Problem Background
Franklin Heights has reached a turning point as it attempts to overcome a myriad of obstacles that have stymied its progress. This paper aims to give a comprehensive analysis of these problems and provide suggestions on how to revitalize the city. We considered the results of prior studies and adjusted our conclusions so that they are more in line with the goals and interests of the target audience for this study.
Problem Analysis
Franklin Heights’ problems are complex and far-reaching, but there are three main ones that need fixing right now. The city’s economy has stalled because it lacks diversified sectors, has few employment openings, and requires an updated infrastructure. Due to its over-reliance on a small number of industries, Franklin Heights has limited its potential for growth and success.
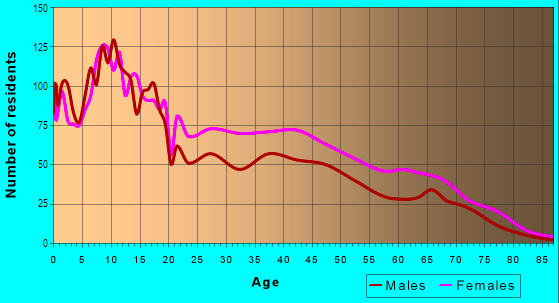
There are long-standing inequalities in the city’s school system – especially taking into account the number of residents of the corresponding age (Appendix A) – and they have serious consequences for the city’s ability to train its future workforce and advance as a whole. The city’s potential for development is stunted by the fact that not everyone has equal access to high-quality education (Poister et al., 2014). Then, residents’ feeling of safety and security has been damaged by growing crime rates and insufficient law enforcement resources. These security issues have a major impact on the quality of life in Franklin Heights and deter potential new residents and companies.
Evaluation of Strategies and Recommendations
Feasibility
Different techniques have varying degrees of potential for actualization. Diversifying the economy is a possibility. The potential long-term benefits in terms of economic development and job creation make it a feasible alternative despite the need for an initial financial commitment and the possibility of political resistance. Building strong public-private partnerships and spending resources wisely are the keys to overcoming obstacles. Whether or not education reform is possible depends on how much money is put into school buildings.
Although it may need new legislation and more spending, the long-term effects on the quality of education and the growth of the local workforce align with the city’s SMART objectives. Overcoming these obstacles may be aided by advocating for legislative improvements and receiving the required financing (Venkataramanan et al., 2018). With the correct resources and assistance, community policing may be easily implemented. While there may be initial costs involved, this is a technique that can help the city achieve its SMART objectives faster and with more success. One way to get around possible resource constraints is to look into federal funding options and encourage community engagement.
Impact
It is critical to grasp how these tactics will affect Franklin Heights. The city’s economic development and employment creation might benefit greatly from more economic diversity. Franklin Heights may secure a more stable and successful future by broadening the range of its economic activities (Poister et al., 2014). This method is consistent with the city’s SMART objectives.
Although the benefits of education reform may take time to become apparent, it is an essential strategy for creating a more capable and competitive labor force in the long run. Consistent with SMART objectives, it will improve the city’s education system and its workforce in the long run, making life better for everyone who lives there. Community policing has the ability to immediately improve public confidence and security. Franklin Heights can better accomplish its SMART objectives if it works to strengthen relationships between the police and the community.
Implementation Plan
Critical duties and possible obstacles must be addressed for a successful rollout. In order to attract new firms and industries, Franklin Heights should create an economic development agency. However, political opposition is possible, and resources must be allocated carefully for this project to succeed. To lessen the effects of these problems, it will be crucial to strengthen public-private partnerships and allocate resources wisely.
Curriculum modernization and intensive teacher preparation are two of the most pressing needs in the field of education reform. These measures are essential but could need new laws and more spending (Venkataramanan et al., 2018). Overcoming these obstacles and successfully implementing this plan will need advocacy for legislative improvements and the acquisition of essential financing.
Franklin Heights’s success in implementing community policing hinges on the recruitment and training of community police who can establish positive bonds with the neighborhood’s inhabitants. While this plan is doable, it may need more funding or opposition from the locals. Applying for government funding and encouraging community cooperation to overcome these obstacles will be crucial.
Resources
Economic Diversification
- Financial: An initial budget allocation of $2 million.
- Human: Economic development experts and city planners.
- Organizational: The creation of a new department and the fostering of interdepartmental cooperation.
Education Reform
- Financial: An investment of $1.5 million for curriculum development and teacher training.
- Human: The recruitment of education experts and trainers.
- Organizational: The establishment of an oversight committee to coordinate efforts with educational institutions.
Community Policing
- Financial: A budget of $500,000 for recruitment and training.
- Human: The hiring of law enforcement professionals.
- Organizational: The formation of a community liaison team to facilitate public outreach and engagement.
References
City-data.com. (2022). Franklin Heights neighborhood in Milwaukee, Wisconsin (WI), 53206, 53216 detailed profile. Web.
Poister, T. H., Aristigueta, M. P., & Hall, J. L. (2014). Managing and measuring performance in public and nonprofit organizations: An integrated approach. (2nd ed.). Wiley. Web.
Venkataramanan, V., Crocker, J., Karon, A., & Bartram, J. (2018). Community-led total sanitation: A mixed-methods systematic review of evidence and its quality. Environmental Health Perspectives, 126(2). Web.
Appendix A. Distribution of Residents’ Ages in Franklin Heights