Introduction
Honda Motors Company has adopted a unique business model that seeks to satisfy the unique desires of every buyer and user of its products. As such it designs its products with the customer’s peculiar characters in mind (Honda motors 2011a).
Honda Motors is headquartered in Tokyo Japan and has more than 390 subsidiaries in over 12 counties. It has established its business operations under three basic principles aimed at guaranteeing utmost joy to its customers. The company’s production philosophy is based on the desire to create a joyful experience of buying, selling, and creating. This philosophy asserts Honda Motors also desires to create not only a joyous experience but also the fulfillment of every person who enters into a contract with it. This has resulted in the creation of affordable products that add value to customers’ lives (Honda Motors 2011a).
Honda Motors Company’s first-quarter performance for the year 2010 was beyond what market analysts had expected. The company performed well beyond expectation due to cost cuts. The company recorded the highest quarterly profits compared to the last five previous quarterly earnings. As such the company outperformed established car makers such as Toyota (Kim 2010).
Financially, it recorded an impressive year with an impressive ¥8,579,174 million turnovers in the year 2010(Honda Motors 2011a). The company prides itself on having several environmentally friendly sustainable features. The company has designed and developed hybrid (electric-gasoline) and advanced combustion gasoline engines that reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
Furthermore, the company has also developed engines that utilize biofuels as well as hydrogen fuel cell-driven engines (Siuru 2007). The result is that Honda motors have been voted the most environmentally friendly manufacture in the world (Honda Motors 2011b). The figure below shows Honda motor’s performance in the US market in the year 2010 to 2011.
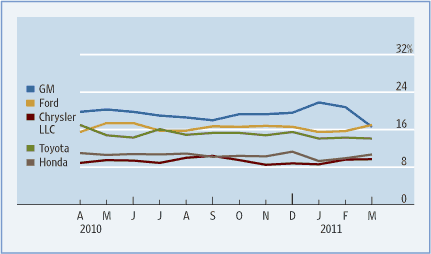
The motor vehicle industry is facing an uncertain future and as such Honda motors have had a paradigm shift to help it survive turbulent times. The company hopes to enhance its motorcycle production as well as enhance its global production chain, which will solidify its position in the global market (Honda Motors 2010). Furthermore, the company has invested in fuel-efficient products (Ito 2010).
The company, in keeping with its desire to produce eco-friendly cars, has adopted a techno-centric approach in fulfilling this dream. Honda Motors see technology as the way to reduce the environmental impacts of its operations and as such is investing heavily in the latest technologies that do not use fossil fuels. The company, therefore, seeks to increase its efforts in investing in technologies such as the fuel cell as well as the solar cell (Honda Motors 2010).
The figure below shows the company’s performance in the world market from March 2009 to March 2010.
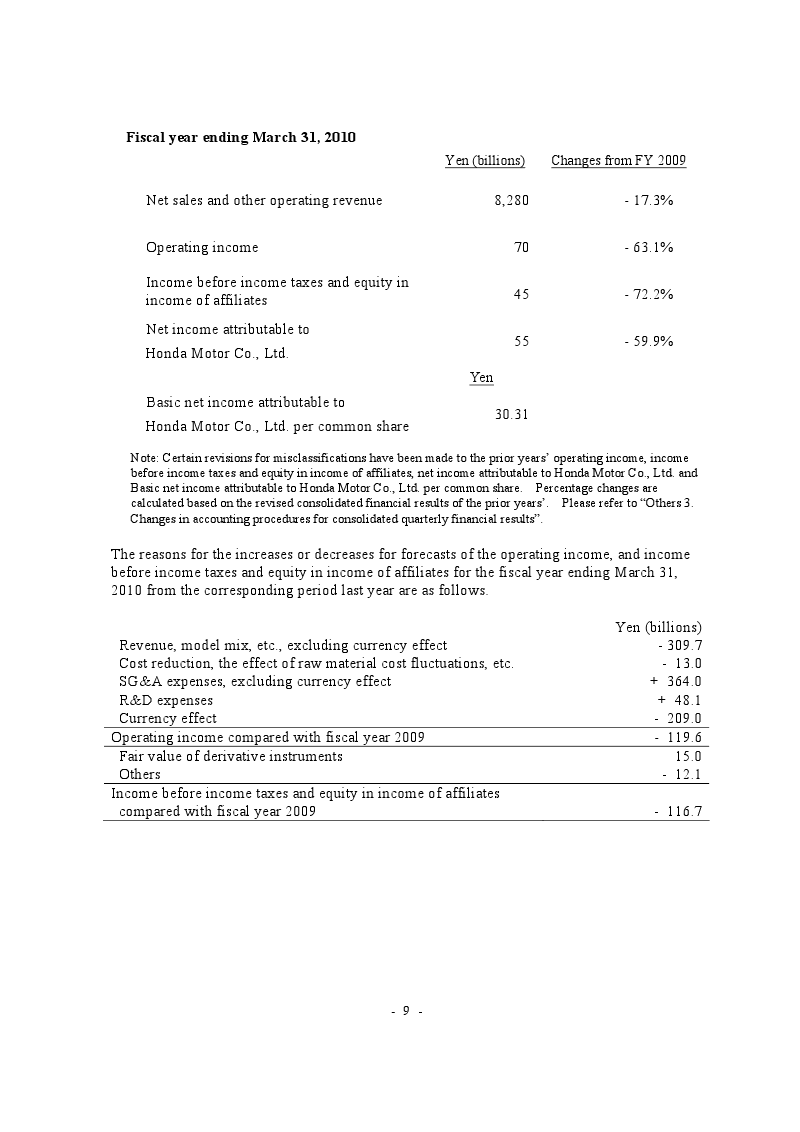
PEST analysis
Several factors affect Honda motors business internationally. In China, the company has moved in to capitalize on the latest economic gains in the Chinese economy zones (Rima 2010). The Chinese government has lifted the currency peg on the Yuan making it appreciate against major currencies such as the dollar, the EURO, and the Sterling Pound (Rima 2010). Furthermore, the Chinese Government has also created special production zones to help manufacturing companies operate at minimal costs.
