Introduction
This functional behavior assessment (FBA) was completed for Joe Wood, a 40-year-old male residing at a psychiatric hospital. Wood was diagnosed with histrionic personality disorder (attention-seeking) and autism. The assessment was conducted by Harold Townsend, who interviewed Ms. Jones, a residential worker at the facility, on 30th July 2022, during the day. The purpose of conducting a Functional Analysis Screening Tool (FAST) is to identify factors that influence the occurrence of the problematic behaviors observed (Candel, 2019; Davin, 2020). In addition, ABC-R data collection offers a framework for understanding the behavior of an individual and the foundation of applied behavior analysis (ABA).
FAST is a tool developed to understand problem behavior and its contributing factors. It elucidates the functional relations between environmental variables and behavior. It is intended to be a tool for primary assessment and consists of sections on social influences on behavior and social and nonsocial reinforcement (“Functional Assessment Screening Tool (FAST),” 2022). ABC concerns the context of a behavioral event, accounting for a three-term contingency relation of antecedent, behavior, and consequences (Cooper et al., 2020; Davin, 2020). ABC-R data is collected through continuous observation and documentation of environmental stimuli and responses to them. Specifically, all stimuli, behaviors, and consequences are to be recorded to understand why behavior occurs and continues (Evans, 2022). In this case, ABC data were collected within the compound of the facility hosting Wood at different times of the day.
Target Behavior
Wood is a 40-year-old adult who has an attention-seeking histrionic personality disorder. He tends to achieve the approval of other people to an extreme extent, which causes him to act in an overly studied and exaggerated manner that is inappropriate as he seeks to gain attention. It is reported that Wood has emotions that shift rapidly, moving from one extreme to another. To attract the attention of those around him, Wood sometimes acts dramatically, throws tantrums, fishes for compliments, and engages in provocative behaviors. His ability to make decisions is affected, with decisions sometimes being made abruptly based on how he thinks will attract the attention of others (French & Shrestha, 2021). In addition, the patient tends to feel uncomfortable when he is deprived of attention.
FAST Results
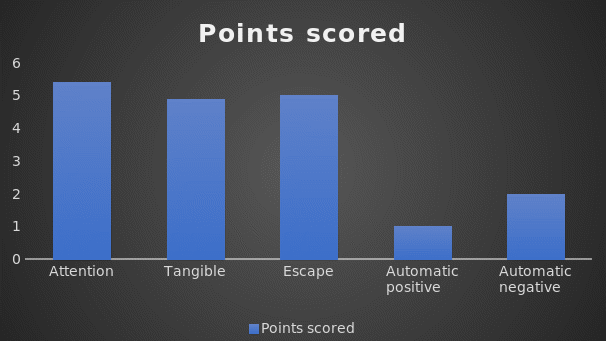
The FAST assessment was completed as an interview between the assessor and Mrs. Jones, the social worker responsible for dealing with Wood. The assessment has 27 questions that seek to identify the circumstances of the problem behavior (See Appendix 1). As the results indicate, Wood’s attention-seeking behavior makes him become tangible and escape (See Figure 1). There is evidence that the automatic function of behavior occurs, as shown in the results, which means that Mrs. Jones sometimes notes this behavior in Wood.
ABC-R Data Analysis and Hypothesized Function
The Antecedent-Behavior-Consequence (ABC) chart is developed to gather objective data on the environmental variables and their effect on the person of interest. The assessor completed the chart with Mrs. Jones’s input at the facility during each event. Throughout the session, Mrs. Jones was trained and involved in all the events and locations. The results from the analysis with the ABC-R indicate that Wood’s attention-seeking behavior most commonly results from the denial of attention or criticism of his behavior by those around him (See Appendix 2). These results demonstrate that Wood acts or speaks out while watching if other people around him are paying attention. However, if people do not look or listen to him, he often frowns, shouts out loudly, and employs physical movements to draw attention to himself. However, the data shows that his anger stops after each episode. The data shows that the behavior is repeated when those around him criticize his behavior. Sometimes, other residents and staff resort to such consequences as telling him to stop acting or shouting. In most instances, he obeys these consequences and stops the acting or shouting behavior, albeit unwillingly.
Considering the collected data on antecedents of behaviors and response to consequences, it is hypothesized that Wood’s behavior is “access to tangible,” given that when he is denied attention or is criticized positively for his behavior, he shows attention-seeking behaviors. Tangible access is the most likely function of his attention-seeking tendencies because the behavior stops when he is told that his actions are inappropriate as he receives attention.
Functional Analysis Procedures and Hypothesis Results
The purpose of functional analysis (FA) procedures is to confirm a hypothesized function of behavior identified in the FBA assessment. In this case, confirming the function of Wood’s behavior is access to tangible requires the following FA procedures.
