Abstract
Objective
The aim of the study is to investigate the connection between eating and stress. The main point is to investigate how our eating behavior influences our emotional state. It also aims at determining whether a lack of food influences our feelings and reactions to human and environmental factors. This study intends to explore all factors determining the link between eating and stress.
Methodology
The study is based on an online survey sample. The survey was based on an interview of 40 female samples aged between 20 and 30 years from Saudi Arabia. Out of 40 selected sample females, only 20 aged between 20 and 25 years completed a questionnaire form.
Hypotheses
There is a link between eating habits and stress. Lack of food influences the way we react to people and our environment. Failure to have a meal or two will cause stress. Finally, people tend to eat a lot of food when they have stress.
Results
The result obtained produced unpredicted outcomes. The results indicated that those under stress eat the same way those who are happy. However, the results were close to the hypotheses in terms of how a lack of food can cause stress. In terms of their relationship, the results were almost similar.
Conclusion
The results demonstrate the purpose of this study, which is to determine the link between eating and stress.
Research Question
- Do you believe the lack of a meal or two can cause stress?
- Do you consume a large amount of food when you are stressed or happy?
- Do you notice any change in your emotions when you are angry?
Introduction
Even though food is essential for the survival of humans, it also contributes to mental development and status. Therefore, food acts as a tranquilizer that stabilizes our emotional status and behaviors towards people and the environment. The rationale of this study depends on the fact that food is essential for our physical and mental development and behaviors. Eating habits may affect the emotional and physical response of an individual to their physical environment and people. At the same time, an emotional state of mind will influence the manner in which a person eats. From the results obtained in the survey conducted on 40 Saudi women, it is clear that there is a close relationship between eating habits and state of mind. This paper tends to explore the relationship between eating habits and stress.
Literature Review
In a study conducted by Nasser and others to determine whether perceived long-term stress among first-year students at King Saudi University causes abnormalities in eating habit and cardio-metabolism. A sample of 120 students: 40 men and 80 women were surveyed. From the research, 58.5 percent of men demonstrated negative results, while 60 percent of women demonstrated positive results (Goodhart, 2011).
Studies of humans have discovered that a decrease or increase in food consumption to respond to a stressful situation depends on the nature and severity of the stressor. The negative image of a person’s body and unhealthy eating can cause stress. However, stress can also cause unhealthy eating habits in an individual (Davis & Eshelman, 2008). The connection between eating and stress can be unfavorable in many ways. Stressful feelings can cause unhealthy eating behavior in different ways. Emotionally and the mentally unstable person may refuse to eat for the whole day. On the other hand, an individual who is overwhelmed with happiness may eat very little or refuse to eat anything at all (Liu, 2007). It is important to note that mechanisms that take place in our body are triggered by various chemical reactions.
Hormones play an essential role in coordinating the functions of the body. They are the chemicals that trigger appetite, stress, and happiness (McComb, 2007). The state of our environment determines the kind of hormones our body releases in order to trigger a certain body function. When an appetite is stimulated, it largely depends on the interaction we are currently having with people and our environment. For instance, if someone is annoyed, he or she will tend to avoid food because of the annoyance (Michelle & Christie, 2012). As a result, an individual in such an environment may tend to eat more food. Furthermore, extreme happiness can make someone feel full because of the excitement caused by his or her achievements.
Many theories have been used to explain the link between stress and eating. The psychosomatic theory explains the association between eating and stress. According to the theory, eating food when stressed up can cause obesity. This is because the body will tend to use them as defense mechanisms for emotional instability. According to theory, obesity does not just come because someone overeats. However, it results from overeating whereby an individual overeats to in order to defeat emotional challenges. It explains that obesity is caused by too much eating to fight emotional stress, anxiety, and anger (Davis & Eshelman, 2008).
According to the study by Goodhart (2011), the abnormal eating habit can increase the level of stress in an individual. However, an abnormal eating habit not only makes the body to have physical stress but also worsens mental stress. The main cause of stress in our body is anxiety, which may be driven by personal or external factors. For instance, a person who has bad relations with his or her partner can develop anxiety and become stressed-up. On the other hand, an individual may develop an unhealthy way of consuming food. Such cases may cause obesity and other food-related illness. In that case, a person may end up becoming stressful. The main limitation of this study is that it does not explain to what extent obesity causes eating disorders.
Hypotheses
There is a connection between eating and stress. Lack of food influences the manner in which we react to people and our environment. Failure to have a meal or two will cause stress. Finally, people tend to eat a lot of food when they have stress.