Honda motors have moved in fast and have established a joint venture with Guangzhou SOE, to establish a manufacturing plant in one of the Chinese manufacturing zones (Rima 2010). The issue of global warming is increasingly gaining political attention all over the world. Governments are increasingly becoming active in ensuring that the levels of carbon emissions are kept low by revaluating policies concerned with manufacturing as well as the increasing emission from transport means.
This has necessitated Honda Motors to increase its interest in the productions of bio ethanol-powered cars which have found an appeal in some markets especially the United Kingdom (Ward-Jones 2008). However, the company is likely to ruffle some political feathers in china as a result of the latest labor disputes in its factory in china (Bremmer and Stewart 2011). Honda motors have established its model on the ‘three joys’ philosophy: all aimed at satisfying the users of the company’s products.
In the USA the company has introduced a delivery and manufacturing process that puts the customers first. Thus, Honda Motors has become popular amongst different social groups in that market as customers not only drive Honda cars but do it “with their own expectations” (Modi, Zein, Kramer, Saudale, Banavadikar, Deshpande n.d.). Furthermore, some states such as California have implemented strict carbon emission control policies while at the same time giving tax-exempts to purchase environmentally friendly motor vehicles (An and Sauer 2004).
The state also promotes the use of hybrid cars thus reducing the amount of carbon emission. Honda Civic Hybrid meets this requirement and as such will be one of the eco-cars with high demand in this market (An and Sauer 2004). Furthermore, the company has enhanced efforts to produce ethanol from plants which it hopes to one day develop into fuel for motor vehicles (Plunkett 2006).
The company has therefore established a plant to run a project testing ethanol-powered cars, which it hopes will yield positive results (Plunkett 2006). Moorvale the company is also looking beyond eco-friendly cars and has built an eco-friendly building in America (Honda Motors 2011a). The figures below illustrate external factors that affect Honda Motors Company operations.
Honda Motors sustainable efforts
According to a 2005 environmental report conducted by Ceres, a national collation of investors in the USA and Europe indicates that the threat of ever-increasing global temperatures is real (Cogan 2006). Temperatures are rising while glaciers are melting at an alarming rate. This has lead to major governments all over the world coming together and signs intergovernmental agreements. These agreements stipulate the rules that manufacturers should follow to ensure that there is reduced emissions of greenhouse e gasses to the environment.
In 2005, the then-British premier, Tony Blair urged corporate as well as political leaders from all over the world to embrace the fight against global warming (Cogan 2006). As such Companies, especially motor vehicle manufacture have awakened to the reality that compliance with these rules is a costly affair that needs an urgent paradigm shift.
