Executive Summary
The demand for footwear products is constantly growing owing to the increased urban population and change in the standard of living. Even though there are a considerable number of footwear manufacturers in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), the demand still surpasses supply. This report focuses on the establishment of a semi-mechanized footwear production unit in the UAE by Hamdan Footwear.
Hamdan Footwear is a company based in Punjab, India, and is planning to venture into the UAE market. The UAE’s production unit will exclusively focus on the production of affordable footwear for ladies. The footwear will be sold directly to wholesalers and retail outlets in major cities across the country. The company will target female consumers between the ages of 18 to 35. Since the company will focus on manufacturing stylish and affordable ladies’ shoes, it will target both lower and upper segments of the market. The shoes that meet the quality standard will be classified as “Grade A”, whereas shoes that fail to meet the standard will be classified as “Grade B”.
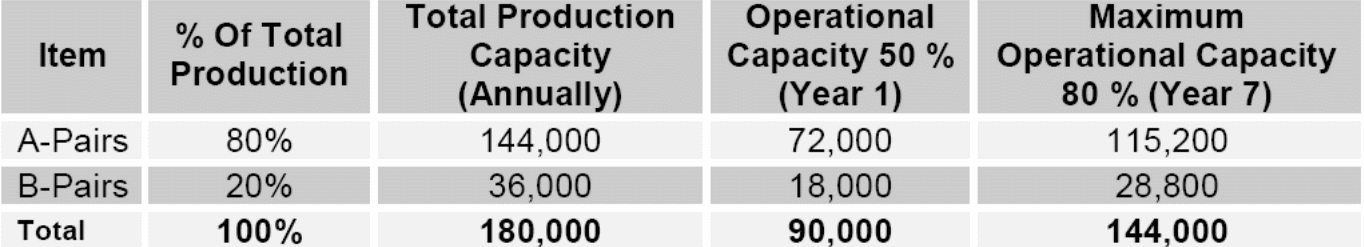
Out of the aggregate output, 80 percent will be “Grade A”, whereas 20 percent will be Grade B”. The shoes that fail to meet the standard will be sold at half the price. The operational capacity of the proposed production unit will depend on the available machinery. The established capacity of the new unit will be approximately 600 pairs of shoes daily. The initial capacity will be 50 percent, while the optimal capacity will be 80 percent. At optimal capacity, the unit will be able to produce 480 pairs daily, which translates to 144000 pairs each year. However, the initial capacity of 50 percent will only be able to produce 300 pairs daily, which translates to 90000 pairs in a year.
This production capacity is deemed financially feasible and validates the capital outlay, as well as the costs of operation. Also, the owner’s extensive knowledge and experience in the footwear industry, excellent shoe quality, reasonable pricing, and strong market connection are the main elements of success for the company. The total cost of establishing the unit is expected to be around 9.93 million Dirham. The project will be financed through borrowing and shareholders’ equity. The tenure of the loan will be 5 years. The yearly markup for short-term and long-term loans will be 16 percent. The Net Present Value (NPV) will be approximately 32 million AED, with an Internal Rate of Return of 55 percent and a payback period of 2.7 years.
Introduction
Business history
Hamdan Footwear is a famous Indian designer and producer of ladies’ footwear under its brand. The company was established in the mid-90s in Punjab, India, and has more than 20 retail stores across the country. It is well-known for a wide range of women’s shoes, including sandals, slippers, and rubber shoes. Nonetheless, Hamdan Footwear is planning to enhance its presence in the Asian market by establishing a semi-mechanized footwear production unit in Abu Dhabi, UAE. The footwear will be sold directly to wholesalers and retail outlets in major cities across the country. Also, the footwear will be under the company’s brand name. The owners of Hamdan Footwear have a long history together, dating back to when they used to work for a local footwear company as shoe designers.
Mission and Vision of the project
The mission of the project is to make the company a top brand and a leading manufacturer of stylish ladies shoes in Abu Dhabi and the whole Gulf region. By setting up an upmarket retail presence in major cities in the UAE, that act as a compliment for the wholesale distribution and maximizing operational processes to reduce costs and time wastage, Hamdan Footwear aspires to control its target market. The project’s long-term vision is to make Hamdan Footwear an exceptional, trendsetting ladies’ shoe company and to increase its presence in the Asian market.