Tangible Condition
It is imperative to start by determining whether the behavior indeed serves a tangible function. Wood will be exposed to an assessment that will allow him to behave in an attention-seeking manner. When he does, he will be told to stop in the next two minutes. If the behavior stops when he is given time to escalate it, it can be said to be serving a tangible function. However, if the behavior does not occur or escalates after the extra time, it cannot be considered tangible access. Specific preparation for the procedure includes setting up a group activity that requires all participants to take turns talking, with Wood being asked his opinion the last.
Escape Condition
It is important to determine whether the behavior serves an escape function. First, a challenging demand will be placed on him. For example, he can be told to listen or watch his peers as they perform some actions such as music because it is well known that he always wants others to watch him dance. If he shows behaviors that can be viewed as attention seeking, for example, throwing a tantrum, he will be told that he can join in the act later. It is expected that the behavior will occur after the demand is placed on him and seize when he is told that he can join the activity. However, if the attention-seeking behavior does not appear after the demand or continues after he is told to join in the action, the assessment will conclude that the function served is not escape.
Attention Condition
This step will involve telling him to do what he likes, such as playing guitar. The assessors will bear in the location but will pretend not to pay attention to his music and perform other tasks such as talking loudly with others. The antecedent of ignoring Wood is the most appropriate for assessing attention conditions. If Wood stops the action when he realizes that nobody is paying attention, others will give him an audience by negatively evaluating his music performance. If the target behavior is observed and serves attention, it is expected that the behavior will occur after attention is denied and cease if it is given. In this case, it is irrelevant whether the attention is positive or negative (Cooper et al., 2020). The task will be repeated several times and in different situations.
Play Condition
The final assessment phase will involve paying full attention to what Wood is doing. The idea is to give Wood his favorite guitar, tell him to perform his best piece of music, and pay full attention to his performance. Granting free access to the preferred item is ideal for testing the play condition (Cooper et al., 2020). The audience can sing along with him and shout in praise of his musical performance. It is expected that the attention-seeking behavior will not occur, which can lead to the presumption that the target behavior does not serve an automatic function.
FA Procedures, Settings, and Hypothetical Results
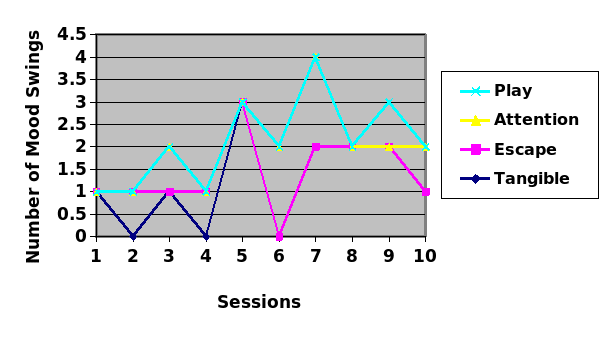
In the planned assessment, the FA procedures will take place within the facility. The assessor, Mrs. Jones, and other staff members will be involved. The primary assessor will be in charge of directing the assessment. It is necessary to repeat all the stages of the FA assessment for approximately three sessions (Davin, 2020). The tasks and settings will be done inside the facility rooms, the hall, and the field. The data will be collected by observing the behavior that occurs as a response to the setup antecedent and the behavioral response to the given consequences. The number of target behavior occurrences in each session will be counted as a frequency count. Data will be filled in the forms provided, which contain structured questions. Then, the total number of behaviors per session can be graphed accordingly, as shown in Figure 2. See FA Data Collection Sheet in Appendix 3.
Conclusion
In summary, it is expected that the FA procedures will reveal that access to the tangible function is the most probable and explain the attention-seeking behaviors shown by Wood. Specifically, it is anticipated that the FA procedures will lead to a greater number of instances of attention-seeking behaviors demonstrated when the tangible condition is tested. However, the attention condition will likely yield a substantial number of target behavior events.
References
Candel, O. S. (2019). Review on the Present Condition of Histrionic Personality Disorder.Buletin de Psihiatrie Integrativa, 82(3), 39-44. Web.
Cooper, J. O., Heron, T. E., & Heward, W. L. (2020). Applied behavior analysis. Pearson Education.
Davin, R. (2020). Implementing Brief Functional Analysis within Clinical Practice. Web.
Evans, A. (2022). Webinar 5. Web.
French, J. H., & Shrestha, S. (2021). Histrionic personality disorder. StatPearls Publishing.
Functional Assessment Screening Tool (FAST). (2022). Community Mental Health for Central Michigan. Web.