However, refusal to comply presents a further risk for motor vehicle manufacturers. Honda motors see the production of energy-efficient vehicles as one of its core corporate social responsibility. As such the company has introduced into the market highly fuel-efficient brands such as the Honda Civic hybrid which have been rated very highly. Other CSR initiatives include safety enhancement features for its new motor vehicles as well as its involvement in community activities to produce long-lasting rice in Asia (Honda Motors 2011c; Cogan 2006).
A new environmental management policy and standards have been established by The International Organization for Standards, ISO. These standards stipulate the environmental management processes, evaluation, and regulations for manufacturers (Tibor & Feldman 1995). Because of the company’s ethical responsibility towards environmental management through its production of eco-friendly vehicles the company has received several international accreditations and awards (Honda Motors 2011d). These accreditations include the ISO 14000 (2010) for investing and producing cleaner motor vehicles (Honda Motors 2011d; Peng 2007).
Other awards include Americas UCS greenest carmaker (2007), highest EPA Fuel Economy Rating (2005) as well as the top ten finish for its Honda Insight in Kelley Blue Book’s (Used and new car brand recognition awards), 2010 greenest car category (Hinda 2011d). Honda Motors has gained a positive rating from the US environmental program agency. The agency uses a variety of parameters to test and accredit among other things motor vehicles for environmental compliance. For motor vehicles the agency tests for efficiency in Plug-In Hybrid-Electric mechanism as well as a test for Highway Fuel Economy (CHING and BYUN 2008).
EPA has noted that Honda Civic Hybrid is one of the most fuel-efficient motor vehicles on American roads (Simpson 2006). According to a motor vehicle, environmental compliance report conducted by National Renewable Energy Laboratory in 2005 Honda Motors performed well overall, as well as coming second to Toyota motors in the motor company category with a score of 62 points (Simpson 2006).
In efforts to maintain the sustainable efforts Honda CEO, Takanobu Ito, explains that the company is planning to improve its Hybrid brands. Furthermore, the company has also made considerable in producing an all-electric car. Mr. Ito adds that the companies will add their hybrid brands to five (Meier 2010).
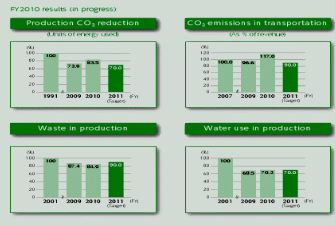
The carmaker is one of the major carmakers that shows concern for environmentally friendly products has made plans to reduce carbon dioxide emission in its production line as well as emissions from its cars. The company had targeted to reduce its carbon dioxide from its automotive production line by 30% (Honda 2010b).. Furthermore the company has recognized the need to conserve water and as such has made targets to reduce its water consumption by 30 % (Honda 2010b).. The figure below reflects on Honda motors carbon dioxide and water consumption reduction rates.
Issues of public concern
There are several issues of public concern relating to the company. The company which has, through its corporate outreach program, provided high utility vehicles during disasters and emergencies has been accused by the American public of doing too little to help America (Alsop 2002). Furthermore, the new Honda electric vehicles have also been subjects of public concerns (McGosh 2008).
Some of the users have argued that the vehicles are too quiet that a driver has to be careful when coming from behind pedestrians or cyclists. Moreover, the Honda’s electric battery cost about US$ 30, 000 which is more than three times the price of a normal small car (McGosh 2008). Thus maintenance of this hybrid car is too expensive (McGosh 2008).
The benchmark for good practice
The production of a hybrid car is a very costly affair. It is estimated that manufacturers of hybrid cars are making losses for every unit of hybrid car they sell. Honda Motors was estimated to lose US$ 8000 for every hybrid insight it sold in the year 2008 to 2010 (Forster 2003). However, the company is using this as the benchmark towards the mass and profitable production of hybrid cars. The company expects to break even in a couple of years through the sales of the Insight. This is because as the prices of gasoline increase the demand for energy-efficient cars will grow (Keown 2007).
The company is using the Honda Insight as the benchmark in testing new technologies that will yield further knowledge on the production of improved hybrid applications that will be used in other cars (Keown 2007). In efforts to beat competition from other hybrid brands such a Toyota Prius, Honda has set new benchmarks in its new version Insight. The improved model has its Intelligent Power Unit strategically placed beneath its cargo boot, therefore increasing cabin space. Furthermore, it has a 1.3 L i-VTEC engine that improves fuel efficiency.