Key Initiative and Strategic Objectives
As already been mentioned, the project’s long-term mission is to make the company a top brand and a principal manufacturer of stylish ladies shoes in Abu Dhabi and the entire UAE. However, its strategic objective includes revenue maximization; establishment of high-status retail presence in major cities in the UAE; expanding the market for its products through vigorous promotion and multi-channel marketing; and optimization of the company’s operations to reduce costs and satisfy customers.
Revenue maximization will be achieved through business expansion, which requires increased brand awareness, increased retail outlets, and hiring qualified sales personnel. The high-status retail presence will be achieved by locating retail outlets at prime locations and through market segmentation. Product promotion will entail the use of mass media, internet marketing, trade fairs, strategic alliances, and contract marketing among others. Optimization of key operations will be achieved by streamlining the cost structure, consumer satisfaction, and constant evaluation of the company’s operations.
Location and facilities
As previously been mentioned, the new administrative and operations offices will be based in Abu Dhabi along with its semi-mechanized footwear production unit. Its retail stores will be spread across major cities in the UAE.
A brief account of the project and product
The footwear market in the United Arab Emirates is estimated to be over a billion Dirham. Most of the footwear is imported from China and Europe, particularly Italy and Spain. Over the last decade, the country’s demand for footwear has increased tremendously. The increase in demand is partly attributed to the rising urban population, change in lifestyle, increased number of tourists who visit the country to shop and changing retail footwear market (ICCI 2).
The market for stylish footwear in the UAE is estimated to be over $1 billion. This market is dominated by women between the age of 18 and 35 living in major cities. The markets for ladies footwear is worth more than $ 100 million and is anticipated to reach $180 million by 2017. Female consumers in the UAE not only buy shoes to protect and soothe their foot but also for image and fashion. Regardless of their small number, women tend to buy more shoes than men. Typically, men always buy around two to four pairs of shoes annually, while women buy up to ten pairs of shoes in a year (Mintel 3).
The UAE market is divided into two segments: the lower segment and the upper segment. The lower segment is made up of relatively cheap plastic and rubber shoes, whereas the upper segment is predominantly leather products. Nevertheless, trend-setting plastic and rubber shoes are also found in the upper segment (ICCI 3). On the other hand, the shoe manufacturing industry in the United Arab Emirates can be classified into two distinct groups, namely: organize sector and the disorganized sector.
The organized sector comprises of major brands like Bata and Aero Soft, whereas the disorganized sector consists of labor-intensive units with moderately mechanized production facilities. The company’s production unit will fall under the second category. It will focus on producing stylish and affordable ladies’ footwear. The footwear will include sandals, slippers, and rubber shoes. The footwear will be under the company’s brand. They will be sold at affordable prices and will range from number 6 to 11. Out of the three products, rubber shoes will be considered to be the main product. However, the production of the three types of shoes will depend on seasonal trends (ICCI 1; Mintel 6).
Company’s competitive edge
The company’s main competitive edge is its unique products, product pricing, and owners’ extensive experience and expertise in the footwear industry. The other competitive advantages include proficiency in production and historical contact with the targeted areas of sales. During the first year, the operations at the new unit will be carried out with a limited number of employees. However, additional workers will be hired in subsequent years. The owners and the employees will work as a team, enabling direct evaluation of all employees and direct participation to make sure that clients’ needs and expectations are met.
The competitive edge of unflagging professionalism will be upheld through prompt response to client inquiries, timely delivery of consignments, and reserving breaks for the employees among others. The company’s products will be unique and stylish and will be sold at reasonable prices. The owners have worked for local shoe companies as designers will also be an advantage for the company. Besides, the company will employ highly qualified staff. The highly qualified personnel will ensure that the project is completed on time and within the budget.
