- The UAE Focus on Healthy Children in the Past and Today
- Health Campaigns for Children
- Hospitals and Health Centres in the UAE
- Abu Dhabi as the UAE Centre of the Children’s Health
- Efficiency of the UAE Health Policies for Children
- Relationship between the UAE Development and Children’s Health
- Conclusion
- References
The special attention is given to the health of children in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Although the country takes the leading position among the developed countries regarding the promotion of health sector, the UAE authorities continue working to improve the health status of children (World Health Organization, 2014, p. 1).
Thus, the “2021 Healthy Children” campaign has been developed recently to decrease the rates of chronic diseases and obesity in children and to address the world health standards (National Program for Government Communication, 2015). The progress of modern campaigns and policies to improve the health of children in the country is directly associated with the UAE economic development (UAE Interact, 2015).
In order to examine this aspect in detail, it is necessary to answer the following research question: How is the authorities’ focus on healthy children in the UAE related to the country’s development? This paper aims to analyse strategies, policies, and campaigns in the UAE that are designed to make children healthy in the context of the UAE economic development.
The UAE Focus on Healthy Children in the Past and Today
The orientation on healthy children became the priority for the UAE authorities in the 2000s. It is possible to observe positive results, while comparing the data for 1995, 2004, and 2012 years. The first step was the increase of the vaccination rates for children from about 90% in 1995 to 94% in 2004.
In 2012, this rate was also 94% (The World Bank, 2015). This step was associated with the improvement of monitoring infectious diseases among children. The second step was the reduction of the infant mortality rates. In 1995, the rate of infant mortality per 1,000 live births was 11, but the health authorities achieved the reduction in the rate to 9 in 2004, and to 7 in 2012 (The World Bank, 2015). No maternal mortality cases were reported since 2004 (Millennium Development Goals, 2015).
Today, the provision of healthcare services for children is one of the UAE social strategic goals. Therefore, the number of health programs for children doubled while comparing the data for 2004 and 2012 (UAE Interact, 2015). The main problems that need to be addressed with the help of action plans proposed by the UAE Ministry of Health are the children’s obesity, high rates of diabetes, and the low rates of physical activity among children and adolescents.
Health Campaigns for Children
The Ministry of Health in cooperation with the Emirates health authorities and the National Program for Government Communication designed the “2021 Healthy Children” campaign. The aim of this campaign developed in line with the UAE Vision 2021 is to educate the citizens of the UAE regarding the healthy lifestyles for children (National Program for Government Communication, 2015; Vision 2021, 2015).
This campaign is launched in addition to many health educational programmes in the Emirates, and it is oriented to guarantee the provision of high-quality healthcare services for the UAE children. The UAE health policies are also developed with the focus on promoting such national programmes as Mother and Child Health Care. In addition, to achieve the goal of raising the generation of healthy children, the UAE government implements health campaigns and partnership programs in cooperation with the US medical centres (The UAE healthcare sector, 2014).
Hospitals and Health Centres in the UAE
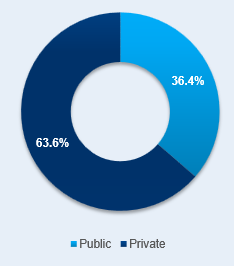
The healthcare providers in the UAE are divided into public and private. Public hospitals and centres present 36.4% in contrast to 63.6% of private centres (Colliers International, 2013, p. 6; Figure 1). In comparison to 7 hospitals and 12 health centres available for the public in 1971, today there are 65 hospitals and more than 150 health-care centres in the UAE. The Ministry of Health pays much attention to establishing and supporting medical centres for school children and health units in the UAE schools. Currently, there are 11 school health centres in the UAE, and each school is provided with qualified nurses to work in health units (UAE Interact, 2015).
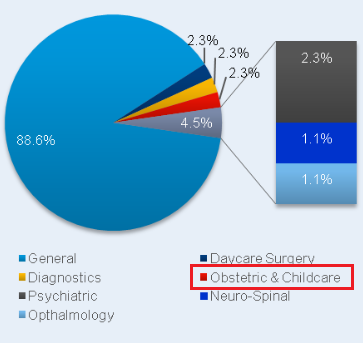
Special centres for mothers and children are opened in the UAE as the part of Mother and Child Health Care programme. Today, there are 10 centres for children in the UAE. The Ministry of Health and the Emirates’ authorities work to improve the access to the health care for children in remote areas and start new hospital building projects like Al Jalila Children’s Speciality Hospital in Dubai (UAE Interact, 2015). These projects are developed to increase the percentage of hospitals and centres dedicated to the child care in the UAE in contrast to the current 2.3% (Colliers International, 2013, p. 8; Figure 2).
Abu Dhabi as the UAE Centre of the Children’s Health
Although Dubai is also characteristic by the developed healthcare system for children in the UAE, Abu Dhabi is as the most progressive Emirate in the UAE in terms of the number of hospitals and medical centres for children and programmes implemented to support the healthcare delivery.