As such this increases cabin space and advantage over another hybrid (Honda 2011e). All this is at a reasonable lower price than the Prius. The Insight is selling at about US $ 19000, which is about the US $ 2000 below the Prius (Welsh 2009). Upon introduction in the market, the Honda Insight was the biggest challenger to the stylish and improved Toyota Prius. In the first month of the introduction of the year 2009, Insight recorded impressive sales at 18000 units in the global market (Welsh 2009).
The record sales were because of the Insight’s considerable lower prices as compared to the Prius. Initially, Toyota was adamant and maintained its prices for the Prius but sooner it was forced to readjust its prices downwards to compete with Honda Insight (McGosh 2008). Honda hybrid however loses in comparison to the new all-electric Nissan Leaf (Boxwell 2011). Nissan Leaf is an all-electric car that reduces carbon emission as well as dependency on petroleum (Boxwell 2011). As such it is more environmentally friendly than Honda’s insight. (Boxwell 2011)
Honda is exposed to a variety of risks and uncertainties. As a result, it has developed several functional strategies to prepare for the tumultuous future. Because the future of the motor industry lies in environmentally friendly products, the company is planning to invest in research and development aimed at developing new application technologies to enhance its eco vehicle policy. To add to this the company is also overhauling its quality control strategy to ensure its products meet the best customer demands (Honda Motors 2010).
Furthermore, the company has implemented several efforts to enhance its production as well as sales efficiencies, to help its products meet international market demand for environmental-friendly vehicles (Honda Motors 2010). These strategies coupled with the company’s capacity and increased effort to develop better engines represent the company’s sustainable framework for the future (Honda Motors 2010). The company’s bottom-line growth can be attributed to several factors (Tidd 2009). The figures below show the performance of Honda insight against other hybrids.
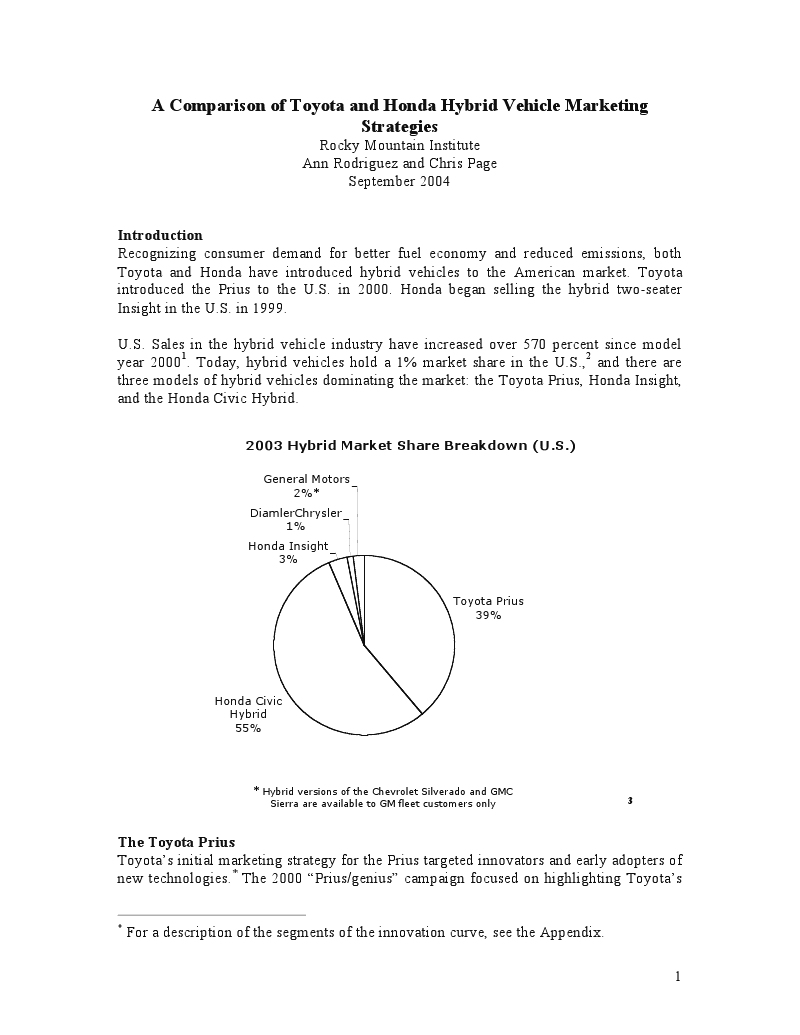
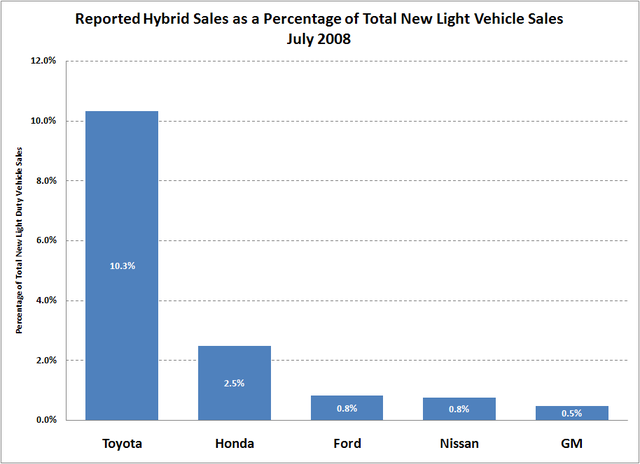
These include the company’s cost-cutting measures as well as increased sales of hybrid vehicles. However, its tendency to hedge in foreign exchange is threatening to negatively affect its bottom line growth in the recent past. Despite this, its bottom-line growth has been boosted by its increased growth in the sale across the globe (Tidd 2009).
Functional strategies
Honda motors have surprised many by the functional strategies it employs. The company seems to very well manage functional dichotomies that ensure successful business outcomes. Many companies seem to be either caught up in being learning or planning, developing the company’s internal resources or strategic market positioning, implementing product-related business models, or having a process-related model among other strategic moves.