Target Market
The company will target female consumers between the ages of 18 to 35. The target market will be major cities in the UAE. Since the company will focus on manufacturing stylish and affordable ladies’ shoes, it will target both the lower and upper segments of the market. The market is characterized by large European and Asian brands. Nonetheless, there is no leading distributor of footwear products. This is attributed to a large number of players in the market. As a result, competition is very stiff.
Pricing Strategy
Hamdan Footwear will set prices, which reflect savings when compared to the actual value of the product. The company’s brand products will be priced at the upper edge to match the general positioning of the company as a high-quality product and service provider. At the initial stage, the company will set prices, which will be a 15% markup on the cost of production and later a markup of 25% on the cost of production. The setting of prices relative to those of competitors is expected to be effective since the target market for Hamdan Footwear’s brand is mostly middle-class city dwellers. Also, low prices are associated with poor quality. The middle-class city dwellers will be the largest consumers of Hamdan Footwear.
Promotional Strategy
To enhance the growth and development of the company’s brand, the activities of advertising, online marketing, discounting, and publicity will be used to entice customers. Promotional strategies will be used in defining and locating the target audience for the product and passing a specific message. The promotional strategies will be employed in creating awareness of the presence of the Hamdan Footwear brand in the UAE market.
The promotional strategy to be used will ensure that the target customers get the right information about the Hamdan Footwear products by making use of the right medium and strategy. It will also ensure that customers easily access the company’s products. By promoting the products, the level of visibility of the products will be maintained and the volume of the demand for the products will be set to an applied margin.
Direct sales could be made from the production center and through the company’s websites. Sales promotions will be implemented during special occasions, for instance, holidays and festive seasons. Discounts and rewards will be offered during sales promotions to increase sales volume. The company will also make use of social media, which has become a very significant platform for marketing in this day and age.
Competencies
This business idea and plan have been validated through market research. The footwear market in the UEA is growing rapidly and is highly valued. Almost every street in major cities in the UAE has retail stores selling footwear products. The location of the company’s retail stores will be very strategic. The product pricing will also be reasonable and competitive. The basis of the market research is to make the company stand out among its competitors. The market research focused on the competitors, whereby it pays close attention to their pricing, products, customer service, and general business (Steele 20).
Capacity Planning
It refers to the practice of determining the requirements of the production process. It also refers to what the company is capable of realizing within a specific period considering the existing constraints, for example, raw material, labor, and capital (Project Management Institute 37).
Established and operational capacities
The operational capacity of the proposed production unit will hinge on the available machinery. The established capacity of the unit is expected to be around 800 pairs per day. The established capacity of the new unit will be approximately 600 pairs of shoes per day. The initial capacity will be 50 percent, while the optimal capacity will be 80 percent. At optimal capacity, the unit will be able to produce 480 pairs daily, which translates to 144000 pairs each year.
On the other hand, the initial capacity of 50 percent will only be able to produce 300 pairs daily, which translates to 90000 pairs in a year. The rate of production is expected to grow by 5 percent every year until it reaches optimal capacity in the 7th year.
The production is expected to be financially feasible and justifies the capital, as well as the cost of operations. The project will employ around 21 individuals, including owners who constitute the management team. Additionally, the company will rent the premise to minimize preliminary capital spending. The shoes that meet the quality standard will be classified as “Grade A”, whereas shoes that fail to meet the standard will be classified as “Grade B”. Out of the aggregate output, 80 percent will be “Grade A”, whereas 20 percent will be Grade B”. The shoes that fail to meet the standard will be sold at half the price.
Material requirements
The materials to be used in the production process can be classified as upper materials, insole materials, outsole materials, grinders, and auxiliary materials. The upper materials are used to make upper shoe components. They include textile materials, rubber, and plastic. Insole materials are used in manufacturing inner sole and comprise of cellulose board, texon, bontex, and special shoe construction textile.
On the other hand, outsole materials are used in making external sole. They consist of polyvinyl chloride, polyurethane, and thermoplastic rubber. Grinderies are other components of shoes, which include shoelaces, zip fasteners, and threads. Last but not least, auxiliary materials are additional materials that are essential in the production process, for example, adhesives, finishing chemicals, and polish (SMEDA 13).
Table 1: Material Budget.
