Full Employment
State of full employment is often referred to as the natural rate of unemployment. The natural rate of unemployment comprises of voluntarily unemployed workers in an economy. At this state, any member of the labor force seeking employment gets it. This state of unemployment is unstable and more than often falls. When it falls, wages rise. Since wages make about 70% of production cost, producers pass on the increase in wages to final consumers.
This causes inflationary pressure in the economy. A number of factors in the economy can cause the stock market to crash. These factors cause a steady deterioration of performance in the stock market. A crash in the stock market leads to failure in banks and businesses. The net result is a soaring employment rate and recession. Thus, this reflective treatise attempts to discuss the possibility of an economy to ‘self-correct’ after a recession caused by a slump in the stock market. The discussion makes use of the income-expenditure model.
Thesis Statement
Based on the income-expenditure model and ideas of the classical economists, the economy can self-correct after a recession. The model explains that there is a tendency of prices to fall after recession resulting in increased aggregate consumption thus, restoring full employment.
Income – expenditure model
The model equates total income (Y) in the economy to a sum of expenditure in the economy. These expenditures are consumption (C), government spending (G), investment expenditure (I), and net exports (X-M). Based on the model, the unemployment level caused by recession creates disequilibrium in the labor market; that is, there is surplus labor supply with a corresponding low demand. The disequilibrium state pushes the market wage rates down, resulting in the low cost of production. This causes a decline in the prices of goods and services. With reduced prices of goods and services, consumers’ real wealth: in terms of purchasing power, increases thus increasing aggregate consumption in the economy. As consumer expenditure rises, the level of aggregate demand increases until the full employment level of output is attained. Therefore, using the income-expenditure model, the economy is self-correcting after experiencing a recession. This model is based on the assumption that there are no government interventions.
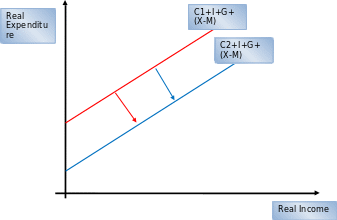
Explanation of the graph
In the diagram above, linear graph C1+G+I+(X-M) shows full employment level assuming that consumption is the only variable that depends on income. Recession causes unemployment and a decline in aggregate consumption. This makes the curve to shift to the right, that is, from C1+G+I+(X-M) to C2+G+I+(X-M). The shift results from the disequilibrium in the labor market which exerts pressure on the household to cut consumption hence the shift.
Notably, the shift is not sustainable since it is disequilibrium. Therefore, the economy ‘self adjusts’ by restoring equilibrium in the labor market through a decline in wages. This results to decline in wages, reduced cost of production, and an increase in aggregate consumption. This restores full employment level.
Conclusion
The model advocates that the economy ‘self corrects’ after experiencing a recession. However, the assumption of no government intervention is not realistic. Besides, if the economy is left to correct itself, it might take a long period as experienced during the 1930s great depression. Use of fiscal policies, such as lowering government taxes and increasing government spending, and monetary policies, such as regulating interest rate, and money supply can correct the economy effectively.