Roots of the global financial crisis
The current global financial crisis traces its roots to the United States of America. It partly started with the collapse of the US sub-prime mortgage market (Williams 2010, p. 5). The Federal Reserve sought to cut lending rates leading to inflation in the housing bubble. The sub-prime mortgage crisis emanated from financial instruments like securitization. This is where banks pooled different loans into sellable assets. In the process, there was a tendency of offloading risky loans.
Because banks could easily earn millions from these loans, they turned them into securities. In the process, banks borrowed more to lend out to the market. Some banks could not rely on savers. A bad loan was considered a problem to the borrower. This made other banks to get into loans with an aim of selling them. After running out on people to lend, banks turned to sub primes (Tett 2009, p. 13).
As a matter of fact, self-certified loans became very popular making banks to buy securities from others. Because of this, Collateralized Debt Obligations were very complicated. As a result of this, they often hid bad loans.
On the other hand, investment banks ended up in the business of mortgages and loans without the right controls and frameworks. This exposed banks to huge risks.
As problems were manifested, lending slowed down. This was as a result of low confidence in loans. Owing to loss in value of assets, lenders were already demanding for a refund of the money they had invested (Tett 2009, p. 18). On the other hand, the market experienced a lot of credit defaults. Credit default swaps were meant to tell if one could pay a loan or not but the market was over speculative.
Banks had little deposits and hence could not meet lenders demand for money. In the process, some of them collapsed drastically. Most banks did not have capital reserves (Atwood 2008, p. 9). The end result was that businesses and individuals that relied on credit could not get cash which led to massive financial problems.
Why it evolved into a world crisis
After affecting the banking and credit sectors in the US, the global crisis slowly crept to other countries and in the process became a world crisis. It became a world crisis by verging on a systematic crisis approach. This was because of the domino effect and other psychological contagions (Williams 2010, p. 13). As a result of this, it was able to spread to other economic and financial areas worldwide.
This can be traced from financial markets because it eventually degenerated to become a market crash. On the other hand, equity funds fell short of cash which made them to get rid of their assets. In addition, there was a large impact on public finance because most financial institutions had to be bailed out to continue with their operations (Atwood 2008, p. 16). Insurance firms and pensions firms could not meet their financial commitments because they did not have enough cash to cater for these.
There was also a problem in Forex because the USD is used as a global currency. This affected various currencies in Europe and Latin America. One of the first causalities outside the US was Northern Rock (a major bank in Britain).The crisis later on entered an acute stage with the collapse of banks and financial institutions both in America and Europe( Cohan 2009, p. 19). Other countries had problems because their currencies lost value. In the process, they could not make payments on loans.
Impact on Australian and world economies
Because of the global financial crisis, Australia has had a lot of current account deficits. This has been mostly on its transactions with the rest of the world. It can be explained from the fact that the country has been financing its deficits from overseas borrowings (Cohan 2009, p. 21). This means that foreign banks that are currently controlled by their governments will not be willing to lend to Australia.
It also implies that Australian banks don’t have the necessary capacity to replace previous lending. Australia’s exports have been affected because of deep recessions (as a result of the global crisis) on its major trading partners. Business and household finances have fallen because of a drop in the country’s share prices (Haigh 2009, p. 28).
On the other hand, business confidence has fallen drastically because of bad news from abroad as a result of the global financial crisis. Although the global economic crisis has affected Australia, there is good outlook from the economic indicators.
GDP and real net national disposable income
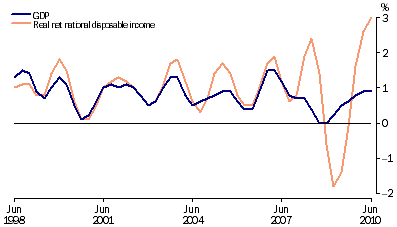
From the graph, GDP and real disposable income are slowly picking up. Foster group is Australia’s leading brewer and as matter of fact it, has been greatly affected by the global economic crisis. The groups wine business has continued to struggle as a result of exchange rate movements and US market conditions (Chappell 2009, p. 4). On the other hand, the global financial crisis has affected the group through a sluggish demand that has created an oversupply.
Sales in Australia have also dropped because people do not have enough disposable income to spend on its products. This means that wine consumers have been switching to less expensive brands as a result of the economic downturn. On the other hand, global wine sales have also drooped by 5.3% (Chappell 2009, p. 7).