Labor requirements
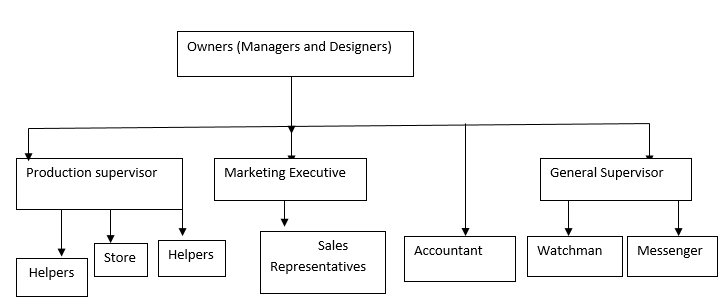
The organizational structure of the manufacturing unit will be as shown in the chart below. The organizational structure simply describes the division, grouping, and coordination of tasks (Clardy 340; Cunningham 4).
The owners will act as the managers, as well as designers due to their vast experience and expertise in footwear design. They will be assisted by production supervisors, general supervisors, and marketing executives. The production supervisor will be in charge of the production unit whereas the general supervisor will be responsible for the general operations in the company. Last but not least, the marketing executive will be in charge of the retail stores and distribution of the company’s products.
The following table offers more information regarding the personnel required for the project together with their monthly earnings.
Table 2: Personnel requirements and monthly income.
Man power and schedule
The company’s manpower will be hired not only based on qualification, but also competency. The owner’s knowledge and experience in the industry will help in the recruitment and selection process. Initially, the number of employees will be around 21, including the managers. Only ten employees will be involved in the production process, that is, 2 production supervisors and 8 helpers. All the employees will be paid a monthly salary, except those involved in the production process. They will all work for 8 hours a day and 40 hours a week. The table below shows the direct labor budget for the first year.
Money
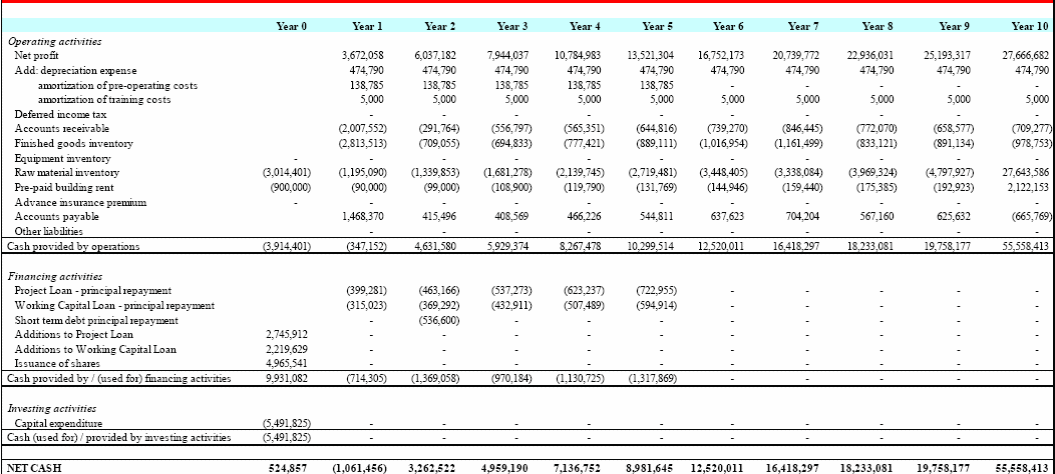
A comprehensive model has been developed to assess the feasibility of the unit. This is based on several cost and revenue assumptions. The assumptions will be hinged on the established capacity of 180000 pairs of shoes per year. Even though 90000 pairs of shoes will be manufactured in the 1st year, only 83,805 pairs of shoes will be sold. The difference between the quantity produced and the quantity sold will be included in the inventory for the 2nd year. Based on the projected financial statements, the Net Present Value (NPV) will be approximately 32665861 AED, with an Internal Rate of Return of 55 percent and a payback period of 2.7 years. The estimated income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow are available in the appendices. The human resource and material budget have already been computed. The project returns will depend on production and management efficiency, as well as shoe quality and design. The project will be funded through a 50 percent loan (4965541 AED) and 50 percent equity (4965541 AED). The tenure of the loans will be 5 years. The yearly markup for short-term and long-term loans will all be 16 percent.