Honda on its part seems to successfully manage these strategic dichotomies. The company is a trendsetter in high-quality brands as well as efficient business and production processes. Furthermore, the company has innovated core competence business applications that have ensured a very strategic position in the global market (De Wit and Meyer 2010).
Sustainable mapping framework
The company has drawn up a framework for future sustainable business. The framework is informed by the company’s ability to manufacture its products with the consumer’s interest at heart. Furthermore, the sustainability framework has identified energy-efficient vehicles as to the future of the motor vehicle industry. As such the company has drawn up a map for sustainable business that attars with the leasing or sale of its new electric vehicles and motorbikes (Honda Motors 2011f).
Sweet spot analysis
The company has endeared itself to the customers by manufacturing not only efficient vehicles and motorcycles but also in manufacturing practicable and easy to use products. In the year 2010, Honda Motors Company has endeared itself to improve the new Honda Insight Hybrid and make it stand out in the hybrid car market.
In this regard, the new insight has gained approval ratings by customers and motor vehicle analyst for practicality as well as affordability and fuel efficiency. For starters, the dashboard of the vehicle displays the efficiency level without interfering with the drive. Furthermore, the company has also found its sweet spot in juggling new engine dynamics that combine VE and cylinder pressure (Kojima 2002).
Triple bottom line
Honda motor company is the only manufacture of numerous products the meets market preferences. Since its inception, the company’s engineers have combined intellect, research, and ingenuity to manufacture no only techno-savvy products but also products the meet its triple bottom line people, planet, and profit (Shook 1988).
Hondas community engagement
The Company’s CSR efforts are not only concerned with the manufacturing of energy-efficient vehicles but also are concerned with engaging local communities. To do this the company has formed the Community Engagement Committee. The committee has the mandate to review charitable community requests. The committee does engage in initiatives that are concerned with health, diversity, and safety issues in communities in such locations as Indiana, USA. In this initiative that CEC wants to portray the company as one that looks beyond the profits (CSR Reports 2007).
Stakeholder concerns
The company has enlisted various stakeholders to improve its business worldwide. These include dealers, suppliers, manufacturers, associates as well as its customers. The company endeavors to establish and maintain a very good relationship with these stakeholders and thru reduce any negative effects that may hinder any relationship. Such efforts to improve relationships include strengthening support from dealers at the same time supplying them with sufficient information from market surveys. The company has also developed a privacy policy to endure confidentiality with its major stakeholders (CSR Reports 2007; Harrison and St. John 2010).