Unfavorable exchange rates are expected to reduce the groups earning in both frontiers. A 9¢ increase in exchange rates with the US dollar will affect profits because the dollar is used globally as far as exchange rates are concerned.
USD Per Australian Dollar Currency Exchange Rate
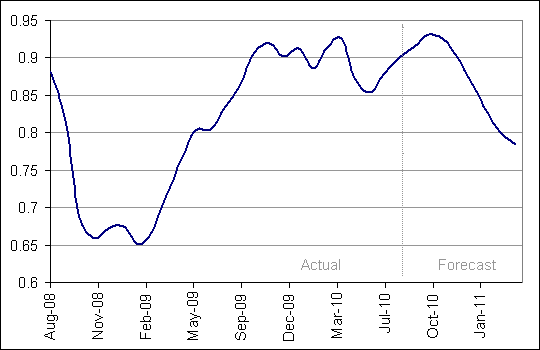
A strong Australian dollar will continue eating into the groups profits (Chappell 2009, p. 8). In addition, poor economic conditions are expected to affect sales volumes in both markets (local and global).
As a result of the global economic crisis, many world economies are likely to initiate a banking shake out. This means that interest rates will have to be reduced for sustainability. Economies have witnessed a significant drop in their economic growth leading to a downward trend in their forecasts (Haigh 2009, p. 28). This is because there is a drop in trade and commodity prices. As a matter of fact, most economies have seen a drop in remittances from abroad.
The future for Australia’s economy
It is evident that regional growth variations will vary as resource boom states come back to life (Ferguson 2008, p. 9). As much as there has been lot of down falls in different economies, Australia’s banking sector is still in good shape. The government has initiated good monetary policies that have worked effectively. This is because interest rates have fallen drastically.
Markets have lost confidence because of the global economic crisis. As a matter of fact, the government needs to initiate good policies in relation to growth theories. For instance, it needs to stimulate aggregate demand in a bid to increase consumer spending (Goodman 2008, p. 23). According to the Keynesian theory, when consumers experience an increased aggregate demand, they will create an excitement in the economy. This creates a good environment for economic growth.
On the other hand, there is need to focus on the three building blocks of economic growth. These include; the saving function, production function and the labor function (Goodman 2008, p. 27). For these to be attained, the Australian economy needs good and strategic fiscal policies. On the other hand, retail property yields have increased by 50-100 points.
According to the Harold Domar theory, growth will depend on national saving ratios. Savings will only increase after an upsurge in economic growth. Australian banks have not been greatly affected by the global financial crisis like other banks in Europe and America (Ferguson 2008, p. 14). This means that banks can still lend to spur growth that will increase consumer spending.
The multiplier theory can also be used to stimulate economic growth. This will be done by increasing the marginal propensity to consume. These will later on increase equilibrium income in these economies. On the other hand, autonomous consumption will increase by large margin.
There is need to enhance the supply of credit and craft good mechanisms that will increase demand for such. Some foreign banks are withdrawing their operations from Australia and this will put pressure on the availability of credit. Because of this, there is need to increase investments in the financial sector (Williams 2010, p. 32). Export prices and commodities are expected to fall in coming months and good measures should be put in place to revert this.
Reference List
Atwood, M., 2008. Payback: Debt and the Shadow Side of Wealth. Toronto: House of Anansi.
Australian Bureau of Statistics, 2010. Australian Economic Indicators. Web.
Chappell, T., 2009. Oversupply and GFC hits Foster’s Group wine sales. Web.
Cohan, W, D., 2009. House of Cards. Tale of Hubris and Wretched Excess on Wall Street. New York: Doubleday.
Ferguson, N., 2008. The Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the World. London: Allen Lane.
Goodman, P, S., 2008. Credit Enters a Lockdown. New York: The New York Times. McGraw-Hill.
Haigh, G., 2009. Stupid Money. Queensland: Griffith University.
Tett, G., 2009. Fool’s Gold: How Unrestrained Greed Corrupted a Dream, Shattered Global Markets and Unleashed a Catastrophe. New York: Simon and Schuster.
Williams, M. T., 2010. Uncontrolled Risk: The Lessons of Lehman Brothers and How Systemic Risk Can Still Bring Down the World Financial System. New York: McGraw Hill.