Project investment
This part provides the capital requirements for the proposed semi-structured manufacturing unit.
Table 3: Project investments.
Machinery and equipment
These are the list of machines and equipment needed for the proposed venture.
Table 4: Machines needed.
Table 5: office equipment needed.
Furniture and fixture
The table below provides a list of furniture and fixture required for the proposed manufacturing unit.
Table 6: Furnishings and fixture needed.
The company will also incur other costs, which include electricity cost, marketing costs, office expenses, communication costs, and many more. The cost of electricity is projected to be around 644144 AED per year. The company will spend 2.5 percent of its total revenue on marketing and promotional activities. Likewise, communication cost and office expenses are estimated to be approximately 2117200 AED and 108600AED respectively for the 1st year.
Projected revenue
The projected revenue for the 1st year is provided in the table below.
Table 7: Projected revenue for year 1.
Layout and facilities
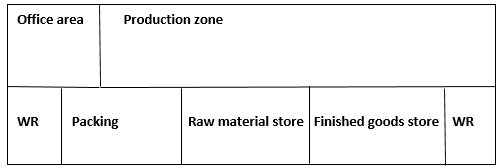
As already been mentioned, the company will rent a building to minimize the initial capital expenditure. For this reason, the company will be forced to acquire space in the industrial area for its operations. The rent will depend on the space required. The proposed manufacturing unit will require an area of around 4500 square feet. The area is computed based on the amount of space required for the production process, management functions, and warehousing. The table below shows the computation of space required.
Table 8: Space required.
The figure below shows the company’s layout:
Equipment/machines and details
The equipment can be classified as office equipment and production equipment. The production equipment will be used in the production process, whereas office equipment will be used in administrative work. The production machinery/equipment will include cutting press, GP4 machine, skiving machine, upper stitching level bed machine, upper stitching horizontal machine, bending machine, sole attaching machine, sole stimulator, zigzag machine, scoring machine, finisher, shoe last, and a generator.
The cutting press uses a hydraulic system to cut materials into different sizes. The GP4 machine trims insole and textile materials. The upper stitching machines are used to sew textile materials, which form the upper shoe components. Bending machines is a machine that assembles all the bent pieces. The sole stimulator softens the inner and outer sole materials for gluing purposes. A zigzag machine is a sewing machine that is used where a straight stitch is not adequate.
The scoring machine creates partial cuts and scores on materials. A sole attaching machine is a machine that attaches upper materials to inner and outer soles. Lasts replicate foot shape. A finisher is a machine that polishes the shoes using fabric brushes. Last but not least, a generator is used to generate electricity during power blackouts (SMEDA 15). The office equipment will include personal computers, UPS, printers, telephone and fax machine. Personal computers are compact computers with a wide range of uses, for instance, managing data, word processing, online communication, and financial analysis among other uses. UPS ensures uninterrupted power supply for computers. On the other hand, the telephone and fax machines will be used for communication purposes (SMEDA 16).
Design of work system
Implementation plan
The implementation process involves activities such as procurement of
- technical expertise;
- dissemination of technology;
- market analysis;
- preparing project reports;
- site selection;
- listing;
- funding;
- purchasing machinery and inputs;
- staffing;
- setting up machines;
- test production;
- actual production.
Simultaneous exercises are necessary to implement the project successfully. According to the CPM-PERT chart below, the implementation process will take roughly 227 days. As a result, 82 days will be saved. Table 1 provides more detail. Kindly note that CPM stands for Critical Path Method while PERT stands for Program Evaluation Review Technique. PERT and CPM are often used in scheduling, organizing, and coordinating project tasks.
