This course focuses on the beginners of nursing care of customers to encourage healthy transition for persons showing occurrences of chronic illness in a well-defined practice setting. It offers an overview of human needs, how to use nursing as a systematic method to address those requirements and nurse’s responsibility in aiding persons in achieving optimal health outcomes. Basic time management ideas are emphasized, and the continuous ability to think critically, clinical judgment, and skills (Kitson, 2018). This course allows nursing students to get the skills they have to meet customers’ demands throughout their lives.
The students in this course will learn the conceptions and theories primary to the art and science in nursing. On the other hand, the students will get an orientation to the perceptions of customers’ requirements, security, communications teaching or learning, critical thinking, ethical-legal, cultural diversity, nursing history, and the program’s philosophy of nursing (Feo et al., 2018). Nurse to patient relationship will also be emphasized to enable the learners to enhance their communication skills and care giving capabilities.
In this course, students will learn about infection control, safety, and necessary measures to keep clients safe from harm. This course also covers the psychomotor nursing knowledge. The program includes skills for ensuring microbiological, physical, and mental safety and skills for treatment modalities. It offers an orientation to the healthcare industry, in terms of teamwork and delivery systems as well. The participants will learn about the function of healthcare practitioners and the variety of healthcare organizations, and the degree of treatment they give.
Gap Analysis
Duration and Contents
The course “Fundamental Principles of Nursing Care Theory” takes one entire semester, with an admission requirement of three credits. This course focuses on the beginners of nursing care of customers to encourage healthy transition for patients with chronic illness in the well-defined practice setting. The course is typically taught in nursing colleges or universities for an undergraduate diploma in nursing. The theory instructions methods are conducted through:
- Lectures and discussions
- Through demos
- Video or giving hand-outs or in the form of YouTube assignments.
On the other hand, examinations and assignments are evaluated in the following manner, where student class attendance is treated as part of an exam:
- Quiz or Unit exam constitutes 20%
- Student attendance is 10% (whether online or on-campus)
- Class assignments 10%
- Midterm exam 25%
- Main examination 35%
Before sitting the unit exam, all assignments must be completed (with NO EXEMPTIONS whatsoever). Absentee on the exam day without a previous professor or management’s consent will result in a ZERO. A Skills Lab is included in this program.
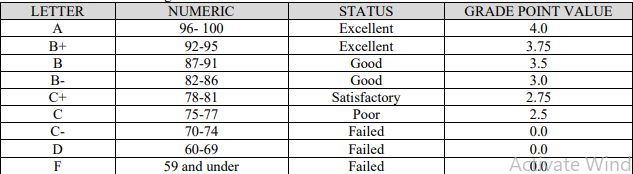
THE GRADING POLICY FOR GENERAL EDUCATION AND THE SCIENCES is as follows, with a pass mark for the course set at 75%. The nursing courses typically need a minimum of 78% for a pass, while the LAB and Clinical are generally graded as P for a Pass and F for a Fail.
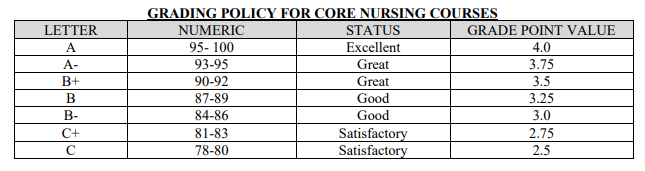
The students are required to attain a minimum of 78% in the nursing core class in their final examinations, irrespective of the quizzes to be considered to have passed in their studies. Any other grading that is below 78% in the core courses is, on the other hand, thought failures where they will be prevented from proceeding to the next level. This will instil hard work, commitment, and responsibility to the student to manage their time well.
Repeating of Courses
A student who receives a “D” or “F” in a subject may repeat it at the School of Nursing. A student who drops out of a class will be able to retake the course up to two times. Credit will be awarded for the previous effort, even though it will be noted that the grade was a repetition, which will be shown by an “R” next to the final grade. A student will be required to withdraw from the school after the second chance of repetition or third attempt. They can then be allowed to choose to resubmit to other short program after a full academic year (Wiggins & McTighe, 2005). A student in the Associate of Science in Nursing Program, for instance, who failed a class on their third try can reapply to the Practical Nursing Program. I suppose a student in the Practical Nursing Program failed a particular course on their third trial, they may reapply to the Nursing Assistant Program. They may apply to get back to their former program, supposing they are successful in a particular program.
Ideas
The three big ideas:
- Learning objective 1: Knowledge – At the entry-level of training, students must apply their understanding derived from professional nursing to the provision of evidence-based nursing care.
- Learning objective 2: Technological Aptitude – At the enrolment level of expertise, students will be able to use technologies to access information needed for discovering patterns, helping to promote quality enhancements, preserving safeness that can provide patient care, and work collaboratively with inter-professional team members, while continuing to progress their nursing careers.
- Learning objective 3: Lifelong learning – Through engaging in scientific inquiry, research, and new knowledge development, students will continue to progress their education to offer high-quality care.
For each of the above three students learning objectives, they should be able to comprehend the following from the “three big ideas”:
- Learning objective 1: The students will have explored and understood the importance of evidence-based practice in providing good nursing care.
- Learning objective 2: Demonstrate familiarity with computer programs used in client evaluation, care, and documenting. Demonstrate understanding of the criteria required for safe and effective documentation that complies with legal and ethical obligations.
- Learning objective 3: Determine the varied functions of nurses in diverse health environments and the responsibilities of other healthcare professions. Address the necessary nursing concepts, professional attitudes, personal attributes, and professional behaviours for exemplary interpersonal inter-relationships involving caregivers, patients, households, and co-workers.
The main objectives essential questions:
- Learning objective 1 – What knowledge will you have acquired by the end of the nursing course?
- Learning objective 2- Having been an expert in technological nursing, how best do you maintain patients’ confidential information?
- Learning objective 3 –After the current course, you are undertaking, what will be your next class in nursing to maintain lifelong learning?
The skills and knowledge acquired from each objective:
- Learning objective 1:
- Knowledge: The knowledge of the fundamental principles of nursing care theory.
- Skills: The ability to implement knowledge in the evidence-based nursing care.
- Learning objective 2:
- Knowledge: Technology is a critical factor in the nursing industry.
- Skills: Critical thinking in the nursing career.
- Learning objective 3:
- Knowledge: Professional nursing necessitates continuous learning to keep the nurse updated on the global changes in the industry.
- Skills: Problem solving abilities in the career.
References
Wiggins, G. & McTighe, J. (2005). Understanding by Design. ASCD.
Shoghi, M., Sajadi, M., Oskuie, F., Dehnad, A., & Borimnejad, L. (2019). Strategies for bridging the theory-practice gap from the perspective of nursing experts. Heliyon, 5(9), e02503.
Kitson, A. (2018). The Fundamentals of Care Framework as a Point-of-Care Nursing Theory. Nursing Research, 67(2), 99–107. Web.
Feo, R., Kitson, A., & Conroy, T. (2018). How fundamental aspects of nursing care are defined in the literature: A scoping review. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 27(11-12), 2189-2229.