New markets
The company establishes that it needs to venture into new markets if it is to make any successful financial gains and also to survive turbulent times in this industry. As such it has had several initiatives to enter into a new market. Some of these initiatives include the company’s efforts to enter into the aviation industry. The company has therefore embarked and made tremendous progress towards manufacturing the Honda Jet (Honda aircraft 2011).
Recommendations
The natural environment is evolving to present new challenges to manufactures and users of manufactured products. The mining and utilization of natural resources are increasingly becoming a concern for the natural environment sustainability. as such the company needs to continues with its long-held reputation of manufacturing eco-friendly cars as well as adopting eco-friendly manufacturing processes. However, the new company hybrid make of automobiles are not as energy efficient as compared to its peers and rivals such as the Toyota Prius and Nissan Leaf.
As such the company should look into the possibility of having all-electric care like the new Nissan leaf to compete effectively in the hybrid car market segment. Because the future of energy efficiency in the motor vehicle is in the development of a better energy conservation battery, the company should also concert its efforts into more research in this field.
Furthermore, the company has lost gainfully to Toyota Prius on the branding of hybrid cars. As such the company should also improve the outwards feel of its new Honda insight hybrid to ensure that its looks more like a finished product than a prototype. Because the company has been a trendsetter in the automobile industry innovations, the company should also exp0lrre the opportunities and possibilities of manufacturing hybrid engines for boats and other means of water transport.
Furthermore e a hybrid motorcycle would be a good idea to automobile consumers who are becoming increasingly attracted to hybrid engines. The company’s sustainable future would not be complete without implementing a well-developed training program. The training should also focus on consumers. It would provide sufficient knowledge on how to consume and utilize Honda motors company’s products optimally. Furthermore, the company should focus only on developing affordable product s fro third world markets such as Africa, Asia, and the Central American
Conclusion
The Honda motors company has stood out in the world of carmakers. This is due to its efforts to manufacturing top durable brands that also assert the consumer’s desires. The company has had a successful recent pas. This is reflected in the company’s 2010 financial returns. The company recorded impressive profits of about ¥8,579,174 in the year 2010. These profits have been necessitated by several factors. The company is the leading manufacture of motorcycles all over the world with reputable brands from utility motorcycles, security racing, and leisure brands.
Furthermore, the company’s efforts to produce energy-efficient motor vehicles have been rewarded greatly. This is because of the impressive performance of its hybrid brands such as the Honda Insight, a semi hybrid car that uses both electric engines as well as gasoline. Against other hybrid cars such as Toyota Prius, the Honda Hybrid has performed extremely well especially in the American markets. The company’s operations are affected by several factors in the company’s that it operates in. The company has moved in to capitalize on the country’s economic boost.
As such it has established manufacturing plants in one of the economic zones. Together with this, the company has seen its rating rise in the American market according to statements by the country’s Environmental Program Authority. Such statements have moved in to reinforce the company’s brand repudiation for production. The company also aims at producing motor vehicles that not only satisfy customers’ unique brand and environmental concerns but also give the best value for the clients’ money. However, the company’s progress has not been without some hindrances.
In the recent past, the company’s social cooperate responsibility has been largely criticized in some communities for not doing enough to help those communities. However, the company’s CSR efforts are concentrated on the manufacturing of eco-friendly motor vehicles. Moreover, the company’s hybrid car has been criticized for not being too pocket-friendly as well as posing new accident risk to other nonmotor vehicle road users. Despite this, the company has been a winner of major international awards such as the ISO 14000 for environmentally friendly products. The company’s currently doing well and is looking to the future with a lot of optimism due to its solid past.
Reference List
Alsop, R., 2002. Perils of Corporate Philanthropy Touting Good Works Offends The Public, but Reticence Is Misperceived as Inaction. The Wall Street Journal.
An, F., and Amada S. 2004. Comparison of Passenger Vehicle Fuel Economy and GHG Emission Standards around the World. Pew Center on Global Climate Change. Arlington, Virginia.
Anthony, S. D. 2008. The innovator’s guide to growth: putting disruptive innovation to work. Chicago: Innosight LLC.
Bremmer, I. and Stewart, T. 2011. China’s State Capitalism Poses Ethical Challenges. Web.