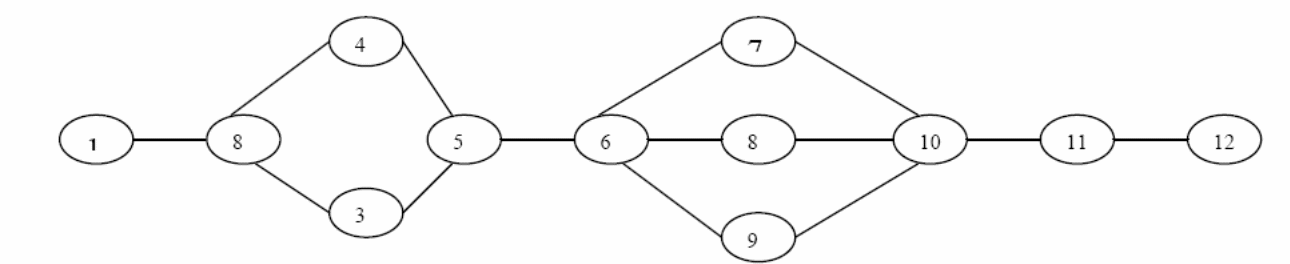
Table 1: Detailed implementation schedule.
The flow of the production process
The production process begins with the creation of footwear designs. Footwear designs can be developed by either in-house designers or contracted designers. However, in-house designers are ideal to maintain the uniqueness of designs in the market (MSME 4). The company owners who are experienced footwear designers will act as managers and designers for the proposed unit. The next step is developing a plastic shape that replicates the foot shape, which is usually known as “shoe last”.
The development of shoe last is followed by the preparation of press cutting and stitching operations for inner and outer parts. Once the stitching is done, upperparts are attached to the linings and sole. The last stage involves finishing, quality check, and packing each pair of shoes ready for the market. Depending on the design and shoe type, special equipment and machines will be used to attach, shape, or stitch different components (MSME 5).
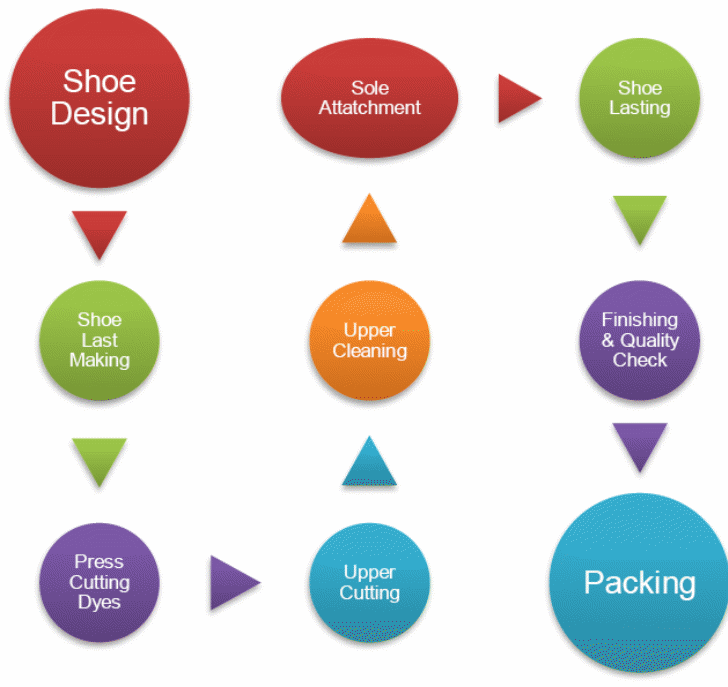
The upper components and linings are fitted together using a sole attaching machine as per the encoded patterns. The components can be folded or skived where necessary. The two components are then stitched together to form the upper part. The upper part can then be shaped using a shoe last. Lasting can be done manually or through a lasting machine. The wrinkles on the lasted shoe can be eliminated using a finishing machine. The upper part is then glued to the sole. The glued upper part and the sole are then pressed using a sole press. De-lasting is only done after excess glue or materials have been removed. As already been mentioned, the last stage involves a quality check and packing. Other machines can be used for specific purposes, for instance, skiving, folding, pounding, grinding, and sewing among others (MSME 6).
Works Cited
Clardy, Alan. “Strategy, core competencies and human resource development”. Human Resource Development International 10.3 (2007): 339-349. Print.