Methodology
This study was conducted through an online survey whereby the correspondents would give their answers to the researchers through their emails. Men subject women in UAE to many stressors. They are exposed to emotional stress on a daily basis. The survey sample consisted of 40 women who were interviewed online. The researchers distributed the questionnaire forms to 40 women aged between 20 and 30 years. Out of this number, only 20 participated and submitted the forms back through email. Those who participated were college students aged between 20 and 25 years. The respondents were evaluated based on the answers they gave to the questions.
Results
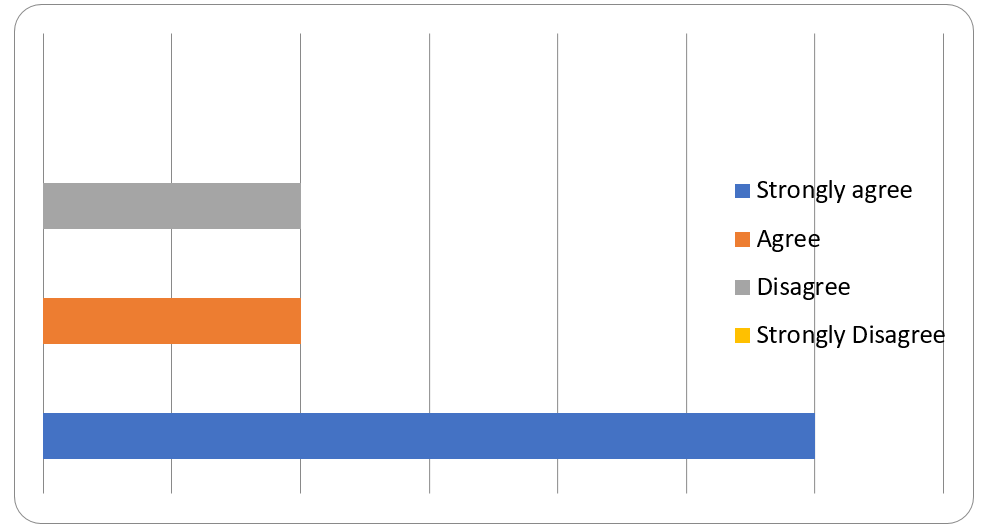
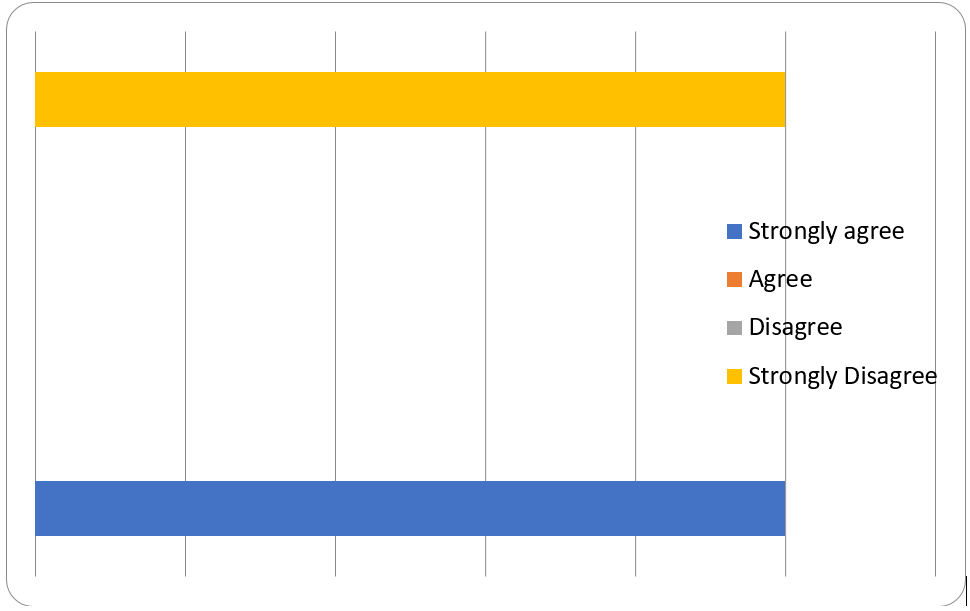
The questionnaire forms had three questions. The first question asked, “Do you believe lack of a meal or two can cause stress?” All 20 respondents answered the question in which 60 percent of them strongly agreed, 20 percent agreed, and 20 percent disagreed. The second question asked, “Do you consume a large amount of food when you are stressed or happy?” Of the 20 respondents, 50 percent strongly agreed, while another 50 percent strongly disagreed. The third question asked, “Do you notice any change in your emotions when you are angry?” All 20 respondents strongly agreed.