Boxwell M. 2011. The 2011 Electric Car Guide. Warwickshire: Green Stream Publishing.
Byun, D., & Ching J. 2008. Science algorithms of the epamodels community multiscale air quality (cmaq) modeling system. New York: Research Triangle Park.
Cogan, D. 2006. Corporate Governance and Climate Change: Making the Connection Boston: Ceres.
Deshpande, A. n.d. Comparison of Asian and North American automobile manufacturing practices. Web.
De Wit, B. and Meyer, R. 2010. Strategy: Process, Content, Context, an International Perspective. Vancouver: South Western Cengage Learning.
Foster, M. S.2003. Nation on wheels: the automobile culture in America since 1945. Michigan: Thomson, Wadsworth,
Gelder, S. 2005. Global brand strategy: unlocking branding potential across countries, cultures and markets. London: Kogan page:
Honda Aircraft. 2011. Assembly of conforming aircraft begins. Web.
Honda motors. 2010. Honda to Build Second Motorcycle production Plant in India. Web.
Honda Motors. 2010b. FY 2011 Japan targets and progress. Web.
Harrison, J., and St. John. 2010. Foundations in strategic management. Ohio; South Western Cengage Learning.
Honda motors. 2011a. Company overview. Web.
Honda Motors. 2011b. News & Views. Web.
Honda Motors. 2011c. Honda CSR report. Web.
Honda. 2011d. Initiatives & Awards. Web.
Honda Motors 2011e. Hybrid: gasoline –electric. Web.
Honda Motors. 2011f. Message from the President and CEO. Web.
Ito, T. 2010. Honda CEO speaks at the 27th Thailand International Motor Expo. Web.
Keown, A. 2007. Foundations of finance: The logic and practice of financial management. London: Prentice Hall Kim, C. 2010. Honda hoists profit forecast, sees further growth. Web.
Kojima, M. 2002. Honda/Acura Engine Performance: How to Modify D, B and H Series. New York: NPB books
Meier, F. 2010. Japanese paper: Honda to have plug-in hybrid by 2013 USA TODAY. Web.
McGosh, D. 2008. Hybrids get real. Vancouver: Popular Science Modi, C., Zein, R., Kramer, L., Saudale, S., and Banavadikar, M. n.d. Logistics and Distribution Systems Design. Web.
Page, F., and Rodriguez, S. 2004. a comparison of Toyota and Honda hybrid marketing Strategies. Web.
Peng, N. 2007. Environmentally-friendly Automobiles: An Analysis of ISO Accreditation of Honda Motors Plunket, J. 2006. Plunkett’s Renewable, Alternative & Hydrogen Energy Industry Almanac 2007. Texas: Plunkett Research Limited.
Pretty, N. 2007. The SAGE handbook of environment and society. London: Sage Reign, G. 2010. Honda reduces carbon dioxide emissions. Web.
Rima, H. I. 2010. The political economy of the undrbalued renminbi. Web.
Shook, R. 1988. Hinda an American success story: revlutionisisng the art of management> New York: prentuice hall.
Simpson, A. 2006. Cost-benefit analysis of plug-in hybrid electric vehicle technology. Presented at the 22nd International Battery, Hybrid and Fuel Cell.
Electric Vehicle Symposium and Exhibition (EVS-22) Yokohama, Japan.
Sperling, D. and Cannon, J. 2009. Reducing climate impacts in the transportation sector. Washington: Springer.
Siuru, B. 2007. Inside the Honda IMA Hybrid System. Green car. Web.
Tibor, T and Feldman, I. 1995. ISO 14000 a guide to the new environmental management standards. Ohio: Irwin Professional Publishing,
Tidd, J. 2009. Identifying Innovative Capabilities. Web.
Narayanan, V. K. and Fahey L. 2001. “Macro environmental Analysis: Understanding the Environment Outside the Industry,” in L. Fahey and R. M. Randall (eds.), The Portable MBA in Strategy, 2nd edn. New York: Wiley.
Ward-Jones, R. 2008. Environmentally friendly cars: promoting and increasing their use in the uk. Earth & E-nvironment 3:282-317.
Wall Street Journal. 2011. Auto Sales. Web.
Welsh, J. 2009. Car Compare: 2010’s Toyota Prius vs. Honda insight Toyota. Wall Street Journal. Web.