Cunningham, Linsey. “Talent Management: making it real”. Development and Learning in Organizations 21.2 (2007):4-6. Print.
ICCI. Footwear Market in UAE. 2014. Web.
Mintel. Women’s Fashion Lifestyles – UK. 2011. Web.
MSME. Project Profile on Canvas Shoes, Kanpur: MSME, 2014. Print.
Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, Pennsylvania: Project Management Institute, 2004. Print.
SMEDA. Ladies shoes manufacturing unit, Punjab: SMEDA, 2014. Print.
Steele, Valerie. Shoes: a lexicon of style, London: Scriptum, 2005. Print.
Appendices
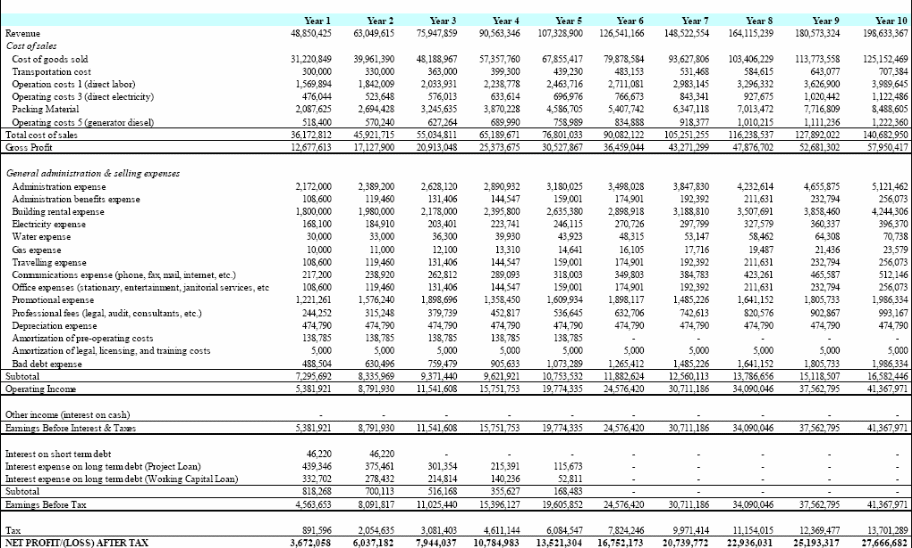
Appendix 1: Income Statement
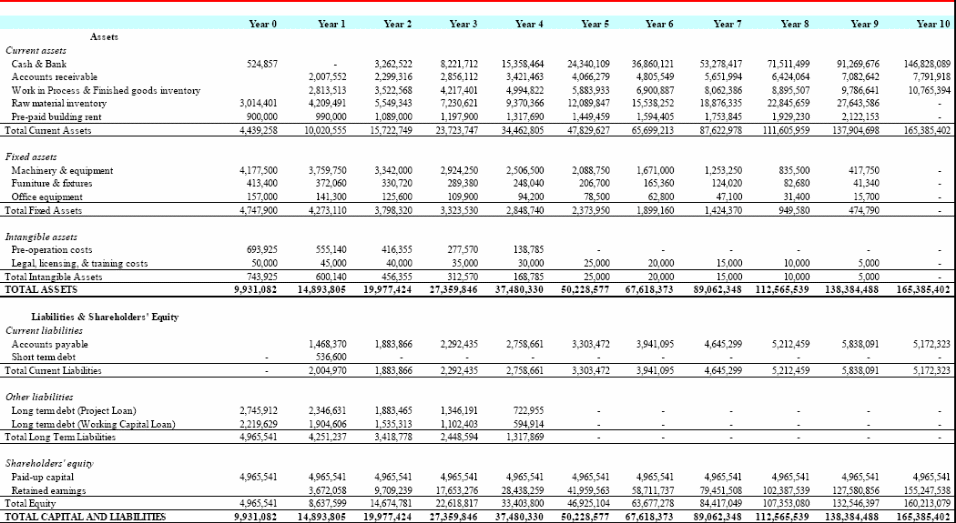
Appendix 2: Balance Sheet
Appendix 3: Cash Flow Statement