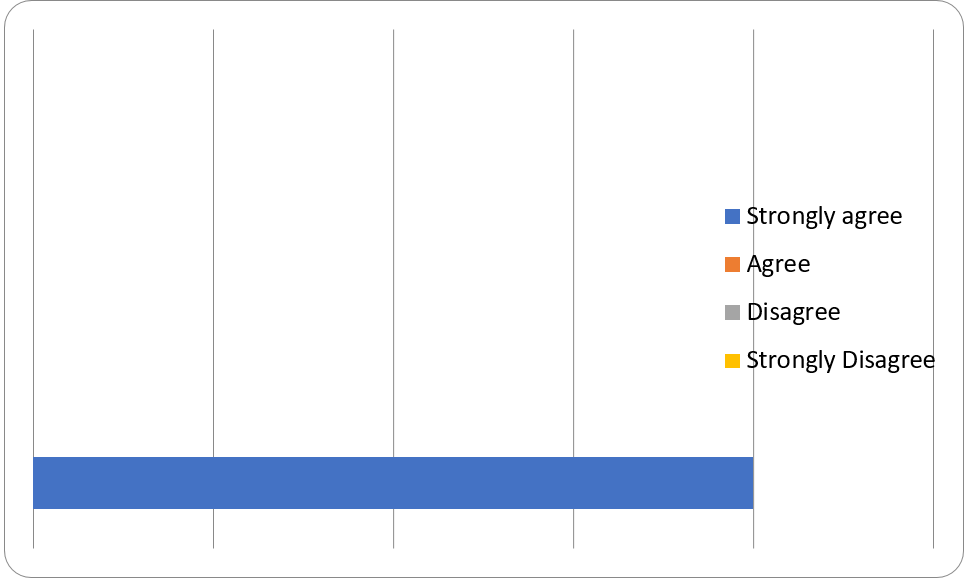
Analysis
The results obtained from the survey support the hypotheses of this study. From the study, we can conclude that there is a relationship between food consumption and stress. Based on the answers given by the sample to question one, going without food can cause stress. When the body fails to respond to a normal habit, it triggers abnormal psychological effects, which can cause stress. However, some people are used to staying without a meal. Such people will not develop stress because they will perceive the situation to be a normal one. The answers to the second question are based on the status of an individual. For instance, when some people are stressed, they tend to avoid food completely. Instead, they isolate themselves from everyone and stop doing everything, including eating. Such people, in many cases, spend the whole day sleeping or just seated.
Discussion
Some people may tend to eat a lot when they are under stress. This is the reason 50 percent of the samples agreed that they eat more when happy or stressed. When a person is sad, he or she tends to find things that will make him or she avoid the adverse situation. One of these things may be eating a lot of food. However, the category of these people likes consuming soft drinks more than any other food. At the same time, there are individuals who lose appetite when they are happy and overjoyed. The extreme excitement they have will make them lose their appetite. On the other hand, some people tend to eat a lot when they are happy
Therefore, we can say that the hypotheses developed for this study were relevant. However, the fact that people tend to eat when they are stressed or happy is uncertain does not mean the hypotheses are irrelevant. It gives equal results on both sides. This implies that eating habits developed when someone is happy or stressed depends on the person. It depends on the strategies an individual uses to avoid a stressful situation. Some people may find relief when eating, while other people may find relief from stress by doing other things. Even though the second question provided the expected result, the hypotheses developed for the study is relevant to findings. This is because the majority of the correspondents tended to agree with the hypotheses. Therefore, the hypotheses remain relevant to this study.
Conclusion
The study is based on the relationship between food consumption and stress. From the study, it is clear there is a close relationship between eating and stress. The manner in which a person eats directly relates to the mental state of that person. On one side, stress influences an individual’s habit of eating. On the other side, eating habits may cause stress. Some people tend to go without food when they are facing stress. Due to emotional instability, they do not think about food. However, some people may eat a lot when subjected to stress. This depends on an individual’s way of trying to overcome stress. For those who eat a lot while under stress, their favorite food is soft drinks and snacks. This may develop into serious health conditions such as obesity if it continues for a long time.
References
Davis, M. & Eshelman, E. R. (2008). The relaxation & stress reduction workbook (6th ed.). Oakland, CA: New Harbinger Publications. Web.
Goodhart, K. L. (2011). Eating disorders in women and children prevention, stress management, and treatment, second edition (2nd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press. Web.
Liu, A. (2007). Gaining: the truth about life after eating disorders. New York: Warner Books. Web.
McComb, J. J. (2007). Eating disorders in women and children: prevention, stress management, and treatment. Boca Raton: CRC Press. Web.
Mitchell, S. & Christie, C. (2012). I’d kill for a cookie: a simple six-week plan to conquer stress eating. New York: Dutton. Web.