help the process of communicating values in a language best understood by investors. From the FRC adoption, the shareholders are put first while in the recognition of non-current value it gets doable through the inclusion of the needs of every other stakeholder (Hoggett 24).
Activities of FRC
The FRC is tasked with setting the standard framework for auditors, actuaries, and accountants. It monitors the implementation of the standards and promotes the best practice of firms and professionals. They do this by issuing guidance and publication of papers. High-quality corporate governance enables the underpinning of the long-term performance of the company. The accounting market is attractive to corporate governance because of the high standards that help in the profession (Grosu and Bostan 17).
FRC activities are promoted to foster investments. The high standards embraced for corporate governance help in setting standards for financial reporting, auditing, and actuarial reporting. Actuarial standards are necessary for the efficient functioning of money and capital markets. Because investors are enabled to make counter-party comparisons through providing assurance. The FRC body has a division charged with codes and standards. This group develops and maintains the standards and guidance for auditing and assurance engagement. The assurance engagements must be performed for public interests. The FRC body also undertakes the oversight functions throughout the state of business, innovation, and skills (Young 30).
This agency is tasked with the sovereign disciplining and investigation for actuaries and accountants. Therefore, the agency is accused of the responsibility to operate and administer independence. FRC’s stakeholders, like institutional investors and individual member insurance policyholders, place their reliance on the actuarial work. The body also monitors audits of the listed and corporations of public interests. This is facilitated by the quality review team facilitates (Kieso 40).
The FRC provides the preparation of financial statements in line with the relevant accounting standards. This seeks to ensure that the balance sheet gives a true and fair view of the company finances at the end of the fiscal year (Kieso 44). On the other hand, a real view of the profits and losses rates has to be given by the profit and loss account.
The standards, however, do not have a definition of the true and fair view, but they are taken to be the accounts that are accurate and not likely to mislead the users (Kieso 47).
Conclusion
The FRC seeks to foster the conditions for sustainable long-term investing, which becomes vital as the market gains confidence in the quality of corporate governing and professional practice standards. The FRC promotes excellent quality of corporate reporting and governance through setting rigorous standards and publishing codes for directors and investors to work on. The integral to corporate governance involves a compliance and explanation principle. This policy seeks to accelerate the best practice for investors who will hold the management to account for any occurrence.
The FRC has arrangements for discipline that contribute to the attainment of the mission. Such efforts include the ability to seek to deter future misconduct and the imposition of appropriate sanctions with the approval of the misconduct. The council provides a system for the investigation, imposing disciplinary measures in instances of potential misconduct. Therefore, the FRC is tasked with safeguarding the interest of the public through protecting them, keeping their confidence, and declaring proper standards of conduct for professionals.
Works Cited
Biondi, Yuri, and Michela Soverchia. Accounting Rules for the European Communities: A Theoretical Analysis of Accounting, Glasgow: Economics and Law Journal Press, 2014. Print.
Fleming, Sarah. FRC Consultation on Auditor Liability Limitation Agreements, Edinburgh: Law Society of Scotland, 2008. Print.
Grosu, Veronica, and Ionel Bostan. Risk Management and Prevention for Financial Instruments Based International Standards of Financial Reporting IAS 32 and IAS 39, Oxford: SSRN Journal Press, 2012. Print.
Hoggett, John. Accounting, Milton: John Wiley and Sons Limited, 2012. Print.
Hughes, Katie. Accountancy. Teddington, Richmond Upon Thames, England: Keynote Limited, 2010. Print.
Kieso, Donald E, Jerry Weygandt, and Terry Warfield. Intermediate Accounting, Hoboken: Wiley, 2012. Print.
Kondor, Peter, and Dimitri Vayanos. Liquidity Risk and the Dynamics of Arbitrage Capital, Cambridge: National Bureau of Economic Research, 2014. Print.
Oppermann, Booysen. Accounting Standards, Lansdowne: Juta, 2001. Print.
Penno, Mark C. Rules And Accounting: Vagueness In Conceptual Frameworks and Accounting Horizons, London: John Wiley and Sons Limited, 2008. Print.
Yaffey, Michael. Variants of the Cash Flow Statement, Sydney: Project Appraisal Journal Press, 1989. Print.