Among 39 public and private hospitals and medical centres in Abu Dhabi, three centres specialise in the child health and care (The UAE healthcare sector, 2014). The health services for children in Abu Dhabi can be discussed as highly developed and supported with the constant research in the area for developing new effective healthcare policies. The medical centres for children and adolescents are well-equipped and highly specialised.
Efficiency of the UAE Health Policies for Children
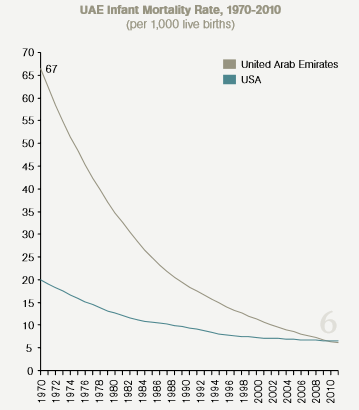
Referring to changes in the basic health indicators, it is possible to state that the UAE authorities have achieved high results in improving the health of children and adolescents in the country. Thus, the rate of infant mortality is reduced significantly in comparison with the data for the year of 1994, and this rate is lower than the rate typical for the United States (United Arab Emirates: 40 years of progress, 2011, p. 12; Figure 3).
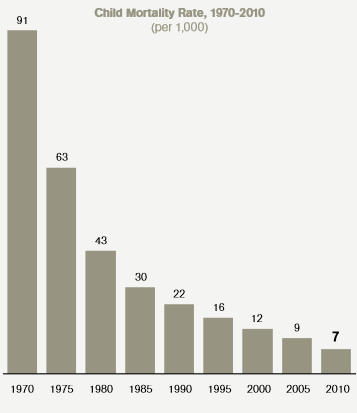
The child mortality rate also decreased significantly, from 67 persons per 1,000 live births in 1970 to 6 persons in 2010 (United Arab Emirates: 40 years of progress, 2011, p. 12; Figure 4).
Although obesity and overweight in children and adolescents in the UAE is still a problem because the rate of overweight children is more than 20% in the country, there are many programmes and policies that are oriented to address the problem in the near future, according to the goals of UAE Vision 2021 (UNICEF, 2015; Vision 2021, 2015). It is possible to state that the level of the UAE healthcare for children is equal to levels in other developed countries, and the health status of children is close to the world health standards.
Relationship between the UAE Development and Children’s Health
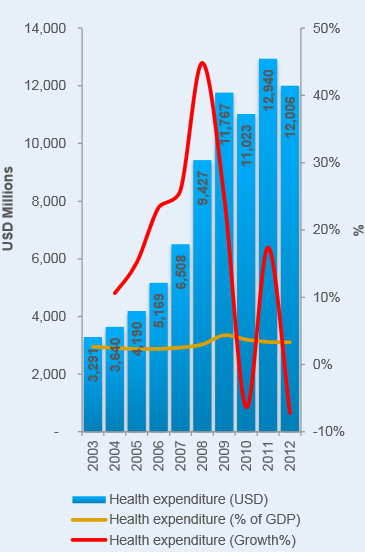
Positive changes in the health status of children in the UAE are directly associated with the country’s economic development. Thus, changes in the expenditure on children’s health and care lead to increasing the number of beds in hospitals and to improving the healthcare delivery. As a result, the high expenditure on the health care as an indicator of the country’s economic progress causes improving the population’s health status. The economic development of the UAE is progressive, and the increase in health expenditure in 2011 is correlated with the economic stability of the UAE during that year.
Furthermore, in comparison to the health expenditure in 2003, the high expenditure in 2011 is also correlated with positive changes in the health status of the UAE children (Colliers International, 2013, p. 6; Figure 5). Health programmes developed as a result of increasing the expenditure cause reductions in mortality rates and improvements in nutrition.
Conclusion
In the UAE, the health of children can be discussed as the national priority. The UAE authorities pay much attention to increasing the number of hospitals and medical centres to improve the child care and delivery of health care for children in all Emirates and remote areas. To address such problems as high obesity and diabetes rates among children, the UAE government also implements additional programmes and campaigns. Positive changes in basic health indicators demonstrate that the governmentally supported initiatives, policies, and strategies are working.
It is possible to state that currently, the UAE healthcare system for children is in line with the highest world standards. However, to achieve higher results in relation to overcoming such problems as the obesity and diabetes rates among children, it is necessary to recommend the implementation of local health programmes for children, involving school heath care providers, in addition to national campaigns. The reason is the necessity of using the individual approach to resolving the community health problems.
References
Colliers International. (2013). United Arab Emirates: Healthcare overview. Web.
Millennium Development Goals. (2015). Web.
National Program for Government Communication. (2015). 2021 Healthy Children. Web.
The UAE healthcare sector. (2014). Web.
The World Bank. (2015). Web.
UAE Interact. (2015). Health. Web.
UNICEF. (2015). United Arab Emirates: Statistics. Web.
United Arab Emirates: 40 years of progress. (2011). Web.
Vision 2021. (2015). World-class healthcare. Web.
World Health Organization. (2014). United Arab Emirates. Web.